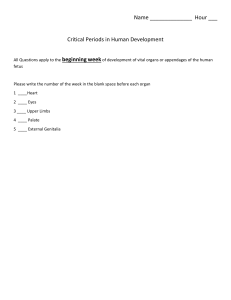
How plants absorb water? Discuss and let us know Maintaining Life Plants and water Root hair cells Function: Provide a really big surface through which water and minerals ions can be absorbed into the plants. Plant roots absorb mineral salts including nitrates needed for healthy growth. For healthy growth plants need mineral ions including: - Nitrate for producing amino acids which are then used to form proteins. - Magnesium which is needed for chlorophyll production. Steps: Water moves from the soil > Cell Wall > Cell Membrane > Cytoplasm Task 1 Science Learner Book page 143: Question 1 and 2 Science Workbook: page 68 and 69 How water moves up the plant. 1) In the centre, there are some very special cells called xylem vessels. 2) These are the water water transport system of the plant. 3) After water is absorbed > moves from outside to inside of the cell > Xylem vessel in the centre of the root. Xylem - Long Tube like cells Dead cells Only cell wall and empty space left inside Wood of a tree truck is made of xylem vessel. They carry water from the roots all the way to the top of the tree Transpiration How water moves through leaves. Steps: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) When water arrives at the leaf, it moves out of the xylem vessels and into the leaf cells. The cells that have chloroplast use some of the water for photosynthesis. Most of the water does not stay in the cell. The liquid water in the cell soaks into the cellulose cell wall and then changes to water vapour - it evaporates. The water vapour diffuses into the air spaces between the cells. These air spaces connect with the air outside the leaf through tiny holes in the underside of the leaf- the stomata. The water vapour can diffuse through these holes and into the air. The loss of water vapour from leaves is called transpiration. Plant cell - Contains a lot of water especially in the vacuoles. Classwork: Science workbook 4.2 Transpiration Complete page 74, 75, 76 and 77 Objectives: 1) To understand the kidney system 2) To identify the parts of the excretory system 3) To understand and explain the flow of the excretory system 4.3 Excretion in humans 1) Excretion is on the characteristics of all living things. 2) Excretion means getting rid of waste materials. 3) Excretion includes all the waste substance that organisms make in their cells, plus any substance that they have too much of that have been part of their body. 1) For animals and human beings: - Carbon dioxide, which body cells make in respiration - Urea, waste substance that is made in liver cells - Excess water that is not needed by the body. Excreting urea 1) When we eat food, any proteins in the food are broken down to smaller molecules inside the digestive system. 2) These small molecules go into the blood. The blood transports them to the liver. 3) If we have more proteins than we need, the liver changes the smaller molecules into urea. 1) Urea is a poisonous substance. It it builds up in the body, it makes a person ill. 2) As soon as urea is made in a liver cell, it is taken away from the liver in the blood. 3) The urea is removed from the blood by the kidney in the excretory system. 4) This system is known as the renal system. Renal means to do with the kidneys. 1) As the blood flows through the kidneys, the kidneys filter the blood. They remove all of the urea from it. 2) The kidneys also remove access water from the blood. The urea dissolves in the excess water. The solution made is urea in water is called urine. 3) The urine made in each kidney flows down a tube called a ureter. 4) This carries it to the bladder, which can store if for a while. 5) The urine can flow out of the bladder to the outside world through another tube called the urethra. Classroom task Science workbook Page 78 (please complete all) Classroom task Complete Science Learner Book Page 158 Questions 1 - 3 Only write the answers Objectives: a) Understand the different nutrients that a person needs to stay healthy. b) Explain the diet of a pregnant women. c) Describe the about fetal and fetus. Diet 1) A good diet during pregnancy has a big effect on fetal health. 2) When a woman is pregnant, a woman needs to eat a balanced diet (different nutrients). 3) She needs a little more than usual because some of the nutrients that she eats are passed to the growing fetus. What is fetal health? Fetal health: the support you need for a healthy pregnancy and delivery. Protein: 1) Help the fetus to produce new cells and grow. So the mother is able to must make sure she eats plenty of food containing protein. 2) Keep muscles strong and working well. 3) Extra Haemoglobin- blood need to transport oxygen around body and and give the fetus enough (Oxygen). Carbohydrate: 1) Supplies energy 2) Glucose is carbohydrate and cells get their energy by combining glucose with oxygen in respiration. 3) Both the mother and fetus required carbohydrate to obtain sufficient energy. Vitamins and minerals Iron: needed to make haemoglobin Calcium: helping the mother and baby to obtain strong bones and teeth. Vitamins: essentials for mothers to obtain during pregnancy. Keeping a fetus healthy A healthy pregnancy: 1) For the first nine months of its life, a new human beings grows inside a mother. During the 9 months, it is called a fetus. 2) A fetus is a baby before it is born. 3) A fetus in growing in its mother’s body. Smoking cigarettes Is smoking healthy? 1) Tobacco contains carbon monoxide, nicotine and tar. 2) When a pregnant women is smoking, carbon monoxide and nicotine diffuse from the blood into the fetus’s blood. 3) Carbon monoxide in the blood reduces the amount of oxygen that haemoglobin can transport. 4) Nicotine is an addictive drug. It can damage blood vessels so it is not good for developing fetus. Recommendation(s) for pregnant women 1) She must stop smoking 2) She should avoid alcohol. 3) She should never take any illegal drugs or any drugs which is not prescribed by the doctor. 4) Most doctors recommend that pregnant women should not drink a lot of coffee or cola. Classwork 1) Complete Science learner Book question 4.4 in page 167 in your exercise book. 2) Science workbook page 79 - 84