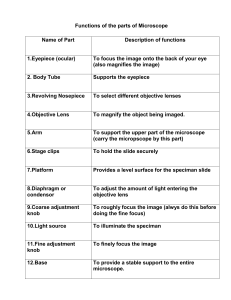
Teacher: Nel Jastien L. Nacario S.Y.: 2024-2025 Date: February 3, 2025 Intended Learners: 7 Content Standards: Performance Standards: Learning Competency: Identify parts of the microscope and their functions Learning Code: S7LT-IIa-1 I. Objectives: At the end of the lesson, the students will be able to: a. Identify and describe the major parts of a microscope, including the eyepiece, objective lenses, stage, coarse and fine focus knobs, condenser, and diaphragm. b. Adjust and manipulate the microscope's focus knobs to achieve clear and sharp images of specimens at various magnification levels. c. Acquire knowledge and apply things learned in laboratory activities. II. Subject Matter: Topic: Parts of the microscope and their functions Materials: Microscope, Pictures of the Microscope parts, References: Grade 7 Quarter 2, Module 1 III. Preliminary Activities: Student’s Activity Prayer : Yes Sir, : Lord, bless each and every student here, as well as our teacher, as we embark on another day of learning. Please give us clear minds and open hearts so we can grasp the knowledge and lessons set before us. Help us to be attentive, and let Your wisdom guide us in our studies. Greetings : Good Day Sir Nacs!! Classroom Structuring : (following teachers instructions) Teacher’s Activity :Okay, everyone lets rise up. Mr. Del, can you lead the prayer? Thank you for that Mr. Del. :Good Day Class. : Class before we start, please pick up the garbage near you, and arrange your arm chairs please. Checking the attendance : Okay Sir. Motivation : (dancing) : Ms. Secretary, kindly check the attendance of the class and forward it to me after, so I can check who are absents. : All of u seem to be sleepy, lets have our energizer first. Let’s do Zumba everyone kindly stand everyone :Good job everyone, please take your sit Review :Since we already finished our first wuarter exams, what was our last lesson about if anyone can remember? Any volunteer? : Me,Sir!! : Our lesson was all about, concentrations : Okay Ms. Antosa. of solutions quantitatively by preparing different concentrations of mixtures according to uses and availability of material : Very Good!! Presentation of the Lesson Objectives: :I would like another volunteer for the class to read the objectives aloud. : okay, Mr. Kahangak : (reads the objectives on the board aloud) : Thank you for that. Student’s Activity Activity : (groups themselves into five) Teacher’s Activity : Okay class, group yourselves into five silently : That will be your group for this whole lecture : Your activity for today class, is to solve the puzzle or parts of that object, put them together, I will give you five minutes, and cooperate with your groupmates. : (After 5 minutes) : It’s a Microscope : Okay class what object did you see? Analysis : Good Job, Everyone : (After 5 minutes) : Okay class what object did you see? :It’s a Microscope : About Microscopes Abstraction : (answers) : Good Job, Everyone : So what do you think is our lesson for today? : That’s Correct!! : So class, our lesson for today is align with the activity you just did, and it is about Microscope. : Who can tell me, what a microscope?? : That very good, A microscope comes from the Ancient Greek micros meaning "small" and skopein, which means "to look", is a tool which can help you see tiny objects and living organism. It makes them look bigger. The science of investigating small objects and structures using such an instrument is called microscopy. :What makes a microscope determine how clearly a small object can be viewed? 1. Magnification- describes how much larger an object appears when viewed : It describes how much larger an object appears when viewed po sir. The magnification is written on the side of the lens. The value could be 4x. 10x 40x or 100x. To calculate the total magnification of the compound light microscope, multiply the magnification power of the ocular lens by the power of the objective lens. For example, 10x ocular lens and a 40x objective would have a 400x total a magnification. :Again, what is magnification class? Yes Ms. Palkog. :Very good, Next is,, 2. Resolution or resolving power the capacity of a microscope to distinguish finer details of an image : Optical and Electron Microscope :Now there are different microscopes that differ from its magnification and resolving power, and those are?? Kindly read : Very good!!, now Optical microscope is describes how much larger an object appears when viewed uses visible light to form an image. It uses glass lenses to magnify and resolve images. The image that was formed can be viewed from an eyepiece. It has two types: A. Compound-uses two or more double convex lenses to magnify the object; it can magnify object up to 1200x B. Stereomicroscope also known as dissecting microscope, it magnifies the object 100x and gives threedimensional image. : The second is, Electron microscope. It uses high energy electron beams to form an image. The image that was formed can only be vie ed can only be viewed from a or from a photographic plate or a computer image magnified can reach up to 2,000,000x. Like Optical microscope class it has also two types, these are: A. Transmission electron microscope (TEM) electron beam pass through an ultra- thin sample the image magnified and focused onto an imaging