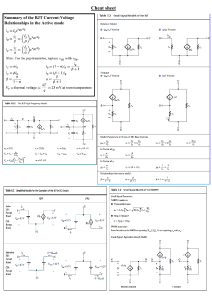
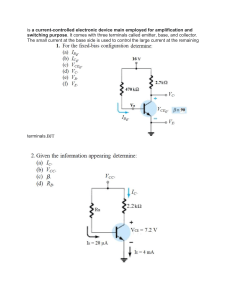
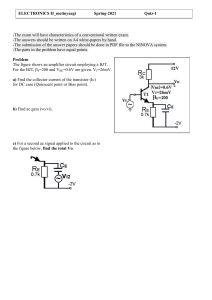
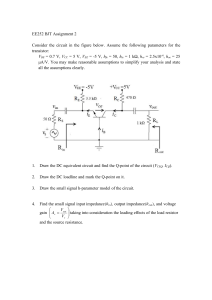
TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 DIODE APPLICATIONS STUDENT INFORMATION CLASS: TT01 STUDENT ID: FULL NAME: Note: name the file according to the syntax CLASS_ID_FullName_Session_[Offset at class?] Eg: T01_1812466_NguyenVanB_Day_1 T01_1812466_NguyenVanB_Day_1_Offset at class T04 (T01 is the student class, T04 is the class that makes up) OBJECTIVES Know how to use Analog Discovery Studio Kit and Software, Lab Instrument. Understand voltage and current properties in series and parallel circuit. Understand I-V characteristic of BJT. PREPARATION Install Proteus version 8.8 or above before coming to the LAB session. TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 1. EXPERIMENT 1 OBJECTIVES: In this lab assignment, we examine input I-V characteristics IB = f(VBE) of BJT, sketch the shape of IB = f(VBE) characteristic and determine open voltage of BJT. CIRCUIT: Given the circuit as shown below. In this circuit: - Q2 is a transistor with product number is 2N5551. - Vo = 5V DC. TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 THEORY: What does I-V characteristics IB = f(VBE) of BJT look like? It has no current running through until the voltage reach the point that it able to penetrate the BJT SIMULATION: Draw a simulation of the given circuit on Proteus. (Picture of simulation circuit on Proteus) 1.4.1. Using TRANSFER GRAPHS to draw IB = f(VBE). (Vo = 5V). TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 (Picture of running TRANSFER GRAPHS) Find the opening voltage of the BE junction. 1.4.2. Using TRANSFER GRAPHS to draw IB = f(VBE). (Vo = 1V and Vo = 10V) TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 (Picture of running TRANSFER GRAPHS) Explain the reason why there is such a GRAPHS. It has no current running through until the voltage reach the point that it able to penetrate the BJT 1.4.3. Using TRANSFER GRAPHS to draw IB = f(VBE). (Vo = 1V to Vo = 10V, 10 steps) TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 (Picture of running TRANSFER GRAPHS) Comment on the characteristic shape as Vo increases. TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 2. EXPERIMENT 2 OBJECTIVES: In this lab assignment, we examine IC = f(VCE) characteristics of BJT, draw IC = f(VCE) characteristic of BJT. CIRCUIT: Given the circuit as shown below. In this circuit: - Q2 is a transistor with product number is 2N5551. - Ib is a 10uA-DC-current source. TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 THEORY: How do you understand the graph below? despite how high the current is, all have the same active region SIMULATION: Draw a simulation of the given circuit on Proteus. (Picture of simulation circuit on Proteus) TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 2.4.1. Using TRANSFER GRAPHS to draw IC = f(VCE). (Ib = 10uA). (Picture of running TRANSFER GRAPHS) TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 From the graph, students make calculations to derive the saturation voltage (điện áp bảo hòa) VCE-sat (approximate value) and gain β (hệ số khuếch đại). Explain how. 2.4.2. Using TRANSFER GRAPHS to draw IC = f(VCE). (Ib = 10uA and Ib = 50uA) (Picture of running TRANSFER GRAPHS) TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 Explain the reason why there is such a GRAPHS. It has no current running through until the voltage reach the point that it able to penetrate the BJT 2.4.3. Using TRANSFER GRAPHS draw IC = f(VCE). (Ib=10uA to Ib=100uA, 10 steps) (Picture of running TRANSFER GRAPHS) Comment on the characteristic shape as Ib increases. As Ib increase the amplitude of Ic also increase. TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 3. EXPERIMENT 3 OBJECTIVES: Understand the schematic diagram of amplifier circuit using BJT. CIRCUIT: Given the circuit as shown below. In this circuit: - BJT is a transistor with product number is 2N5551. - Rc is a 10-Kilo-Ohm resistor. - The resistance of Re is 100 Ohm. - R1 has a resistance of 44 Kilo-Ohm. - R2 is a potentiometer with a resistance of 10 Kilo-Ohm at MAX. - Vcc is a 12V-DC source. - Using DC Voltmeter, Ammeter to find VCE, IC. ` TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 SIMULATION: Draw a simulation of the given circuit on Proteus. (Picture of simulation circuit on Proteus) Adjust rheostat R2 to VCE=6V, then how much is R2 and Ic?. (Picture of simulation circuit on Proteus) TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 R2 =2800Ohm Ic =0.56mA Add 3 1uF-capacitors as the below picture. Vi is a sine waveform with an amplitude of 100mV, frequency at 100Hz and offset = 0V. Using SIGNAL GENERATE to create Vi. Using Oscilloscope to observe Vin and Vo (Note that in this lab, it is no need to adjust the scale for the 2 channels to be the same). (Picture of simulation circuit on Proteus) TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03 Find the amplitude of Vi and Vo. Vi=100mV Vo =2.4V How many times is Vo amplified? It amplified 24 times What if we increase or decrease Vi, how does the voltage waveform of Vo change? It will decrease its amplitude, because the Vo waveform is depended on the Vi amplitude What if we increase or decrease R2, how does the voltage waveform of Vo change? If we increase R2 the amplitude of Vo waveform will decrease. And the opposite with when we decrease R2. TT03 ECE LAB ONLINE 5 – BJT APPLICATIONS 03