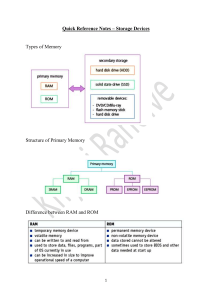
UNIT 01: INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEFINED TECHNOLOGY has reshaped our lives at home, at work and in education. Almost all businesses have an online presence, and most business processes require the use of computers in some way. INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY is the use of any computer, storage, networking, and other physical device to create, process, store, secure and exchange all forms of electronic data. IT focuses on the information processing from the collection, to the processing, and the sharing of information. IT deals with the methods and tools used in the information processing. Information is now a necessity in today's society, sometimes even provided realtime and reaches people in different parts of the world. This is an engagement in the 21st century that is lucrative in a business setting. IT, beyond communications, offers many personal career paths and company growth leading to competitive advantage in each respective field. To become more competent in each respective field, one must know basic computer skills and must build a foundation using the fundamental technology concepts. We go beyond learning the basic definition of information technology in the classroom, but also in an online or digital presence. An individual's ability to find, evaluate, and compose clear information through writing and other media on various digital platforms is known as digital literacy. Computer literacy is also known as digital literacy. An individual must keep up with the changes in technology and become computer literate. Now why do we need to study information technology? Simply because we use these technologies in our everyday lives, and we need to further understand how these hardware and software are working. Computer skills are needed regardless of setting and field, whether at home, work, school or play. By understanding computers, you become self-sufficient whether you use it for research, communications or time management. By mastering fundamentals, you will develop a strong base to support furtherance of your knowledge in the years to come. SOME COMPUTER ROLES IN OUR LIVES: 1. Tiny embedded computers control alarm clocks, entertainment centers and home appliances 2. Today's automobiles cannot run efficiently without embedded computer systems 3. An estimated 10 mil people work from home instead of commuting to work because of pcs and networking technologies. 4. People use social media for communications nearly 10 times as often as snail mail and 5 times more than a telephone. 5. Routine daily tasks such as banking, buying groceries are affected by computer technologies. In a world that is being defined by technology and digital trends, the demand for digital literacy has increased exponentially. We need to expand our knowledge to avoid unfamiliar situations and modernize our skills to stay relevant in a dynamic work environment. That is why it is important for us to learn the fundamentals of information technology. UNIT 02: COMPONENTS OF A COMPUTER SYSTEM A lot of people believe that computers are extremely complicated devices because of the tasks they perform. Like any machine, there are components that are complicated from an outsider's perspective, but as soon as you learn about these components, the complexity unravels and becomes understandable. A COMPUTER SYSTEM (All the different parts of a computer, including the devices you plug into it, are known collectively as ‘a computer system’.) A computer system is a collection of parts, a computer combined with hardware and software used to perform desired tasks. No matter the size and capability, a computer system consists of four components: HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, DATA, and the USER. HARDWARE This is the first component of a computer system. It refers to the tangible, physical computer equipment and devices which provide support for the major functions of the computer system. Mainly the mechanical aspects of the computer. The hardware controls the input of data into the computer system and the output of information from the computer system. All these devices are interconnected with each other. Kinds of According to Function: INPUT DEVICES, OUTPUT DEVICES & INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES 1. INPUT DEVICES Used to enter data or instructions into a computer system. Input devices fall into two categories: MANUAL INPUT DEVICES (needs to be operated by a human to input data) and automatic input devices can input data on their own. EACH INPUT DEVICE is concerned with a specific type of data: Scanner documents or images, Digital Camera - still moving images. 2. OUTPUT DEVICES Used to convey information from the computer system to one or more people. When raw data has been processed it becomes usable information. Output devices are pieces of hardware that send this usable information out of the computer. Output devices send information out temporarily and some send information out permanently: temporary output device (monitors) and permanent output devices (printers which output information onto paper as hard copy). 