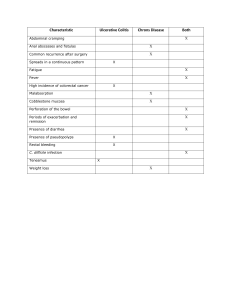
Urinary Fistulas: Understanding the Condition and its Prognosis Urinary fistulas are abnormal connections between the urinary tract and another organ or the skin, causing urine leakage outside the bladder. These fistulas can occur due to various factors, including: • Surgery: Complications from abdominal or pelvic surgeries can damage urinary structures. • Trauma: Pelvic injuries or burns can create fistulas. • Infection: Chronic infections can erode tissues and form fistulas. • Radiation therapy: Side effects of radiation therapy can damage urinary tissues. • Certain medical conditions: Inflammatory bowel disease or cancer can contribute to fistula formation. Disease progression and danger: The severity and complications of urinary fistulas depend on various factors, including: • Location: Fistulas near vital organs pose a higher risk of infection and other complications. • Size and type: Larger fistulas lead to greater urine leakage and potential skin irritation. • Underlying cause: The cause of the fistula can influence its severity and treatment options. Prognosis: Fortunately, most urinary fistulas can be successfully treated. Treatment options vary based on the factors mentioned above and may include: • Medications: Antibiotics can manage infections while awaiting surgery. • Minimally invasive procedures: Depending on the type and location, minor fistulas may be closed using catheters or embolization techniques. • Surgery: Open surgery is often necessary for complex fistulas, involving repair of the affected tissues and closure of the abnormal connection. Leaving urinary fistulas untreated can have a range of potentially serious consequences, both immediate and long-term. Here are some of the negative outcomes that may occur: Immediate Dangers: • Severe infections: Untreated fistulas provide a pathway for bacteria to enter the body, leading to recurring and potentially life-threatening infections in the urinary tract, kidneys, and surrounding tissues. These infections can cause fever, chills, pain, and organ damage. • Chronic skin problems: Constant exposure to urine can cause severe skin irritation, inflammation, and even ulcers. This can be particularly painful and debilitating, especially in sensitive areas like the vagina or perineum. • Electrolyte imbalance: Urine contains essential electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride. Untreated fistulas can lead to significant loss of these electrolytes, disrupting the body's delicate balance. This can cause symptoms like fatigue, muscle weakness, confusion, and even heart problems. Long-Term Complications: • Kidney damage: Chronic infections and inflammation caused by untreated fistulas can damage the kidneys, potentially leading to impaired kidney function and even kidney failure. This can require dialysis or kidney transplantation. • Reduced lifespan: In severe cases, untreated fistulas can contribute to serious health problems like sepsis or kidney failure, potentially shortening a person's lifespan. General information about urinary fistulas: • National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38120908/ • Urology Care Foundation: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002365.htm • Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vaginal-fistulas/care-at-mayoclinic/mac-20355765 Complications of untreated urinary fistulas: • International Journal of Women's Health: https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-az/b/bladder-fistula • World Journal of Urology: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4434500/ • Journal of Women's Health (London): https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26922407/ Importance of early treatment: • The Journal of Urology: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5321457/ • Canadian Urological Association Journal: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26372035/ • Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada: https://www.miklosandmoore.com/files/2016/08/6-Vesicovaginal-Fistula-FailingMultiple-Surgical-Attempts-JMIG.pdf