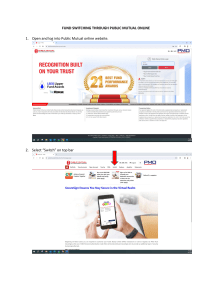
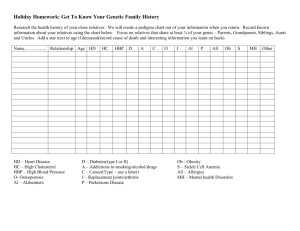
PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT IMPORTANT TERMINOLOGIES: 1. Relationship - is a state of connectedness between people (especially an emotional connection) 2. Personal - relationships are relationships between people, especially those between friends, lovers and family members 3. Attraction - the act, power, or property of attracting Attractive quality; magnetic charm; fascination; allurement; Enticement - A person or thing that draws, attracts, allures, or entices 4. Love - is a strong affection for another arising out of kinship or personalities (maternal love for a child) 5. Commitment - is the act of binding yourself (intellectually or emotionally) to a course of action and a message that makes a pledge 6. Responsibility - is the social force that binds you to the courses of action demanded by that force - A form of trustworthiness; the trait of being answerable to someone for something or being responsible for one’s conduct Relationship - every kind of relationship is a two-way traffic which means that all parties should learn how to give and take. Personal relationships - refer to close connections between people, formed by emotional bonds and interactions. - these bonds often grow from and are strengthened by mutual experiences. - not static; they are continually evolving, and to fully enjoy and benefit from them we need skills, information, inspiration, practice, and social support. In our model there are three kinds of personal relationships: A. Family - "two or more persons who are related by birth, marriage, or adoption and who live together as one household." (The Bureau of the Census) - some typical characteristics of a family are support, mutual trust, regular interactions, shared beliefs and values, security, and a sense of community. B. Friends - close ties between two people that are often built upon mutual experiences, shared interests, proximity, and emotional bonding. Friends can turn to each other in times of need. - the average person has about six close ties—though some have more, and many have only one or none. (Nicholas Christakis and James Fowler) - online friends don’t count toward close ties—research indicates that a large online network isn’t nearly as powerful as having a few close, reallife friends. C. Partnerships Romantic partnerships, including marriage, are close relationships formed between two people that are built upon affection, trust, intimacy, and romantic love. Three Stages of Love or Falling in Love (proposed by Helen Fisher) 1. Lust- urge or desire that motivates sexual activity 2. Attraction- a stage when a person loses sleep and appetite and becomes excited about someone while daydreaming. Factors affecting one’s Attraction: A. Physical Attractiveness- one of the determinants of romantic attraction especially in the early stages of dating. B. Proximity- people get to be attracted to people who are geographically closer to them and interact with them frequently. They develop feelings of mutual familiarity and an increased level of comfort. C. Similarity- people pick partners who have similarities with them. D. Reciprocity- people like others who like them back. 3. Attachment- a deep and enduring emotional bond that connects one person to another across time and space. Robert Sternberg's (1988) Triangular Model of Love, suggests that there are 3 main components of love. 1. Intimacy- an intimate interpersonal relationship that involves physical or emotional intimacy. It involves closeness, connectedness, and bondedness. 2. Passion- intense emotion, a great desire for something. 3. Commitment- attitude of someone who works very hard to do something. It is an act deciding consistently fulfill and live by agreements made with another party. 7. Philautia (Self Love) - a healthy love towards one’s self. It is recognizing your self-worth and don’t ignore your personal needs. 8. Agape (Selfless Love) - empathetic attitude of love for everyone. It is the highest form of love. It is giving without expecting anything back. Ancient Greek and Lee Types/Styles of Love: 1. Philia (Affectionate Love) - runs deep through friendship. It is called brotherly love when people share the same values and respect each other. 2. Pragma (Enduring Love) - mature love that develops over time. Commitment and efforts are needed. 3. Storge (Familiar Love) - naturally occurring rooted in parents and children as well as best friends. It’s an infinite love built upon acceptance and deep emotional connection. 4. Eros (Romantic Love) - a personal infatuation and physical pleasure. A passionate love displayed through physical affection 5. Ludus (Playful Love) - flirting and beginning stages of intimate love. Contains teasing, playful motives and laughter. 