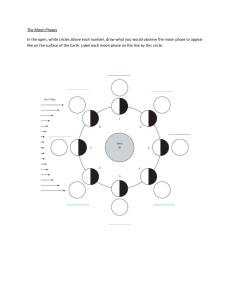
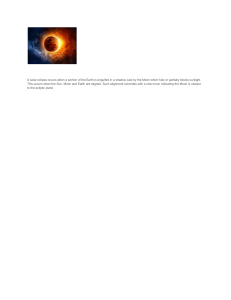
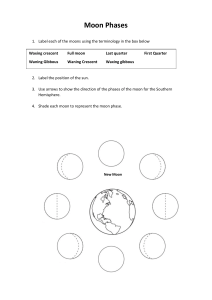
Lesson 2 Astronomical Phenomena Before the Advent of Telescopes Activity No. 1 – ARRANGE ME PLEASE!! Arrange the following jumbled letters, each letters are worth 1 point. The group that has the most points wins the activity. 1. OONM 2. PESLICE 3.ALROS 4.NURLA 5. MYASNOROT After going through this module, you are ex pected to: 1. Enumerate the examples of astronomical phenomena 2. Describe the phases of 3. Differentiate lunar and before the advent of the moon; solar eclipses; telescope; 4. Appreciate the importance of astronomical phenomena and how they affect your life. Even before the advent of the telescopes, ancient astronomers were able to observe the following: • 1. rising and setting of the Sun in the east and the west, respectively, • 2. phases of the moon, • 3. lunar eclipse, • 4. solar eclipse, • 5. daily and annual motion of the stars, and • 6. planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn. Activity 2 – Unpack Me! Each group will be given a certain topics, read the assigned topics to your group and answer the guide questions that are provided. You will be given 10 minutes to complete the activity. After 10 mins leaders will going to select the precentor of their output. Rising and setting of the Sun in the east and the west, respectively • Babylonian and Egyptian civilizations used a primitive version of a sundial, called gnomon, in systematically observing the motion of the sun. By looking at the shadows that the gnomon casts, they were able to observe that the sun rises in the eastern part of the sky, reaches its highest point in midday, and sets in the western part of the sky. Rising and setting of the Sun in the east and the w e s t , r e s p e c t i v el y • Also, they recorded that the points where the sun rises and sets on the horizon varies over a year and these variations happen periodically. They observed that these variations are related to weather and so concluded that seasonal changes in climate happen during a course of one year. Phases of the Moon • A moon, also called a satellite, is a relatively small object that is orbiting around a planet. Earth’s moon is the fifth biggest moon in the solar system. • The gravity of the Earth pulls on the moon such that one face of the moon is always facing us, and we can never see the other side. Just like the Earth, half of the moon is always lit by sunlight and the other half is in shadow. Phases of the Moon • As the moon orbits the Earth, we see a different phase of the moon. It takes 27 days, 7 hours, and 43 minutes for our Moon to complete one full orbit around Earth. This is called the sidereal month, and is measured by our Moon's position relative to distant “fixed” stars. However, it takes our Moon about 29.5 days to complete one cycle of phases (from full Moon to full Moon). Phases of the Moon New moon • A new moon appears only when the moon is on the side of the earth most directly in line with the sun. There is no illumination on the earth’s side, so it is also sometimes called the dark moon. Phases of the Moon Waxing crescent • During this phase, the lit- up part of the Moon increases from 0.1% to 49.9%. Waxing means that it is growing, while crescent refers to the curved sickle shape Phases of the Moon First quarter • The 1st Quarter Moon is a primary Moon phase when we can see exactly half of the Moon's surface lit up Phases of the Moon Waxing gibbous The waxing gibbous phase is between a half moon and full moon. Waxing means it is getting bigger. Phases of the Moon Full moon • The whole side of the moon is now illuminated to viewers from the earth. The full moon rises in the east as the sun sets in the west. It stays up all night long, reaching its highest point about midnight. Phases of the Moon Waning gibbous • The Waning Gibbous phase is when the lit-up part of the Moon shrinks from 99.9% to 50.1%. It starts just after Full Moon and lasts until the Third Quarter Moon. Waning means that it is shrinking and getting smaller, while gibbous refers to the oval-to-round shape. Phases of the Moon Last quarter • A last quarter moon, also known as a third quarter moon, rises around midnight and sets around noon. The Moon is nearly back to the point in its orbit where its dayside directly faces the Sun, and all that we see from our perspective is a thin curve. Phases of the Moon Waning crescent • The Waning Crescent phase occurs when the illumination of the Moon decreases from 49.9% to 0.1%. Lunar Eclipse • A total lunar eclipse takes place when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon and its shadow covers the Moon. Solar Eclipse An eclipse of the Sun happens when the New Moon moves between the Sun and Earth, blocking out the Sun's rays and casting a shadow on parts of Earth.