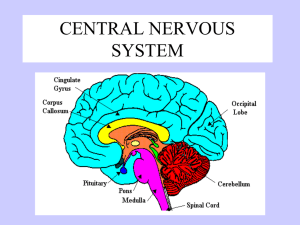
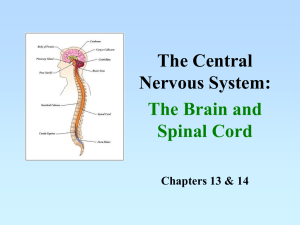
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Brain Dominance • Right Brain – non-verbal – Concrete – Holistic (big pic) – Intuitive – spontaneous • Left Brain – Logical – Language – Verbal – Sequential/linear (Math) – Abstract…math/science – Planner http://www.web-us.com/BRAIN/braindominance.htm Objectives • To learn protective parts/features of CNS • To learn structure and function of the Spinal Cord • To understand the brain structure and function as well as development. Protection of the CNS • Bones • Meninges Protection of the CNS • The brain & spinal cord are protected by bones, membranes, and fluid A. Bones –*8 skull bones encase the brain –*30 vertebrae encase the spinal cord Can you name the bones? – B.) Meninges - Membranes surrounding CNS • 3 Layers encasing the brain –a.) Dura mater »outermost membrane: attached to periosteum of the skull »contains many blood vessels & nerves »tough, white fibrous connective tissue –b.) Arachnoid Mater »middle layer »thin net-like membrane »No blood vessels »Sub-arachnoid space lies deep to this layer and is filled with CSF which serves as a cushion for brain –c.) Pia Mater »inner layer that clings to brain surface »very thin delicate connective tissue »many nerves & blood vessels = nourishment »dips into grooves and contours inner layer that clings to brain surface Meningitis • What does the word Mean? • Caused by: – Bacteria or virus • Affects: – Mainly arachnoid and pia maters – Younger or older generations – People with suppressed immune systems • Complications of disease: – Loss of vision, hearing paralysis, mental retardation…death C. Ventricles – Interconnected cavities within the cerebral hemispheres and brain stem – Continuous with central canal of spinal cord – Filled with CSF cerebral spinal fluid – D. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) – Secreted by Choroid Plexus – Circulation: Ventricles 1&2 --> 3rd --> 4th --> central canal --> reabsorbed into bloodstream – Approx. 1 liter is secreted daily: Secreted and reabsorbed continuously – Functions: cushion & circulation of nutrients/wastes The Brain Structures and Functions Brain Lobes Forebrain prosencepahlon • Includes hypothalamus, thalamus and cerebrum Midbrain mesencephalon • Connects cerebrum to spinal cord • Reflex center for eye and some head movements Hindbrain rhombencephalon • Cerebellum • Medulla oblongata • Pons Cerebrum • Largest part of brain • Contains many folds and bumbs – Sulci vs. gyri • Corpus callosum is found b/t the L and R • Responsible for reasoning, intellectual fxn and critical thinking Brain Dominance • Right Brain – non-verbal – Concrete – Holistic (big pic) – Intuitive – spontaneous • Left Brain – Verbal – Sequential/linear – Abstract…math/science – Logical – Planner http://www.web-us.com/BRAIN/braindominance.htm Cerebral Cortex • Thin layer (2-5mm); largest and most anterior structure of brain • Contains 75% of neuron cell bodies in NS • Memory, attn, thought processes, language cerebellum • Regulates balance • body position • Posture • Muscle coordination Medulla oblongata • Vital Reflex center – Visceral activities: – blood pressure, respiratory – cardiac • Part of the brain stem • Injuries often fatal Corpus callosum • Deep bridge of nerve fibers • Connects L and R brain • Intercommunication b/t hemispheres is not completely understood Optic chiasma Limbic System Limbic • Includes the hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala • Important in emotions and formation of memories Limbic • Hypothalamus • Part of diencephalon • Secretes hormones – Dopamine, oxytocin, growth hormones • Regulates body temp, heart rate, hunger/weight, alertness • Center involved with emotion Thalamus • Part of diencephalon • Motor control • Receives visual and auditory senses Pineal gland • Produces melatonin; controls circadian rhythm • Size of a pea; 8mm • Think about it… – Stimulated by dark – Inhibited by light c Pineal body Pituitary gland • Endocrine gland; secretes hormones • Examples – growth hormones; – regulate breast milk production; sexual hormones – possibly blood pressure Pons • b/t midbrain and medulla oblongata • Regulates rate and depth of breathing • Homeostatic mechanisms Mammillary body • Named for resemblance of 2 breast • Associated with memory • Damaged by alcoholic intoxication Hippocampus • Part of limbic system • Emotions, inhibition • Long term memory • Alzheimer’s disease – First to be damaged If damaged, what do you predict would be the results? Reticular formation • Brainstem and diencephalon • Alertness, arousal, sensory integration, motivation • connects to areas in the thalamus, hypothalamus, cortex and cerebellum http://www.web-us.com/BRAIN/braindominance.htm