3. INPUT AND OUTPUT DEVICES - are hardware devices that have the capability to accept data and information and at the same time send them. 3.1 HEADSET is a Headphone combined with a microphone. Used in call centers and by people in telephone-intensive jobs, headsets provide the equivalent functionality of a telephone handset with hands-free operation. 3.2 ALL IN 1 PRINTER is a single printer device that serves several functions, including printing, faxing, scanning, and copying. 3.3 MOBILE DEVICE is a computing device small enough for a user to hold in his or her hand. 3.4 MP4 DEVICE is a device that lets you listen to music, watch movies, listen to the radio, has a built-in microphone that lets you record up to 16 hours, can view photos, and can read e-books. Almost all input and output devices are known as 'PERIPHERAL DEVICES'. These are nonessential hardware components that usually connect to the system externally. Peripherals are called non-essential because the system can operate without them. COMMON PERIPHERAL DEVICES 3. SYSTEM UNIT - houses the electronic components to process data • Motherboard-This is the main circuit board of the system unit. The motherboard is central to any computer system. • All components are plugged into the motherboard either directly (straight into the circuit board) or indirectly (vis USB ports) MEMORY • Electronic component that store instructions waiting to be executed and data needed by those instructions. • There are two types of internal memory. These two memories are used to store computer data, and this can be directly accessed by the CPU. • The RAM and ROM device are sometimes referred to as 'PRIMARY STORAGE'. ROM (READ ONLY MEMORY) • ROM is used to permanently store instructions that tell the computer how to boot (start-up). It also loads the operating system (e.g. Windows). • These instructions are known as the BIOS (Basic input/output system) or the boot program. • Information stored in ROM is known as READ ONLY. This means that the contents of ROM cannot be altered or added to by the user. • ROM is fast memory. Data stored in ROM can be accessed and read very quickly. • ROM is Non-Volatile memory. This means that stored information is not lost when the computer loses power. PROCESSOR • The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of the computer. • Electronic component that interprets and carries out basic instructions. • The CPU 'controls' what the computer does and is responsible for performing calculations and data processing. OTHER EXAMPLES OF ROM INCLUDE: • DVD/CD ROMS bought in stores containing pre-recorded music and movie files. These are played back at home but cannot be altered. • ROM in printers which is used to store different font types. RAM (RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY) • RAM is used to temporarily store information that is currently in use by the computer. This can include anything from word documents to videos. • RAM can be read from and written to and so the information stored in RAM can change all the time (it depends what tasks you are using the computer for). • RAM is a fast memory. Data can be written to and read from RAM very quickly. RAM is generally measured in GB (Gigabytes). • • RAM is Volatile Memory and stores date 'NON- PERMANENTLY'. This means that information stored in RAM is deleted as soon as the computer is turned off. The more RAM you have installed in your computer -- the faster it can perform. You can open and use more programs at the same time without slowing the computer down. OPTICAL STORAGE DEVICE - uses lasers and lights as its mode of saving and retrieving data. * BLU-RAY DISC - A digital optical storage device which was intended to replace the DVD format. * CD-ROM DISC - An optical storage device that is read-only or cannot be modified nor deleted. * CD-R AND CD-RW DISC - CD-R is a recordable disc that can be written to once, while * CD-ROM DISC - An optical storage device that is read-only or cannot be modified nor deleted. * CD-R AND CD-RW DISC - CD-R is a recordable disc that can be written to once, while CDRW is a rewritable disc that can be written to multiple times * DVD-R, DVD+R, DVD-RW and DVD+RW disc - DVD-R and DVD+R are recordable discs that can be written to once, while DVD-RW and DVD+RW are rewritable discs that can be written to multiple times. The difference between the + and - is in the formatting 4. STORAGE DEVICES - Holds data, instructions, and information permanently for future use. It records (writes) and/or retrieves (reads) items to and from storage media. Secondary storage devices are used to store data that is not instantly needed by the computer. Secondary storage devices permanently store data and programs for as long as we need. These devices are also used to back-up data in case original copies are lost or damaged. There are two categories of storage devices: internal storage (internal hard disk drives) and external storage (external hard disk drive, memory sticks, etc.) Hard EXAMPLE OF STORAGE DEVICES • MAGNETIC STORAGE DEVICE - one of the most popular types of storage used. * HARD DRIVE - An internal hard drive is the main storage device