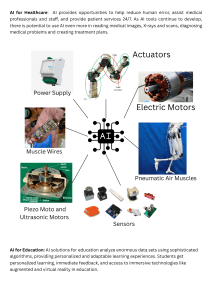
1343 Artificial Intelligence THE CHARTERED ACCOUNTANT Harnessing AI: Transforming the Landscape of Chartered Accountancy Artificial Intelligence (AI) encompasses technologies that enable machines to perform tasks requiring human intelligence, such as data analysis, decision-making, and pattern recognition. This includes machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and predictive analytics. Evolution of Artificial Intelligence CA. Dayaniwas Sharma Member of the Institute E valuating the progression of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is crucial as it highlights its cyclical evolution from theoretical concepts to its current state of rapid development and widespread integration into everyday life. Birth of AI (1941–56): AI’s conceptual groundwork was laid, highlighted by Alan Turing’s ideas and the formal introduction of “artificial intelligence” in 1956. CA. Umesh Sharma Member of the Institute Early Successes (1956–1974): AI thrived with the development of programs that could solve mathematical problems and mimic human reasoning, which spurred widespread interest. First AI Winter (1974–1980): Overhyped expectations led to disappointment, resulting in reduced funding and a decline in AI research. Boom (1980–1987): A resurgence occurred with the creation of expert systems and renewed investment, pushing AI into practical applications. Second AI Winter (1987–1993): The limitations of rule-based AI systems became apparent, leading to another period of disillusionment and cutbacks. Recovery and Growth (1993–2011): AI gained momentum again with advances in machine learning and broader computational capabilities. Deep Learning Era (2011–2020): Breakthroughs in deep learning and big data analytics propelled AI to new heights, enabling complex tasks like image and speech recognition. Current Era (2020–present): The development of large 1941–1956 1974–1980 1987–1993 2011–2020 Birth of Computational AI First AI winter Bust: second AI winter Deep learning, big data Early successes Boom AI Large language models, AI Era 1956–1974 1980–1987 1993–2011 2020-present MAY 2024 23 www.icai.org 1344 Artificial Intelligence THE CHARTERED ACCOUNTANT Table 1. CONTEXTUAL UNDERSTANDING CREATIVITY AND INNOVATION JUDGMENT AND DECISIONMAKING EMPATHY AND EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE ADAPTABILITY AND FLEXIBILITY ETHICAL AND MORAL REASONING INTERDISCIPLINARY AND HOLISTIC PERSPECTIVES COMMUNICATION AND COLLABORATION language models has revolutionized AI, enhancing its understanding and generative capabilities and integrating AI more deeply into various sectors. professional settings. The collaboration between AI and human intelligence can yield more effective, humane outcomes across various professional fields. Importance of Human Intelligence in AI From static data to predictive data – True perspective Human intelligence is important in artificial intelligence (AI) because it helps ensure the integrity of data and information. For example, human intelligence can help identify errors, biases, or gaps in AI data. It also provides judgment, intuition, and ethical decision-making that AI systems lack. The future of AI is likely to involve collaboration between humans and machines. AI can enhance human capabilities, allowing humans to focus on higher-level tasks that require human ingenuity and expertise. Moving from static data to predictive data represents a significant shift in how organizations leverage data to drive insights and AI decision-making. A perspective on this transition in Table 2: The transition from static to predictive data signifies a proactive, forward-thinking approach in data analysis and decision-making Enhanced Insight, Operational Optimization, Balanced Approach, and Integrated Decision-Making. This strategic pivot helps organizations stay competitive and responsive in a dynamic business environment. Remember, AI serves as an augmentation to human capabilities, not a replacement. It’s a creation of human intelligence, designed to extend our abilities and enrich our endeavours. Where AI can be used? AI is making significant inroads across various sectors, showcasing its broad applicability and transformative potential. Key areas of AI deployment are given in Table 3: Professional Intelligence over Artificial Intelligence Artificial intelligence (AI) excels in speed, accuracy, and cost-efficiency, and can identify patterns and make predictions, whereas professional intelligence distinguishes itself from qualities in table 1. These examples highlight just a glimpse of AI’s capability to innovate and transform industries. As technology progresses, the scope and impact of AI continue to grow, presenting new opportunities for advancement in numerous fields. AI’s capabilities, while impressive, do not replace the deep, multifaceted intelligence humans bring to Table 2. Static Data Predictive Data Traditional data sources are often static and Predictive data involves analysing historical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships that can be historical, providing a snapshot of past events or used to forecast future outcomes. transactions. Static data is typically structured and stored By applying advanced analytics techniques such as machine learning and predictive modelling, in databases or spreadsheets, representing organizations can extract actionable insights from data information at a specific point in time. to anticipate and prepare for future events. While static data is valuable for reporting and descriptive analytics, it has limitations in terms of Predictive data enables organizations to move beyond reactive decision-making and proactively anticipate providing real-time insights or predicting future changes, risks, and opportunities in their business trends. environment. MAY 2024 24 www.icai.org 1345 Artificial Intelligence THE CHARTERED ACCOUNTANT Table 3. Healthcare Education Finance Marketing Retail Manufacturing Transportation Smart Cities Cybersecurity Natural Language Processing (NLP) Entertainment Customer Service AI and Its Impact on Chartered Accountants responses, real-time insights, and personalized services. Meeting client expectations enhances satisfaction and loyalty. For Chartered Accountants (CAs), learning about AI is essential