Evolution Worksheet: Earth History, Darwin, Natural Selection
advertisement

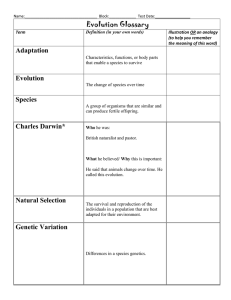
Evolution Earth’s History The Earth was formed about ______ _________________ years ago. By 2.2 billion years ago, the Earth probably looked like it looks today ___________________ was not believed to be in abundant supply in Earth’s early atmosphere. Oldest known cellular fossil (3.5 billion years old) traces back to a place in Australia. Were probably _____________________________, photosynthetic unicellular prokaryotes First prokaryotes were probably anaerobic – Why? ______________________ = a principle that states the same __________________ processes that occur today occurred in the past. These processes occur very ________________, requiring organisms to change as well (very slowly). Origins of Life 1 billion years of chemical change to form the first cells, followed by about 3.7 billion years of biological change. Types of Evolution ______________________ ___________________ – the formation of organic molecules from inorganic substance. ______________________ ___________ – Chemicals in the early ocean giving rise to organic, and eventually, _______________ matter. _________________ ______________________ – the changing of a species into something different by the accumulation of small changes over time. What was early Earth like? Earth was ___________! Little or no ______________ Gases in atmosphere: Hydrogen cyanide (poison to you!) Hydrogen sulfide Carbon Dioxide Carbon Monoxide Nitrogen Water Vapor pg. 1 How did Life Begin? Miller - Urey Experiment _______________ and ____________ conducted an experiment to determine if __________________molecules could be formed under the conditions of ______________Earth? They placed ____________ in a flask and they added the _______________ that simulated the early atmosphere. They _______________ the water and ______________________ it many times. Eventually this process produced _______________ ___________. Endosymbiotic Theory First proposed by Lynn Margulis in the 1960’s who was looking for an explanation for the ______________________ of ___________________________. Proposed that similarities between prokaryotes and organelles, together with their appearance in the fossil record, could best be explained by “____________________”. Her hypothesis proposed that ________________________ are the result of endocytosis of _______________ _________________ and __________________ are the result of endocytosis of _________________________ __________________ entering primitive _____________________________ cells. In both cases large anaerobic bacteria would not be able to exist in an aerobic environment. This arrangement became a ______________________ _______________________ relationship for both cells (___________________________). The result is a cell with a double-membrane bound organelle. The inner lipid bilayer would have been the bacterial cell's plasma membrane, and the outer lipid bilayer came from the cell that engulfed it. Evidence of Endosymbiosis They have their own _____________ (which is circular) They have __________________ that are similar to prokaryotes They have a double membrane and the inner membrane has ________________ similar to prokaryotes They are roughly the ____________ ______________ as bacteria and are susceptible to the antibiotics They _____________________ their DNA and use the mRNA to synthesize some of their own proteins. They can only be produced by ______________________ of pre-existing mitochondria and chloroplasts. pg. 2 Endosymbiotic theory Evolution __________________________ is a theory on the origin of life? False – It is a theory explaining the origin of species How old is the human species (Homo sapiens)? ~195,000 years old What is the name of the theory that teaches that humans evolved from monkeys? _______ theory teaches that humans evolved from monkeys. Evolution indicates Humans and modern monkeys share a _________________ _________________. _______________________: the process by which all living organisms have developed and ________________ from earlier forms __________ ____________. Evolution is Just a Theory pg. 3 ______________________ _______________: a well-supported explanation of phenomena that have occurred in the natural world that is confirmed through observation and experimentation. Examples: Cell Theory, Theory of Plate Tectonics, and Theory of Evolution Charles Darwin Father of evolution Darwin’s theory of evolution The Theory of Evolution is: an explanation as to why organisms are so ________________, but seem to be __________________. an explanation as to how organisms undergo ___________________________ ________________ over generations. Darwin joined the crew of the __________________________ in 1831 as a naturalist. It was a five-year voyage that took him around the world. The map below shows the route of the HMS beagle from England to South America, the Galapagos Island, Australia, South Africa, and back to England Wrote “On the Origin of Species By Means of Natural Selection” Published 1859, _______ years after his return home Darwin observed differences among island species. _____________________: difference in a physical trait of an individual compared to others in the same group Galapagos tortoises that live in areas with tall plants have long necks and long legs