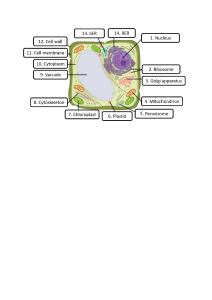
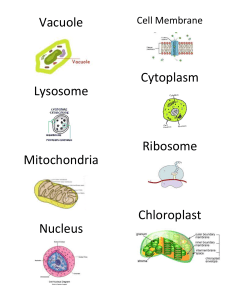
Biology Chapter 2 - Cells Cells are the basic unit of life, organisms are made of cells Animal Cells (under light microscope) Plant Cell (under light microscope) Animal Cell (under electron microscope) Plant Cell (under electron microscope) Cell Structure and Function Cellular Components Characteristics Functions Nucleus - The largest organelle in the cell - Consist of three main components: - Control all cellular activities - Control all cellular activities - Consist of three - Contain genetic main components: material (DNA) 1. Nuclear which determine envelope: separates the characteristics the contents of the of the cell and its nucleus from the metabolic functions cytoplasm 2. Chromatin: carries genetic material in the form of DNA 3. Nucleolus: a darker and dense region Cytoplasm - Refers to everything in between the cell membrane and the nucleus - Watery jelly that fills the cell - Acts as a medium where biochemical reaction and most living processes occurs within the cell Cell Membrane/ plasma membrane - Thin membrane around the cytoplasm - Semi-permeable or selectively permeable - Separates the contents of a cell from its external environment - regulate he movement of substances entering and leaving the cell - Allow the exchange of nutrients, respiratory gases and waste products between the cell and its environment Cell wall - Fully permeable - Is the rigid cellulose layer surrounding the plasm membrane of plant cell - made of tough cellulose fibers - Provide support and protection for the cell - Prevent the cell from bursting in dilute solution - maintain the shape of plant cell Vacuole - A large space that is filled with cell sap containing water, dissolved sugars, salts, pigments, waste or other materials - some animal cells have small vacuoles or vesicles - store chemical such as organic acids, sugar and amino acids - helps to keep the cell shape / maintain the shape Chloroplast - A lens-shaped organelle - Have inner and outer membranes - contain a green pigment called - Have inner and outer membranes - often contain starch gains - contain a green pigment called chlorophyll - carrying out photosynthesis Rough endoplasmic - Is a flat sealed sac - Transport protein recticulum that is continues made by ribosome with the nuclear membrane - Is ER with ribosome embedded on its surface Smooth Endoplasmic Recticulum - Does not have ribosomes -May extend separately from the outer membrane of the nucleus or extend from the rough ER - Synthesis (produce) and transport lipids/oil - carries out detoxification of drugs Mitochondrion - Cylindricalshaped - Have double membrane - Site of cellular respiration - provide energy Ribosome - Are small dot-like organelles - are either attached to the Endoplasmic - The site of protein synthesis (produce) attached to the Endoplasmic reticulum or occurs freely in the cytoplasm Vesicle - Fluid - filled sacs - Stores and transports substances throughout the cell Golgi apparatus - membrane covered sacs called cistern that look something lie a stack of deflated balloons - Packaging, processing and transporting the vesicle - build lysosome Lysosome - membraneenclosed organelles that contain enzymes - function as digestive system of the cell - capable of breaking down unwanted substances or complex molecules - proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids Similarities and differences between animal and plant cell Animal Cell Features Plant Cell Generally smaller than plant Size Generally larger than animal cell does not have a fixed shape Shape has a fixed and regular shape absent (does not have cell wall) Cell Wall Has a thick, has cellulose cell wall - usually not Vacuole present - many small and temporary ones are pesent a matured cell has a large central vacuole absent Chloroplast Present glycogen Carbohydrate storage starch Unicellular vs Multicellular – Unicellular are organisms which consists of a single cell – Multicellular are organisms that consists of more than one cell Level of organisation . Cell – E.g. Red blood cells . Tissue – Made up of cells . Organ . System . Organism Types of cells Red blood cells – Disc shaped but centre dip inwards (biconcave disc) – Large surface area, so that oxygen can pass through – Does not have nucleus Nerve cells – Neurone, have long thread-like extensions – send electrical signals through the body Sperm and egg cells – Together known as gametes – fuse together to produce zygote (胚胎 Ciliated epithelial cells – Cilia are microscopic hair like extension on the surface of the cytoplasm – The cilia wave to and fro and carry hair, mucus, trapped dust and bacteria up to the back – of the throat where it can be swallowed move the ovum through the fallopian tubes to the uterus Root hair cells (plant) – have long thin extension – have a large surface area – speed up absorption of water Palisade cells – located under the upper epidermis – tail and closely packed and contain most of the leaf’s chlorophyll – absorb maximum light, most of the photosynthesis occurs here Xylem Vessels – to conduct water ions dissolved salts from the roots to stem leaves, flowers and fruits Size of specimen – magnification = size of drawing / size of real object