as it transforms the accounting field. AI helps to streamline processes, increase accuracy, and provide new insights, significantly influencing the financial sector. With AI becoming increasingly integral to accounting, it is crucial for CAs to embrace these technologies to improve their practices and make better strategic decisions. Selecting the Right AI Tools for Accounting: Key Considerations When choosing AI tools for accounting, consider these essential factors given in table 4: These criteria will help you select an AI tool that effectively meets your accounting needs and operational standards. Why AI Tools Matter for CAs Efficiency and Accuracy: AI tools automate repetitive tasks, such as data entry, reconciliation, and basic analysis. By doing so, they free up valuable time for CAs to focus on higher-value activities. Additionally, AI reduces the risk of human errors, leading to more accurate financial reporting. Key AI Tools for Chartered Accountants Chartered Accountants have a variety of AI tools at their disposal to enhance efficiency and accuracy in their practices: Insights and Decision Support: AI can analyse vast amounts of data quickly. CAs can leverage AI tools for financial forecasting, risk assessment, and trend analysis. These insights empower better decisionmaking and strategic planning. Automated Accounting Software: Streamlines tasks such as data entry and bank reconciliations. Popular options include QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks. Predictive Analytics Tools: Useful for financial forecasting and risk assessment, with tools like Tableau, IBM Watson Analytics, and custom-built ML models leading the way. Client Satisfaction: Clients expect CAs to be techsavvy. By using AI tools, CAs can provide faster Table 4. Specific Needs: Clearly define the tasks you need to enhance, such as auditing or financial analysis, to identify the most suitable tools. Integration Ease: Ensure the AI tool can seamlessly integrate with your existing systems to avoid workflow disruptions. Reliability and Accuracy: Evaluate the tool's precision and consistency through user reviews and performance metrics. MAY 2024 25 Data Security: Choose tools that comply with data protection laws and prioritize client confidentiality. www.icai.org Support and Training: opt for tools that offer comprehensive training and reliable customer support to ensure ease of use and a smooth transition. 1346 Artificial Intelligence THE CHARTERED ACCOUNTANT Fraud Detection: AI algorithms detect anomalies and irregularities in financial data, helping to prevent fraud and manage risks. Audit Automation Tools: Facilitates audit processes and fraud detection, with CaseWare IDEA and ACL Analytics being notable examples. Natural Language Processing (NLP) Tools: Extracts insights from unstructured texts like contracts and legal documents, essential for document analysis. Chat GPT: Aids in various accounting tasks including financial reporting, and tax planning, significantly boosting productivity. AI is not here to replace CAs but to augment their capabilities. By embracing AI, Chartered Accountants can streamline processes, improve accuracy, and provide better insights to their clients. Regulatory Compliance: AI helps ensure adherence to evolving regulations and simplifies regulatory reporting. Enhanced Client Communication: AIdriven chatbots and virtual assistants offer round-the-clock client support, improving satisfaction and communication efficiency. Copilot by Microsoft: Enhances firm productivity by automating tasks, analysing data, and streamlining workflows. Professional Development: AI platforms provide customized continuing professional education (CPE) opportunities, keeping CAs updated with the latest industry knowledge. Blue Dot: Specializes in automating VAT and other tax compliances, using AI to ensure accuracy across different jurisdictions. Competitive Edge: Adopting AI allows CAs to differentiate their services, providing innovative solutions and superior insights that set them apart from competitors. Zeni: An AI-powered platform that manages financial operations for startups, offering real-time insights and daily bookkeeping. These benefits highlight how AI can revolutionize the accounting profession, making practices more effective, client-focused, and adaptable to new challenges. Docyt: Reduces manual effort in financial document analysis by using machine learning to categorize and analyze data. These tools collectively help CAs automate routine processes, gain insightful analytics, and manage compliance more effectively, allowing them to focus on more strategic aspects of their work. Conclusion AI is not here to replace CAs but to augment their capabilities. By embracing AI, Chartered Accountants can streamline processes, improve accuracy, and provide better insights to their clients. As the accounting profession continues to evolve, CAs who embrace AI will be better positioned for success. Key Benefits of AI for Chartered Accountants Artificial Intelligence (AI) significantly enhances the capabilities of Chartered Accountants (CAs) by offering the following advantages: Remember, AI is a tool—a powerful one—but it still requires human expertise to interpret results and make informed decisions. So, as a Chartered Accountant, stay curious, learn about AI, and explore how it can enhance your practice! Automation of Tasks: AI automates routine tasks such as data entry, transaction processing, and reconciliation, freeing up time for more strategic work. Accuracy and Efficiency: AI tools perform calculations and audits with higher speed and precision, minimizing errors and enhancing overall efficiency. Reference Data Analysis and Insights: AI analyses vast volumes of data quickly, uncovering trends and patterns that aid in strategic decision-making. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_artificial_ intelligence#Large_language_models,_AI_era_ (2020%E2%80%93present) Predictive Analytics: AI models forecast financial trends and identify risks, enabling proactive decision-making to leverage opportunities and mitigate potential pitfalls. MAY 2024 Personalized Client Services: AI personalizes client interactions by tailoring recommendations and services to individual needs. Authors may be reached at eboard@icai.in 26 www.icai.org