in a computer. An external hard drive is also known as removable hard drive. It is used to store portable data and backups. FLASH MEMORY DEVICE - is now replacing magnetic storage device as it is economical, more functional, and dependable. * MEMORY CARD - An electronic flash memory device used to store digital information and commonly used in mobile electronic devices. * MEMORY STICK - A memory card that is removable. * SSD (SOLID STATE DRIVE) - A flash memory device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to save data steadily. * USB FLASH DRIVE, JUMP DRIVE OR THUMB DRIVE - A small, portable storage device connected through the USB port. ONLINE AND CLOUD STORAGE - is now becoming widespread as people access data from different devices. * CLOUD STORAGE - Data is managed remotely and made available over a network. Basic features are free to use but upgraded version is paid monthly as a per consumption rate. * NETWORK MEDIA - Audio, Video, Images or Text that are used on a computer network. A community of people create and use the content shared over the internet. CLASSIFICATION OF MEMORY AND STORAGE DEVICES ACCORDING TO DATA RETENTION A. VOLATILE MEMORY - Device requires power to retain its stored data - data is lost as soon as power is cut-off from the device B. NON-VOLATILE MEMORY - Device can retain stored data even after computer power is turned-off 5. COMMUNICATION DEVICES - Enables a computer to send and receive data, instructions, and information to and from one or more computers. A hardware device capable of transmitting an analog or digital signal over the telephone, other communication wire, or wirelessly. Examples: Bluetooth devices, Infrared devices, Modem (over phone line), Network card (using Ethernet), Smartphone, Wi-Fi devices (using a Wi-Fi router) ACCORDING TO ACCESS TECHNIQUE A. RANDOM ACCESS - Data stored in the device can be accessed in any order, i.e. random B. SEQUENTIAL ACCESS - Data stored in the device can be accessed only in sequential order from start to finish - Example: A movie stored in a BluRay Disc is accessed in sequential order so that the movie stored therein can be viewed from start to finish ACCORDING TO ACCESS RIGHTS A. READ/WRITE ACCESS - The device allows data to be read and written onto it. B. READ-ONLY ACCESS - The device only allows data to be read from it - its contents is prefabricated during the production of the device. SOFTWARE Software is a collection of instructions that enables a user to interact with the computer or have the computer perform specific tasks for them. Without any software the computer would be useless. Software is a generic term for organized collections of computer data and instructions, often broken into two major categories: system software that provides the basic non- task-specific functions of the computer, and application software which is used by users to accomplish specific tasks. SYSTEM SOFTWARE is responsible for controlling, integrating, and managing the individual hardware components of a computer system so that other software and the users of the system see it as a functional unit without having to be concerned with the low-level details such as transferring data from memory to disk, or rendering text onto a display. Generally, system software consists of an operating system and some fundamental utilities such as disk formatters, file managers, display managers, text editors, user authentication (login) and management tools, and networking and device control software. APPLICATION SOFTWARE, on the other hand, is used to accomplish specific tasks other than just running the computer system. Application software may consist of a single program, such as an image viewer; a small collection of programs (often called a software package) that work closely together to accomplish a task, such as a spreadsheet or text processing system; a larger collection (often called a software suite) of related but independent programs and packages that have a common user interface or shared data format, such as Microsoft Office, which consists of closely integrated word processor, spreadsheet, database, etc.; or a software system, such as a database management system, which is a collection of fundamental programs that may provide some service to a variety of other independent applications. Software is created with programming languages and related utilities, which may come in several of the above forms: single programs like script interpreters, packages containing a compiler, linker, and other tools; and large suites (often called Integrated Development Environments) that include editors, debuggers, and other tools for multiple languages. KINDS OF OPERATING SYSTEM 1. MICROSOFT WINDOWS- PC and IBM compatible operating system. Microsoft Windows is the most commonly found and used operating system. 2. APPLE MACOS MACINTOSH OPERATING SYSTEM - Apple computer operating system. The only Apple computer operating system. 3. UBUNTU LINUX - A popular variant of Linux used with PC and IBM compatible computers. 4. GOOGLEANDROID -operating system used with Android compatible phones. 