6. Mania (Obsessive Love) - madness over a partner.It leads to unwanted jealousy or possessiveness. Tips on how to keep healthy relationships with others. Stay happy. Happiness gives you the feeling of satisfaction for both abstract and concrete things. Be empathic. Empathizing with another is acting with greater cooperation and overall selflessness—the desire to help, even at a potential cost to the self. Keep open communication. It provides an opportunity to size up the trustworthiness of a person by verbally committing to cooperate with another. Always trust. Working with others toward a common goal requires a level of faith that others will repay our hard work and generosity. Supporting their interests is also showing your trust. Show respect. People are likely to give respect to others by being polite, honest, and by showing kindness all the time. Be a helping hand. In times of trouble (e.g., mentally/ emotionally), make him/her feel that he/she always has you on his/her side. know you have someone whom you can pleasingly offer and share the blissful feeling of a victorious life with. MODULE 3-4 6. Build a beautiful person within you. Having all the positive attitudes towards life and oneself can really create a good aura. Portraying good personalities can even make you appear and feel young and lovely. Now that you are aware of the good things you get out from being in a relationship, this time get yourself hooked with our discussion on how you can push yourself to be responsible in your own relationships with your loved ones. Some of the importance of relationships are: 6 Major Elements of Becoming Responsible in a Relationship 1. Lead us to make healthy relationships. All kinds of relationships can give you the opportunities to establish a stronger relationship with your shared experiences and feelings with your loved ones. These six elements of becoming responsible in any form of relationship will make you gain and maintain a stronger relationship with your family, friends, and special someone. 2. Help us see our potential. People who love you will always see the wonderful things in you. Through this loving and supportive atmosphere, you little by little grow as a person, seeing your worth with your capabilities and unique gift and talent. 1. Mutual Respect - Respect plays a crucial role in fostering a positive environment and encouraging mutual regard among individuals. Drawing from the Golden Rule, which emphasizes treating others as one would want to be treated, it becomes evident that respect is reciprocal. By employing supportive language, embracing individual differences, and embracing forgiveness, we cultivate respect in our relationships and communities. 3. Boost our confidence. It makes you feel you’re the luckiest person in the world whenever someone trusts you sufficiently enough. It makes your spirit enthusiastic and gives you a delightful feeling of selfassurance. 4. Give you a sense of direction. The idea and feeling of a sense of belongingness is such a great source of direction. If you care to give yourself the reward of having a good life and reputation, you will absolutely do more for the people you dearly love. 5. Clear our life goals and aspirations. Relationships will help you focus on one goal and concentrate in achieving it because as the sun sets you 2. Value Quality Time - Taking time for enjoyable activities can enrich your life with cherished memories. Deepening your bond with loved ones often involves prioritizing meaningful moments over mere quantity of time spent together. A minute of heartfelt connection can outweigh a day filled with discord, emphasizing the importance of quality interactions. 3. Trust and Honesty - The person who consistently receives someone’s trust will grow up trusting him/herself based on how others trust him/her. Indeed, positive encouragement may create a positive outlook in life. Trust is the heart of all relationships, and because of its presence, other things follow like confidence, loyalty, and most of all honesty. 4. Well-Communicated Love - Open communication is crucial for maintaining relationships. Demonstrating love through simple gestures like a tap on the shoulder, a kiss, or a smile fosters well-communicated affection. These genuine acts strengthen the bond between individuals. 5. Reliability and Security - This virtue emphasizes acknowledging others' imperfections and offering support, fostering connections and security. By extending a helping hand, individuals feel cared for and supported, encouraging a sense of responsibility for their actions. Ultimately, this cycle of understanding and assistance strengthens relationships and encourages positive behavior. 6. Non-judgmental Listening and Presence - Listening with integrity, devoid of judgment or discrimination, enhances presence in relationships. Cultivating the trait of being a good listener fosters stronger connections with others. True commitment in relationships involves offering the best of oneself while patiently awaiting reciprocation. 1. Set an example - a good leader sets the best example. It is the first rule. Walk the talk. Do not compromise anybody in the organization or team integrity. Never take shortcuts. 