Galapagos tortoises that live in areas with low plants have short necks and short legs Galapagos finches (Darwin’s finches) that live in areas with hard-shelled nuts have strong beaks Galapagos finches that live in areas with insects/fruit have long, thin beaks Darwin observed ______________and ____________________ _________________ supporting an ancient Earth. Darwin found fossils of extinct animals that resemble modern animals Darwin found marine fossil shells high up in the Andes mountains pg. 4 Ancient organisms resemble modern organisms. _________________: preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms By studying fossils scientists have been able to infer why the ancient organism no longer exist. Ideas That Shaped Darwin’s Thinking ______________________ _______________________ How could a farmer use selective breeding to get cows with larger horns? In order for selective breeding to work you need natural variation. __________________ ___________________: individual organisms of the same species can have different characteristics. Darwin called this process Artificial Selection. ______________________ _____________________: nature provides the variation and humans select those they find useful. pg. 5 All of the different plants produced from wild mustard by ____________________ ___________________________. Darwin’s Theory of Evolution Darwin proposed Natural Selection as the mechanism of evolution. _________________ ____________________: the process by which organisms with variations most suited to their environment survive and produce more offspring. 3 criteria for natural selection to occur: Natural Variation Struggle for Existence Survival of the Fittest __________________ ______________________ There must be ____________________ among the individuals of a population (they have ________________characteristics). The traits must be _________________________. ________________ _______ ____________________ pg. 6 Species must ___________________ for limited resources and avoid predators. __________________: the organism’s ability to survive and reproduce. __________________ ______ _______ ___________________ Only the most “________” individuals will be able to ________________ and __________________________ to pass on their adaptations. __________________________: any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s fitness (ability to survive and reproduce) Evidence of Evolution Scientists must determine the age of the fossil to determine where the organism fits in the geologic time scale. _________methods of determining ______________ _________ pg. 7 ___________________ _________________ Where is it in the rock layer? Deeper layer = older fossil Can’t tell you exactly how old a fossil is, just that it is older or newer than another fossil ___________________ _____________________ _________________ By knowing the _________ _____ ___________ (half-life) of a radioactive element, the age of an object can be determined. ____________________ is the time it takes for half of the radioactive element to decay…that is…half of the element to change from parent to daughter. With each half-life, the amount of parent remaining is cut in half Half-life of carbon-14 is 5,710 years Ideas That Shaped Darwin’s Thinking Geology In Darwin’s time, most people believed the Earth was a few thousand years old. Geologists began to gather evidence that the continents have been forming for ___________________ of years. How did this information help Darwin form his theory of evolution? Evidence of Evolution Geographic Distribution of the Living Species ______________ __________________ – similar organisms in _________________ locations were the product of different lines of __________________________ _____________________. pg. 8 Animals found on different continents share similar features with other species but are more closely related to other animals living in their habitat because of a shared ______________ ____________________. Similar ecological conditions, similar pressures of natural selection Continental Drift In 1912, _______________ ___________________ hypothesized about Continental Drift. He had an idea that at one time 200 million years ago on different sides of the Atlantic, there were ___________________ animal fossils. Wegener compared the east side of South America to the west side of Africa and found that they ________ together like puzzle pieces. Some other evidence he used was climate, rocks, and other fossils. Though he was criticized and rejected about his theory at first, it was later accepted 20 years after his death in 1930. Continental Drift is a hypothesis that all continents were once connected in a single large landmass (___________________) that broke apart 200 million years and drifted slowly to their current position. pg. 9 pangaea Geologic Time Scale: a timeline of earth’s history. Major changes in fossils separate segments of time (periods). The end of each “Era” is usually a mass extinction. 