5. iOS - Operating system used with the Apple iPhone, iPad. TYPES OF UTILITY SOFTWARE a. DISK DEFRAGMENTER is Windows designed to increase rearranging files stored on a utility in Microsoft access speed by a disk to occupy contiguous storage locations. Disk Defragmenter also reduces system startup times. b. DISK CLEANER is a computer maintenance utility included in Microsoft Windows designed to free up disk space on a computer's hard drive. The utility first searches and analyzes the hard drive for files that are no longer of any use, and then removes the unnecessary files. c. DISK PARTITIONER it is the dividing of a hard disk drive into multiple logical storage units referred to as partitions, to treat one physical disk drive as if it were multiple disks. d. BACKUP UTILITIES are computer programs used to perform backup; they create supplementary exact copies of files, databases, or entire computers. These programs may later use the supplementary copies to restore the original contents in the event of data loss. e. ANTI-VIRUS UTILITIES is software used to prevent, detect and re such as computer viruses, adware, backdoors, malicious BHOs, dialers, fraud tools, hijackers, keyloggers, malicious LSPs, rootkits, spyware, trojan horses and worms. Computer security, including protection from social engineering techniques, is commonly offered in products and services of antivirus software companies. KINDS OF APPLICATION SOFTWARE A. WORD PROCESSING SOFTWARE is usually what leads people to using a computer for their work. Word processors will normally have the following capabilities built into them: Spell checking Standard layouts for normal documents Have some characters appear in bold print, italics, or underlined. Center lines, make text line up on the left side of the paper, or the right side of the paper. Save the document so it can be used again. Print the document. Two of the most common word processing programs are WordPerfect and Microsoft Word. Instructor schedules Some of the most commonly used database programs are Microsoft Access and dBASE. D. GRAPHIC PRESENTATION SOFTWARE. The presentation programs can make giving presentations and using overheads easier. Other uses include: Slide Shows Repeating Computer Presentations on a computer monitor Using Sound and animation in slide shows The most recognized graphic presentation programs are Microsoft PowerPoint and Harvard Graphics. E. DESKTOP PUBLISHING SOFTWARE is a tool for graphic designers in creating visual communications for professional or desktop printing as well as for online and onscreen electronic publishing. Example of desktop publishing software is Microsoft Publisher. B. SPREADSHEET SOFTWARE. The spreadsheet packages are designed to use numbers and formulas to do calculations with ease. Examples of spreadsheets include: Budgets Payrolls Grade Calculations Address Lists F. GRAPHIC SOFTWARE is a program that enables the user to manipulate visual images on a computer. Example of graphics software is Adobe Photoshop. The most commonly used spreadsheet programs are Microsoft Excel and Lotus 123. H. ENTERTAINMENT SOFTWARE is a program designed to listen to music and watch video clips using the computer. Example of an entertainment software is Windows Media Player. C. DATABASE SOFTWARE is an application software that allows users to create, access, and manage a database. A database is a collection of data and records. Database programs are designed for these types of applications: Membership lists Student lists Grade reports G. MULTIMEDIA SOFTWARE is a program that can combine text, graphics, full-motion video, and audio into an integrated package. Example of multimedia software is Windows Movie Maker. DATA - This is the third component of a computer system. It consists of individual facts or pieces of information that are used by the computer system to produce information. Data by themselves may not make much sense to a person. The computer's primary job is to process data in various ways, making them useful. Without data, the computer wouldn't be able to function properly. Example: The grades of fifty students in one class, all different pieces of data which doesn't make much sense yet, but when a chart is created from the data, and frequencies are developed. This now makes sense at a glance. USERS - This is the fourth component of a computer system. The operator of a computer is known as 'peopleware', other books call them liveware, or human ware. The user commands the computer system to execute on instructions. Some computer systems are complete without a person's involvement, but not all computers are totally autonomous. Basically, anyone who communicates with a computer system or uses the information it generates. Example: programmer, developer, teacher using MS Excel, student using MS Word Knowing the parts of a computer system allows us, users, to understand better each function of the computer system and our make the experience of using the computer system more efficient. Management Information Systems (MISO) IT Director Systems Analyst Programmer Computer Technician Encoder UNIT 03: COMPUTER TYPES AND VARIETIES Before we learn the types of computers still being used today, let us define what a computer is. A