2. Show Initiative- find out what needs to be done. do not wait for anyone to tell you what to do. 3. Willing to serve- this quality is known as a servant leader. Showing these kinds of characteristics can inspire the thoughts and actions of your constituents. 4. Show empathy- Try to understand where people are coming from and their point of view. Put yourself in the other people’s shoes. 5. Delegate work- sharing work among members at the organization should be divided into a manageable task. Explain completely what you are asking the person to do. 6. Learn to appreciate- If someone has done great with the assigned tasks, be sure to let them feel they are appreciated. Simply saying thanks will do. This will motivate them to work hard. Do not get easily annoyed if an untoward incident happens. Hold your temper. Role of an Effective Follower that Leaders Need Role - defines a set of norms, values, behaviors, and personality characteristics attached to a status such as leader, follower, or club president. 1. Courage to do responsibility- Effective follower feels a sense of personal responsibility and ownership for his or her behavior in the organization. Every leader assumes role in a society. They are expected to behave a pattern usually determined by individuals in the society. 2. Courage to participate in transformation- Effective followers view the struggle of change and transformation as a mutual experience shared by all members, support the leader, and are not afraid to confront the changes. To become a great leader, you must be a Roles of an Efficient Leader that can influence people: 3. A ‘can-do’ attitude- A leader’s job becomes smoother when he or she has followers who are positive and self-motivated, can get things done, accept responsibility, excels in required tasks, and willingly accept difficult assignment. 4. Courage to serve and subservient- Effective follower understands the needs of the organizations and seek to serve those who need. 5. The passion to drive personal growth- Leaders want followers who seek to enhance their own growth and development rather than depending on the leader to do it. MODULE 5-6 Perception - involves processing and understanding information to guide behavior, shaped by beliefs, values, and norms acquired through interactions in society. - includes how we see others and how they see us, influenced by familial, social, and cultural contexts. These experiences continually refine our self-perception and understanding of others, enhancing adaptability in various situations. Social influence - refers to behavior changes prompted by those who hold power, affecting how individuals adapt to various situations. This phenomenon encompasses conformity, compliance, and obedience as its key categories. Conformity, as outlined by Asch (1955) in Ramirez (2020), involves altering one's behavior to align with the group's norms. In the scenario described, seeking the grandmother's blessing at a friend's home exemplifies conforming to shared cultural customs to avoid social disapproval. By adhering to these norms, individuals gain acceptance within the group, demonstrating their ability to conform to its standards. Compliance is granting a request or demand asked by another individual in exchange of either a reward or a punishment. For example, during examination day, you are required to take the test to finish the grading period and failure to do so may result in a failing grade. Obedience means changing your behavior to follow the demand given by an authority or an adult you have high regards with. For instance, as a maturing adolescent, you want to contribute to development through inviting other friends to exercise proper waste disposal. Whether you do it purposely as you try to give the leader your respect or purposefully as it empowers you to participate actively as a follower. Whatever your reason is for obeying; it leads to social facilitation. This happens when you are given a sense of responsibility that allows you to perform better if you are with other individuals. Social relationships rely on interaction and influence among individuals, shaping behaviors that either support or hinder fulfilling social roles. Inevitable disagreements arise due to differing perspectives and values, reflecting the imperfect nature of societal dynamics. Thus, encountering dissent is common in navigating social landscapes. Social relationships - refer to the connections that exist between people who have recurring interactions that are perceived by the participants to have personal meaning. This definition includes relationships between family members, friends, neighbors, fellow workers, and other associates. Relationship is how two or more people or groups regard and behave toward each other. o Family and relatives are individuals connected through kinship, such as parents, siblings, grandparents, aunts, uncles, or step-parents. Friends are chosen individuals with whom one shares a bond of mutual affection, distinct from familial or romantic relationships. Acquaintances are people encountered frequently but not considered friends or relatives, like neighbors, colleagues, or casual acquaintances from social events. Community