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth are extinct pg. 10 Evidence of Evolution Comparative Anatomy _________________________ ___________ ______________________ Body structures shared by related species that have a ___________________ ___________________ but ___________________ ____________________. Supports the theory that organisms evolved from a ______________ ______________________. _________________________ ____________________ These are remnants of organs that were ____________ _____________________, but they serve ________________or ______ ____________________presently (wisdom teeth, appendix, tonsils, Darwin’s bump, and tailbone). pg. 11 Comparative Embryology Closely related organisms look more ___________________in the early stages of _______________________ ____________________________. Comparative Biochemistry Genetics All living things have the _________same ________________ ___________. A group of 3 DNA nucleotides will code for the same amino acid in all organisms. ________________ __________________ organisms have a ________________ _________ sequence. Influences on Darwin Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1809) proposed first hypothesis of evolution “_____________________ _______________ _________________” – Organisms “willed” themselves to change by using or not using certain body parts. “_________ _____ ______________” – Organisms acquired traits during their life by the use or disuse of organs. These new traits could then be passed on to offspring. “__________________________ _____ _________________ ___________” –Traits acquired during life were passed on to offspring. Lamarck’s ideas turned out to be _______________, but he was the _________ to propose a testable means by which ____________________ ____________ could occur. It just turned out that when his ideas were tested experimentally, the results disproved his hypothesis. pg. 12 Thomas Malthus (1798) If left unchecked, _______________ _________________________will grow beyond the space and food needed to sustain it. Believed it would __________________ the likelihood of war, famine, and disease. James Hutton (1785) and Charles Lyell (1833) _____________________ who helped scientists realize that Earth is millions of years old, and the processes that __________________ ______________in the past are the _____________ processes that operate in the present. Alfred Russell Wallace (1858) Developed a theory of evolution very _________________ to that of Charles Darwin Worked in the East Indies where he made some new discoveries about species there Wrote to Darwin speculating on evolution by Natural Selection based on his studies of plants and animals ____________________Darwin to ________________ his book, On the Origin of Species, in 1859 – _______ years after his voyage on the Beagle. Common Descent with Modification Darwin proposed that organisms ____________________ from common ancestors Idea that organisms change with time, _____________________ from a common form Caused evolution of _____________ ____________________ pg. 13 Common Descent Adaptive Radiation _______________ ____________________: When a ______________ species evolves into _________________ different species over time. All organisms share a __________________ _______________: All living organisms __________________from a _________________ common ancestor that lived billions of years ago. Over time, that organism evolves in different ways to give to rise to _______ of the modern living organisms. Organisms are _________________ __________________ if they share a recent common ancestor. Patterns of Evolution How are new species formed during adaptive radiation? _______________________: The formation of a _________species through _________________________. Populations must be _______________________ _____________________ from each other Populations can be isolated by ___________________, _________________, or ________________. Speciation can result when members of a population become isolated from one another Speciation is the creation of _________ different species from _________. Populations become ___________________ isolated when there is _____ gene flow between them due to some type of separation. ___________ __________is the exchange of genes between populations through sexual reproduction. pg. 14 Mechanisms of Speciation Natural Speciation by Isolation of Small Populations Geographical Isolation Geographical _________________ __________________ two populations Mountain ranges Deep canyons Bodies of water Ecological Isolation Organisms of _________ populations require __________________ habitats Reproductive Isolation the ___________________of a species _____ ___________ successfully with related species due to geographical, behavioral, physiological, or genetic barriers or differences Modes of Speciation Allopatric Speciation (Geographic Isolation) A _________________ barrier arises and ________________ gene flow between populations. Speciation occurs when the members of the divergent populations _______ longer interbreed. Sympatric Speciation (Reproductive Isolation) A new species may form within the home range of an existing species (there is _____ __________________ __________________) May be: Temporal Mechanical Behavioral Speciation through Isolation _____________________ Isolation - type of reproductive isolation due to the _____________________ to physically mate. _____________________ Isolation – type of reproductive isolation due to ______________________ at _______________________ times. ______________________ Isolation – reproductive isolation due to _______________ in mating or courtship behavior even though they ________ physically interbreed. Parapatric Speciation (Reproductive