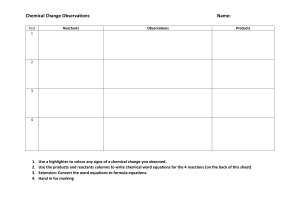
Grade 10 Science April 22, 2024 CHEMICAL REACTION In this module , you will further understand how a chemical change proceeds, how bonds are broken and new bonds are formed, and how chemical reactions are translated into chemical equations, where rearrangements of atoms causes the formation of new substance/s. A lot of these chemical changes made the quality of our lives better. Multiple Choice. Choose the correct answer. 1. During a chemical reaction, a. atoms are destroyed b. atoms are rearranged c. elements are destroyed d. new elements are produced 2. A chemical reaction is a process in which a. all reactants change state b. products change into reactants c. the law of conservation of mass applies d. all of these 3. What determines an atom’s ability to undergo chemical reactions? a. protons b. neutrons c. innermost electrons d. outermost electrons 4. How is a chemical equation is balanced? a. changing subscripts b. erasing elements as necessary c. adding coefficients d. adding elements as necessary 5. What are the products in the equation below? Zn + CuSO4 -----> ZnSO4 + Cu a. Zn and Cu b. Zn and CuSO4 c. ZnSO4 and Cu d. Zn only 6 -10 Write true if the statement is correct and false if incorrect, and change the underlined word/s to make the statement correct. 6. Generally, the higher the concentration of the reacting substances, the faster is the reaction. 7. At lower temperature, chemical reactions occur at slower rates. 8. The bigger the surface area of the reactants, the faster the rate of reaction. 9. Catalysts increase the rate of reaction by providing a reaction pathway with a higher activation energy. 10. The minimum energy required to start a reaction is called bond energy. IV. Reading Resources and Instructional Activities KEY CONCEPTS: When a physical change occurs there is no breaking and forming of bonds. There are certain things that will help us identify if a chemical reaction has taken place. We call these evidences of chemical reactions. 1. Production of light 2. Evolution of gas 3. Temperature change 4. Change in intrinsic properties (color, odor) 5. Formation of precipitate Oxygen is vital to life. One interesting reaction which involves oxygen is the production of fire. Fire has fascinated people for so long, that the ancient people even regarded it as one of the earliest elements. Fire was so important to them and they described it as an element that changes everything. The earliest theory about burning was the Phlogiston Theory. This theory by George Ernst Stahl in the 17th century stated that when a material burns, it releases a substance known as phlogiston, and this theory was accepted for a very long time. Antoine Lavoisier through his careful observations from his experiments, debunked the phlogiston theory as he discovered that instead of releasing a substance (phlogiston) a material accurately burns as it reacts (uses) with oxygen. This is now known as the Theory of Oxidation, and this is accepted up to this day. For burning to occur, 3 factors should be present in proper conditions and proportions. 1. Fuel 2. Oxygen 3. Heat Grade 10 Science April 23, 2024 A. Reactants and Products. Reactants are substances that are used up to form new substances in a chemical reaction. The following chemical reactions took place in Activity 1 procedure A to E. 1. Iron reacts with copper sulfate (CuSO4) and forms iron (II) sulphate (FeSO4) and copper. 2. Magnesium combines with oxygen gas (O2) to produce magnesium oxide 3. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the presence of manganese dioxide (MnO2) produces water and oxygen gas. 4. Acetic acid (CH3COOH) and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) produce sodium acetate with the release of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas and water. 5. Copper sulfate (CuSO4) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to produce insoluble copper (II) hydroxide Cu(OH)2 and sodium sulphate (Na2SO4 ) solution. Fill in the table below with the Reactants and Products from the chemical reactions above. Below each number, write the symbol or formula of the reactant and product. Table 6. Reactants and Products Reaction Reactants Products 1 Answer: Iron, Copper sulfate Answer: Iron (II) sulphate, Copper Fe, CuSO4 FeSO4, Cu 2 3 4 5 B. Symbols used in Chemical Equation There are other symbols used in writing a chemical equations: Using the symbols and formulas in Table 6 and the symbols in Table 7, write the chemical reaction using these symbols to complete chemical equation. Table 8. Chemical Reaction Reaction 1 2 3 4 5 Chemical Equation Grade 10 Science April 24, 2024 ASSESSMENT Classify the following unbalanced chemical equations according to the six types of chemical reactions. A. Combination B. Decomposition C. Single displacement D. Double displacement E. Combustion F. Acid-base KEY CONCEPTS: Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass is conserved in a chemical reaction. The total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. No new atoms are created or destroyed, there was only grouping or regrouping (rearrangement) of atoms. Steps in Balancing Equations: Write the unbalanced chemical equation, make sure you have followed correctly the rules in writing formulas of compounds. • Take note of the elements present in the reactant and product side. • Count the number of atom/s of each element present in the reactant and product side. • Apply the Law of Conservation of Mass to get the same number of atoms of every element on each side of the equation. Balance chemical equations by placing the appropriate coefficients before the symbol or formula. Do not change the subscripts of the formula in an attempt to balance the equation as it will change the identity of the components. Let’s Practice! Grade 10 Science April 25, 2024 Writing Chemical Equations Part A – Translate all the formulaic equations to word equations. Part B – Translate all the word equations to formulaic equations and then balance them. 1.Sodium combines with chlorine to produce sodium chloride. 2. When solid copper reacts with aqueous silver nitrate, the products are aqueous copper II nitrate and silver metal. 3. Solid iron III oxide and carbon monoxide gas produce iron metal and carbon dioxide gas. 4. Sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide react to form sodium sulfate and water. 5. Vanadium II oxide with iron III oxide results in the formation of vanadium V oxide and iron II oxide. 6. Aluminum reacts with oxygen to produce aluminum oxide. 7. Mercury II oxide decomposes to produce mercury and oxygen 8. Sodium carbonate decomposes to produce sodium oxide and carbon dioxide 9. Carbon dioxide gas reacts with solid lithium hydroxide to produce solid lithium carbonate and water. 10. Ammonia gas reacts with oxygen gas to produce nitrogen monoxide gas and steam. 11. Solid ammonium nitrate decomposes to produce dinitrogen monoxide gas and water. 12. Carbon monoxide reacts with hydrogen to produce methanol. 13. Liquid carbon disulfide reacts with oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide gas and sulfur dioxide gas. 14. Aluminum metal reacts with aqueous copper II chloride to produce aqueous aluminum chloride and solid copper. 15. Solid ammonium chloride decomposes to produce ammonia gas and gaseous hydrochloric acid.