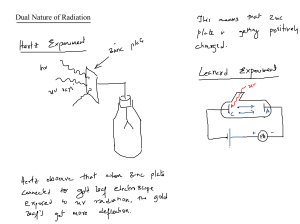
Scalars: Distance, speed, time, mass, energy and temperature Vectors: Force, weight, velocity, acceleration, momentum, electric field strength and gravitational field strength Mass: Measure of quantity of matter in an object at rest relative to the observer Weight: Gravitational force on an object that has mass Velocity: Speed in a given direction Circular motion: (a) speed increases if force increases, with mass and radius constant (b) radius decreases if force increases, with mass and speed constant (c) an increased mass requires an increased force to keep speed and radius constant Moment: force x perpendicular distance from pivot Centre Of Gravity: The point where all the weight of an object seems to act Energy may be stored as: Kinetic Gravitational potential Chemical Elastic (strain) Nuclear Electrostatic Internal (thermal) Can be transferred by: Forces (mechanical work done) Electrical currents (electrical work done) Heating Electromagnetic, sound and other waves Solar Advantages: 1. Renewable 2. No pollution or greenhouse gases Disadvantages: 1. Intermittent supply (Not always available) 2. Uses a lot of space 3. Expensive to setup Biofuels Advantages: 1. Renewable energy resource 2. Relatively cheaper in cost 3. Carbon neutral Disadvantages: 1. Environmental pollution from gases produced contributes to global warming 2. Plants take time to grow Hydropower Advantages: 1. Renewable energy resource 2. No pollution Disadvantages: 1. Expensive to set up 2. Damages surrounding environment Geothermal Advantages: 1. Clean source of naturally available thermal energy 2. Renewable Disadvantages: 1. Environmental pollution caused by the release of poisonous gases such as hydrogen sulphide into the atmosphere 2. Not widely available Fossil Fuels Advantages: 1. Widely available at a large sale 2. Relatively cheaper cost of production Disadvantages: 1. Environmental pollution from gases produced causes global warming 2. Non-renewable Nuclear Advantages: 1. Reliable 2. No pollution Disadvantages: 1. Non-renewable 2. Risks of accidents and pollution from the improper disposal of radioactive wastes Transverse: 1. Electromagnetic Radiation 2. Water Waves 3. Seismic S-waves (Secondary) Longitudinal: 1. Sound Waves 2. Seismic P-waves (Primary) Snell’s Law: sini x n1 = sinr x n2 Refractive index in air = 1 Fixing Long-sightedness: Converging Lens Fixing Short-sightedness: Diverging Lens Monochromatic: Light of a single frequency Uses: Radio Waves: Radio and television transmissions, astronomy, radio frequency identification (RFID) Microwaves: Satellite television, mobile phones (cell phones), microwave ovens Infrared: Electric grills, short range communications such as remote controllers for televisions, intruder alarms, thermal imaging, optical fibres Visible Light: Vision, photography, illumination Ultraviolet: Security marking, detecting fake bank notes, sterilising water X-Rays: Medical scanning, security scanners Gamma Rays: Sterilising food and medical equipment, detection of cancer and its treatment Harmful Effects: Microwaves: Internal heating of body cells Infrared: Skin burns Ultraviolet: Damage to surface cells and eyes, Leading to skin cancer and eye conditions X-Rays and Gamma Rays: Mutation Or Damage of Cells in body Higher Frequency = Higher Energy Speed of Electromagnetic Waves In Vacuum: 3.0 x 108 m/s Benefits Of Digital Signals: 1. Increased Rate of Transmission Of Data 2. Increased range due to accurate signal regeneration Speed Of Sound: 1. Air: 330-350 m/s 2. Liquid: 1500 m/s 3. Solid: 5000 m/s Ultrasound: Sound with frequency greater than 20kHz Used in non-destructive testing of materials, medical scanning of soft tissue and sonar Magnetic Field: A region in which a magnetic pole experiences a force Electric Field: A region in which an electric charge experiences a force Direction Of Magnetic Field at a point: Direction of the force on the North pole of a magnet at that point Electric Current (I = Q/t): The charge passing a point per unit time E.m.f: The electrical work done by a source in moving a unit charge around a complete circuit Potential Difference: Work done by a unit charge passing through a component Kilowatt-hour(kWh): Electrical energy used by a 1 kW appliance in 1 hour Operation of an iron-cored transformer: ● Alternating current in primary coil generates changing magnetic field ● Iron core transfers magnetic field to secondary coil ● Secondary coil cuts magnetic field ● E.m.f induced in secondary coil Scattering of alpha-particles provides evidence for: 1. A very small nucleus surrounded by mostly empty space 2. Nucleus containing most of the mass of the atom 3. Nucleus being positively charged Nuclide Notation A = Mass Number Z = Atomic (Proton) Number Sources Of Background Radiation: 1. Radon gas 2. Rocks and Building 3. Food and drink 4. Cosmic Rays Isotopes can be reactive due to an excess of neutrons in the nucleus and/or nucleus being too heavy Half-life: Time taken for number of radioactive nuclei in the particular sample to halve Safety Precautions for ionising radiation: 1. Reducing exposure time 2. Increasing distance between source and living tissue 3. Using shielding to absorb radiation Light Year = 9.5 x 1015 m Diameter Of Milky Way = 100000 light-years Hubble’s Constant = 2.2 x 10-8/s Redshift = Increase in the observed wavelength of electromagnetic radiation emitted from receding stars and galaxies Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation: Microwave radiation of a specific frequency which is observed at all points in space around. It was produced shortly after the universe was formed and has expanded into the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum as the Universe expanded Speed at which a galaxy is moving away from Earth can be found from change in wavelength of the galaxy’s starlight due to redshift Distance of a far galaxy can be determined using the brightness of a supernova in that galaxy