Isolation) Populations are ________ isolated by a ________________ _______________ and are “beside” each other; nothing is stopping the individuals in the entire population from mixing and mating. It just _______________ happen. Peripatric Specation (Geographic Isolation) Extreme case of geographic isolation where only a ________ individuals are ____________________, perhaps by some sort of disaster that kills off all but a few of the isolated population. pg. 15 Geographical Isolation Geographical Isolation is the separation of two populations by a physical barrier. Caused by the geographical barriers A form of reproductive isolation Darwin’s finches are a main example Reproductive Isolation Reproductive isolation is the separation of two populations in such a way they cannot interbreed and produce a fertile offspring. Caused by behavioral barriers, temporal barriers, and geographical barriers The major cause of speciation One example is temporal isolation of redlegged and yellow-legged frogs. Patterns of Evolution Convergent Evolution ___________________ organisms evolve _________________ adaptations because they live in _________________ environments pg. 16 Sharks and dolphins do _______ share a recent common ancestor. They have similar characteristics because they ____________ a similar environment. Does NOT support Evolution! ______________________Structures Body parts in different species that is similar in function but _________ in structure Structures evolved in response to a similar environmental challenge. Supports ____________________ evolution Analogous Structures Coevolution The evolution of ________ or ________ species, each adapting to ________________ in the other Occurs when species ____________________ closely with each other. Ex: Cheetah and Gazelles have co-evolved to become the fastest and second fastest land animals Rates of Evolution Punctuated Equilibrium: Species do not evolve for _________ periods of time and then go through ___________ period of _____________evolution. What causes the period of rapid evolution? ___________ ________________________: Many species die out in a short time. _________________________: A group of individuals get isolated from the main population. pg. 17 Punctuated Equilibrium Gradualism Organisms have evolved at a __________ and ________________rate. This theory is in contrast with punctuated equilibrium. Evolution as Genetic Change Evolution, in genetic terms, is a _______________ in the allele frequency of a population over time. ___________ ____________: the combined genetic information of all the members of a population __________________ ______________________: the number of times that an allele occurs in a gene pool compare to the total number of alleles Natural selection affects polygenic traits differently than single gene traits. Single-Gene Trait Controlled by one gene that has two alleles Two distinct phenotypes Ex: Tall or Short Pea Plants pg. 18 Polygenic Trait Controlled by more than one gene with many alleles Many possible genotypes and phenotypes Ex: Human Height Natural selection can affect the distributions of polygenic phenotypes in any of 3 ways: Directional Selection Stabilizing Selection When individuals at one end of the curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle or other end. Entire ______________ _____________ Favors _______ of the extreme variations Individual in the center of the curve have higher fitness than those at the ends of the curve. Center remains __________ but _____________ entire graph Favors ___________ individuals Ex: weight of human infants Disruptive Selection: pg. 19 When individuals at each end of the curve have higher fitness than those in the middle Favors _________ ________________variations Creates _______ distinct phenotypes (can lead to speciation) Genetic Drift: ______________ change in allele frequency of a _____________population due to _______________. Does ________ increase the overall fitness of the population More likely to occur in ______________populations. Genetic Equilibrium: when the allele frequencies in a population remain __________________over time. The population is __________ evolving Hardy-Weinberg Principle A population will not evolve if the following conditions are met: Random Mating Large Population No Migration No mutations No natural selection Modern Classification is based on Evolution pg. 20 Cladograms A ______________________ is a diagram used to show evolutionary relationships. Cladograms show ________________________ between organisms Are assembled using evidences of evolution Can be changed with new data Clade A group of _____________________, such as a species, whose members share _____________________ features derived from a _________________ ________________________. Derived character: trait shared by clade members. Node: where a branch splits in two How to read a cladogram This diagram shows a relationship between 4 relatives. These relatives share a common ancestor at the root of the tree. Note that this diagram is also a timeline. The older organism is at the bottom of the tree. The four descendants at the top of the tree are DIFFERENT species. This is called SPECIATION pg. 21 Cladistics is classification based on Ancestry _______________________ is the evolutionary history for a group of species. shown with branching tree diagrams pg. 22 pg. 23