device such es as fluorescent screen, examined in fine detail to be : Okay Sir. B. Scanning electron microscope (SEM)-electron beam bounces oft from the surface of the sample: thus the image provided is threedimensional : (raises the part, eye piece) : Eye piece or Ocular lens this in the part used to look through the microscope. : (raises the part, Lens Tube) : Now class lets proceed, to the parts of the Microscope, in your activity I made you form the puzzle of the microscope, right?? You will see at the back part it is the use of this specific part now I will give you what does this part means and raise the right answer, what I say I not necessarily the same with the meaning that is with you okay?? So try to understand properly : Body tube or Lens tube is connected with the eyepiece and its main task is to hold it. : So first, it is where you put your eyes to see the specimen 3,2,1 go : (raises the part, Revolving Nosepiece) : Good Job, now Group 1 kindly read what is Eye Piece or Ocular lens. : Revolving Nose Piece holds the objective lenses. It is movable and it can revolve the objective lenses depending on the magnification power of the lens. : Very Good, Next it is the one who holds the lens 3,2,1 : Good Job, now Group 2 kindly read what is Body tube or Lense Tube. : (raises the part, Arms) : Arm, this is the part connecting the base and to the head and the eyepiece tube to the base of the microscope. It gives support to the head of the microscope, and it is also used when carrying the microscope. : (raises the part, Arms) : Objectives/ objective lenses are the major lenses used for specimen visualization. Most schools have light microscope with three objectives and others have four. Usually, the shortest one marked 3x 4x or 5x is called scanner. The lower power objective (LPO) is marked 10x or 12x, while the high power objective (HPO) is marked 40x, 43x or 60x. The objectives magnify the object to :Good, lets go to the third part, is spins so that we can use the different lenses. : Good everyone is correct, now group 3 kindly ready what it is use for. : Great Job, next the part that connects the head and base of the microscope. : Nice, So group 4 what does it do?? : Good job, next part is the lenses of the microscope. be observed to a certain size as indicated by the 3x 10x or 40x, etc. marks. : Good, now group five what is objective lens? : Okay, Sir : Great job everyone, since every one participated I will give additional points to all of you, the rest of the parts will be explained by me okay?? : Okay the next part is the... Stage is the platform that holds the specimen or sample for viewing. Next is Stage clips, it hold the specimen slides in place. Diaphragm controls the amount of light that passes through the specimen. Another part is the Coarse adjustment, it focuses images under the scanner and the low power objectives. There is another adjustment part, and it is Fine adjustment, it focuses images under the high power and oil- immersion objectives. Next is the Light source, it provides light for the specimen (could be a lamp or a mirror). Last part is the Base, the base supports the microscope. Application : Yes Sir!! :Finally, class that wraps up our lesson for the day : Now class lets have another activity, I will assign each group a microscope, your task is to identify what part is this. The specific part will be assigned with a letter, and write the correct in a ¼ sheet of paper, and since this is a group activity I want you to cooperate with each other okay?? You will have 5 minutes so use your time wisely. V. Assessment 1. What is the function of the eyepiece (ocular lens) in a microscope? a. Magnifies the specimen b. Controls the amount of light c. Holds the objective lenses d. Supports the microscope 2. Which part of the microscope is responsible for adjusting the amount of light passing through the specimen? a. Objective lenses b. Diaphragm c. Stage d. Coarse adjustment knob 3. What is the purpose of the fine adjustment knob on a microscope? a. Changes the objective lens b. Sharpens the focus c. Adjusts the stage height d. Rotates the nosepiece 4. Where is the objective lens located on a microscope? a. Above the stage b. Below the stage c. In the eyepiece d. Rotating nosepiece 5. Which part of the microscope supports the slide and specimen being observed? a. Stage b. Coarse adjustment knob c. Base d. Arm 6. What is the function of the condenser in a microscope? a. Holds the objective lenses b. Adjusts the amount of light c. Magnifies the specimen d. Rotates the nosepiece 7. Which part of the microscope is used to switch between objective lenses? a. Diaphragm b. Coarse adjustment knob c. Fine adjustment knob d. Rotating nosepiece 8. What is the purpose of the arm on a microscope? a. Supports the microscope b. Holds the objective lenses c. Adjusts the stage height d. Rotates the nosepiece 9. Which part of the microscope should be used to move the stage up and down for coarse focusing? a. Coarse adjustment knob b. Fine adjustment knob c. Stage clips d. Diaphragm 10. What is the function of the iris diaphragm in a microscope? a. Holds the objective lenses b. Adjusts the amount of light c. Magnifies the specimen d. Rotates the nosepiece Prepared by: Nel Jastien L. Nacario Student Teacher Checked and Reviewed by: Abdul J. Jamara MAEd EDUC 222A Instructor