computer is defined by Peter Norton as "An electronic device that processes data according to a predetermined set of instructions that convert data info information useful to people. They perform specific tasks based on the instructions provided by a software or hardware program". Also, according to Gary Shelly, a computer is defined as "An electronic device operating under the control of instructions stored in its memory that can accept data, process the data, produce and store results for future use". Computers can also store data for future use with the appropriate storage devices. A computer is a programmable device that can automatically perform a sequence of calculations or other operations on data once programmed for the task. It can store, retrieve, and process data according to internal instructions. Computers can be categorized in many ways: by size and capacity, by data handling and operating system capabilities, based on the number of microprocessors, and based on the number of users. In this module, we're going to classify computers according to the size and capacity. Before cloud computing and the use of digital systems, large companies use (01) SUPERCOMPUTERS because they required a big amount of computing power. A supercomputer has an incredibly high level of performance. These are usually used on a large-scale operation like industrial function, space exploration, weather forecasting, and nuclear testing. A supercomputer is a computer at the leading edge of data processing capability, with respect to calculation speed. Supercomputers are used for scientific and engineering problems (high performance computing) which crunch numbers and data, while mainframes focus on transaction processing. (02) MAINFRAME COMPUTER are like big centralized machines that contains the large memory, huge storage space, multiple high-grade processors, so it has ultra- processing power compare to standard computer systems. The use of the primary memory and having multiple processors are done by mainframe computers. These are used in moderate data processing, banking, and insurance. It handles bulk data processing, statistics, and analysis them. The term originally referred to the large cabinets called "main frames" that housed the central processing unit and main memory of early computers. Later, the term was used to distinguish high-end commercial machines from less powerful units. Most large-scale computer system architectures were established in the 1960s, but continue to evolve. Mainframe computers are often used as servers. (03) MINICOMPUTERS were introduced in the mid-1960s. It has the most of the features and capabilities of a large computer but more compact in size. This is also called a midrange computer. Minicomputers were primarily used for process control and performing financial and administrative tasks, such as word processing and accounting. Some machines were designed for medical laboratory and teaching aids. (04) A MICROCOMPUTER has a central processing unit (CPU) as a microprocessor. These are also known as personal computers (PC). Microcomputers are primarily used for word processing, managing databases or spreadsheets, graphics and general office applications. A microcomputer is a small and relatively inexpensive computer that has a microprocessor as its central processing unit. It includes memory, a microprocessor, and minimal input/output circuitry built on a single printed circuit board. Micro-computers are classified into workstations - Also known as desktop machines, workstations are mostly used for intensive graphical applications, personal computers-more affordable and easier to use than workstations and are self-sufficient computers intended for one user, laptop computers and Mini PCs - Mini PCs are tiny computers that can fit in the palm of your hand. KINDS OF MICROCOMPUTER DESKTOP COMPUTER LAPTOP COMPUTER PALMTOP CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTER ACCORDING TO PURPOSE GENERAL PURPOSE COMPUTER SPECIAL PURPOSE COMPUTER (05) AN EMBEDDED COMPUTER, which is an integral component of most embedded systems, is a combination of hardware and software that is designated to perform a highly specific function. For example, the type of embedded computer in a washing machine will not be the same as the embedded computer in a Nikon camera. Because the software in embedded computers is designed to only execute certain tasks, the computer's software in one device can be totally distinct from that of another. UNIT 04: EVOLUTION OF A COMPUTER The history of computers is a remarkable journey that spans several centuries, witnessing transformative advancements that have revolutionized human society. From ancient calculating devices to the powerful supercomputers and smartphones we have today, this course aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the evolution of computers, highlighting key examples that illustrate major milestones in this remarkable progression. 1. PRE-COMPUTER ERA (PRE-20TH CENTURY) A. ABACUS: One of the earliest known calculating devices, the abacus has roots dating back to around 2400 BCE in ancient Mesopotamia and China. It allowed users to perform basic