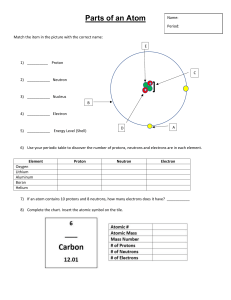
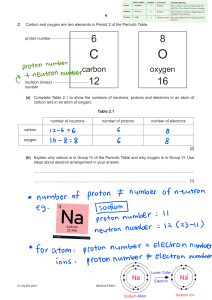
QUARTER 3 WEEK 6 ATOMS: INSIDE OUT DETERMINING THE NUMBER OF PROTONS, NEUTRONS, AND ELECTRONS IN A PARTICULAR ATOM. PREPARED BY: MRS. MARITESS SIÑEL OBJECTIVES: -- Determine the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons in positive ions (cation) --Determine the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons in negative ions (anion) --Illustrate how the sub-atomic partivles are distributed in an atom/anion/cation LET’S REVIEW MASS NUMBER = PROTON + NEUTRON ATOMIC NUMBER = PROTON PROTON = ELECTRON IN EQUAL STATES CATION AND ANION First let’s define ION and what its difference on a NEUTRAL ATOM ION is a particle with unequal number of proton and electron -if there are more protons the charge is positive (+) -if there are more electrons the charge is negative (-) Meanwhile, Neutral atoms are elements that they contain the same number of protons as electrons Meanwhile, Neutral atoms are elements that contains the same number of protons and electrons When the neutral atom lose its electron and become an IONs with more number of protons than its electron it is called CATION - e When the neutral atom gain an electron and become an IONs with more number of electron than protons it is called ANION e FLUORINE ATOM (F) FLUORINE ION (F-) ALWAYS REMEMBER! Proton do not move to other place (/elements) or go out from the nucleus. Electrons is the one going out or going in from an atom. We consider the charge of an ION base on the number of proton and electron in an atom. If electron is release from a neutral atom we call CATION and if the neutral atom gain one or more electrons we call it an ANION Atoms and chemical elements lose or gain electrons when they react in order to gain stability. Thus, typically, metals lose electrons to nonmetals, thereby forming positive ions. The number of electrons depends on elements and their position on the Periodic table (in simple terms). for example, group I metals lose one electron to form +1 ions, group II lose 2 electrons to form +2 ions etc. Non-metals gain electrons from metals in order to achieve full outer shells. Thus, metals will typically react with non-metals, exchanging electrons to form a compounds. Outermost shell Valence Electrons are the electrons found in the outermost shell of an atom = THE END