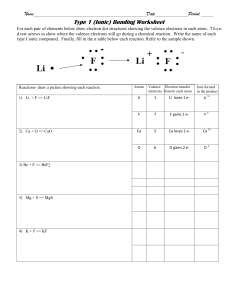
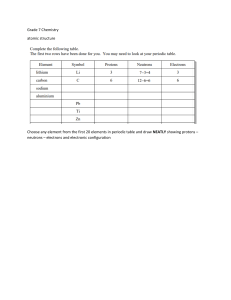
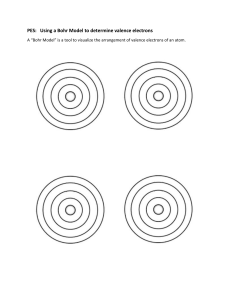
ATOMIC STRUCTRE PROTONS. NUETRONS, ELECTRONS AND ORBITALS Atomic Structure and Isotopes • Welcome to our presentation on "Atomic Structure and Isotopes: Understanding the Building Blocks of Matter." In this exploration, we will delve into the intricate arrangement of electrons in an atom, electron configuration, the significance of the valence shell, and the roles of protons, neutrons, and electrons in shaping the nature of elements. Additionally, we will explore the concept of isotopes and delve into their chemical notations, concluding with an overview of radioactivity. Introduction • Understanding the atomic structure is fundamental to grasping the properties and behavior of matter. At the heart of this understanding is the arrangement of electrons, the key player in chemical reactions. This presentation aims to unravel the mysteries of atomic composition, guiding you through the intricacies of electron configuration, valence shells, and the roles of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Subatomic particles: • Protons reside inside the nucleus and are positively charged • Nuetrons: they also reside inside the nucleus but are neutral • Electrons reside in the electron shell outside the nucleus but are negatively charged Subatomic particles: • Protons, positively charged particles, identify an element. Neutrons, electrically neutral, contribute to the stability of the nucleus. Electrons, with a negative charge, engage in chemical interactions, facilitating the formation of compounds and molecules. Together, these subatomic particles define the unique characteristics of each element. Electron Arrangement • Electrons are arranged in Valenc shells. • With the exception of Hydrogen and Helium whose outer valence shells can only hold 2 electrons most elements wants to have an octet of 8 electrons in their Valence shells Electron Arrangement Electron Arrangement Electron Arrangement Valence Shell and Valence Electron • The outermost shell of an atom is called the valence shell, and the electrons in this shell are valence electrons. These electrons play a crucial role in chemical bonding and reactions. Elements with similar valence electron configurations often exhibit analogous chemical behavior, forming the basis for the periodicity observed in the periodic table. Valence Shell and Valence Electron CHARGE ON AN ATOM • The charge of an atom is determined by the balance of protons and electrons. An equal number of protons and electrons result in a neutral atom, while an imbalance leads to a charged ion. Understanding this balance is fundamental to comprehending the behavior of atoms in chemical reactions. CHARGE ON AN ATOM CHARGE ON AN ATOM • Video play ELEMENTS • PERIODIC TABLE ISOTOPES • Isotopes are variants of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This diversity gives rise to variations in atomic mass. Isotopic notation is employed to represent these variations, allowing for a precise description of an isotope. Isotopes Radioactivity • Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of radiation from unstable atomic nuclei. This phenomenon, crucial in fields like medicine and energy production, encompasses various types of decay processes. Understanding radioactivity is essential for harnessing its benefits while mitigating potential risks.