relations refer to a company's interactions with the community where it operates. Filipinos prioritize close family ties, hospitality, and a strong sense of community, reflected in their desire to talk about extended family. The concept of home-school partnership emphasizes cooperation, coordination, and collaboration to enhance students' academic, social, and emotional development. Recognizing that schools alone cannot fully prepare youth for adulthood, leaders advocate for school-community partnerships to leverage resources and strategies for the benefit of all youth and their families. Mini-surveys are carefully focused on a specific topic. It contains only fifteen to thirty questions. It is given to a small sample of twenty-five to seventy people. It usually uses more closed than open-ended questions; that is, they use questions that force the respondent to choose from a small set of alternative answers, rather than inviting a freely expanded comment. Some Uses of the Mini-survey are: • To get a picture that will help you to design the next stages of your research • To assess the feasibility of a project • To get reactions from beneficiaries • To evaluate projects. Steps in conducting a mini-survey Step 1: Clarify Your Objectives Step 2: Find Out What Else Has Been Done Step 3: Choose the Respondents Step 4: Develop the Questions MODULE 7-8 Family is the basic unit of society. composed of individuals living together in one household either connected by marriage, blood, or by legal arrangement. comes from the Latin word familia which means group of people living in the household. related by blood, by birth, or by other relationships. smallest organization in the community. Family Structure Definition Nuclear Family It is also known as “conjugal” or “traditional” family, consisting of married couples and their offspring. Extended Family This type of family includes all relatives in proximity, such as grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins. These relatives typically live together, and all share daily household duties. Single Parent Family Step Family Foster Family Adopted/Adoptive Family Bi-racial or Multi-racial Family Trans-racial Adoptive Family Conditionally Separated Family Childless Family Gay or Lesbian Family Migrant Family Immigrant Family This family type includes one parent and their children only. A single parent family could be the result of a divorce, the death of one parent, or even a single parent adoption. A family where the parents have divorced and remarried, bringing children from other unions together to form a new nuclear family. It is also known as “blended” family because two families were combined. A family includes parent who serves as a temporary guardian for one or more children to whom they may or may not be biologically related. A family wherein parents may adopt a child to whom they share no blood relationship, or one parent may adopt the child of the other parent. A family wherein parents are from different races A family wherein parents adopted a child with a different race A family wherein one of the family members is conditionally separated from the others. This separation may be due to their job or employment or could be due to hospitalization. Married couple without children A family wherein one or both parents have a different sexual orientation and part of the LGBT community It is a family who settles together in a different place; it could be from one place to another due to some circumstances such as the father’s job. A family wherein one or both parents are already an immigrant of other country. Their children may be or may not be an immigrant. Example Mother, father, and children A family living together with mother, father, children, grandparents, aunts, uncles, and other relatives in one roof Father with his children or a mother with her children living in one household Mother, children, stepfather, and his kids Father, children, stepmother, and her kids Parents, children, foster child Parents (mother and father), adopted child Filipina mother, American father, children American parents, adopted Filipino children A family living together except for the father working abroad or a family living together except for the eldest child serving in the military Mother and father only A lesbian mother and her children with a gay father A family who migrated from a place because the father is a military officer Santos family whose mom is already an immigrant of Canada -- their mother is already a Canadian citizen but the rest of the family members are not. A genogram (pronounced: jen-uh-gram) (also known as a McGoldrick–Gerson study ) is a graphic representation of a family tree that displays detailed data on relationships among individuals. A genogram is a more complex family tree because it describes not only the family’s physical and social relationships, but also the emotional connections and other family attributes. Genograms were first developed and popularized in clinical settings by Monica McGoldrick and Randy Gerson through the publication of a book in 1985.