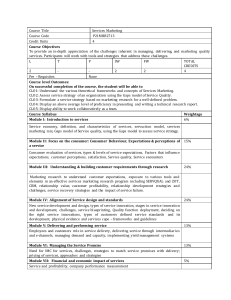
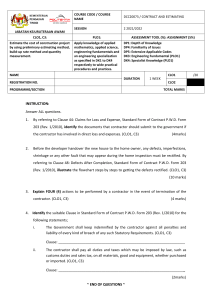
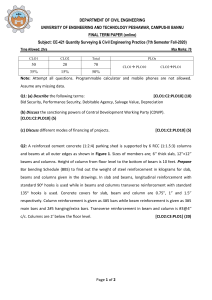
Writing Learning Outcomes Dr. M. Rafiqul Islam Director, IQAC, BUET & Professor Department of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology September 24, 2018 Information presented in this talk is collected mostly from Dr. Nazri’s (Prof. of UiTM, Malaysia) lecture and publicly available sources. All these sources are gratefully acknowledged Different Levels of Learning Outcomes Programme Educational Objectives (PEO) Program Outcomes (PO) Few years after Graduation – 4 to 5 years Employer Survey, Alumni Survey Upon graduation – Program Outcomes Competent engineers who are leaders in ….. ..will be able to demonstrate critical thinking skills to solve Employer survey, Exit Survey, Prog.Survey, Alumni Survey Course Outcomes (CO) Upon course completion Use BLOOM'S Taxonomy of Learning Domains (C/A/P) .. will be able to explain the physical principles of …… Sum/Form/Cont. Assessments Upon topic completion Use Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning Domains (C/A/P) Sum/Form/Cont. Assessments .. will be able to explain Archimedes principle of …… WRITING PROGRAM EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (PEO) PEOs • 4-5 statements on what the graduates are in 4-5 years time • Must include all learning outcomes in the statements (for degree program and above) • Usually in-line with the industry/profession’s needs • Can include non-measurable verbs such as understand, know, acquire, etc. Aims The Faculty's engineering programme shall produce Civil Engineers who are: PO1 PO2 PEO1 Knowledgeable and technically competent in civil engineering discipline inline with the industry requirement. . PO4 PO9 PEO2 Effective in communication and demonstrate good leadership quality in an organization. PO5 PO3 PO3 PEO3 Capable to solve civil engineering problems innovatively, creatively and ethically through sustainable approach. PO6 PO8 PO7 PEO4 Able to demonstrate entrepreneurship skills and recognize the need of life long learning for successful career advancement. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Knowledge Practical Skills Thinking and scientific skills Communication skills Social skills, teamwork and responsibility Values, ethics, moral and professionalism Information management and lifelong learning skills Managerial and entrepreneurial skills Leadership skills WRITING PROGRAM OUTCOMES (PO) POs • Statements on what skills the students will have upon graduation (in line with program standards or professional bodies) • Must include learning outcomes in the statements (for degree programs and above) • Can include non-measurable verbs such as understand, know, acquire, etc. At the end of this programme, students will be able to: PO1 PO1: Acquire and apply knowledge of sciences and engineering fundamentals to civil engineering field. PO 2 PO2: Demonstrate comprehensive technical expertise in civil engineering. PO 3 PO3: Identify, formulate and provide creative, innovative and effective solution to civil engineering problems. PO4 PO4: Communicate effectively both in written and spoken form with engineers, other professionals and community. PO5 PO5: Function individually or in teams, effectively, with a capability to be a leader. PO6 PO6: Understand and commit professionally, ethically and with humane responsibility, in line with the engineer's code of conduct. PO7 PO7: Recognize the need for and to engage in life-long learning and professional devePOpment. PO8 PO8: Self motivate and enhance entrepreneurship skills for career devePOpment. PO9 PO9: Realize and demonstrate effective leadership responsibility. WRITING COURSE OUTCOMES (CO) Characteristics of a Good Course Outcome should be mapped to the learning domain in Blooms or other Taxonomy . Must state the major skills, knowledge, attitude or ability that students will acquire. expressed in terms of measurable and/or observable behaviors (hint: ask yourself how you would test the outcome). more general than behavioural objectives. Characteristics of a Good Course Outcome (Cont.) Each course will usually have between 3 and 5 major outcomes. Should be written in clear language and in the future tense Begin with an action verb (e.g., write, install, solve, and apply). 3 components of a course outcome 1) Action verb (describes what the learner will be doing, or the behaviour) By the end of this course/semester, students should be able to: • describe the principles used in designing X. • evaluate the strengths and weakness of … Avoid these words Well-written verbs must be (SMART) - understand - Specific - appreciate - Measurable - know - Achievable - learn - Realistic - aware - Time frame - Observable - familiar 3 components of a course outcome 2) Condition (context under which the behaviour is to occur) • describe the principles used in designing X.(V) • orally describe the principles used in designing X. (V&C) • design a beam. (V) • design a beam using Microsoft Excel design template . (V&C) 3 components of a course outcome 3) Standard (criteria of acceptable level of performance) • describe the principles used in designing X.(V) • orally describe the principles used in designing X. (V&C) • orally describe the five principles used in designing X. (V&C&S) • design a concrete beam. (V) • design a concrete beam using Microsoft Excel worksheet. (V&C) • design a concrete beam using Microsoft Excel worksheet based on MS EN 1992-1-1: 2010 (NATIONAL ANNEX) (V&C&S) Course Outcomes: An example Identify the a) verb b) condition c) standard. • From the first principles, calculate the beam deflection at the centre to within one decimal point. Identify the a) verb b) condition c) standard. • write an effective course outcomes that include PO lower and higher order cognitive skills for a one-semester course. Common weaknesses in writing CO • Non-observable/Non-measurable CO At the end of the course, the students should be able to: 1. understand the theory of X. 2. know how to write an effective learning outcomes 3. appreciate the importance of keeping the environment clean. • Vague CO that are too broad or general By the end of the course, students should be able to: 1. use the computer. 2. make presentations. 3. comment on designs. 4. design research What level of learning should the subjects offer? • Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning – Cognitive, Affective, Psychomotor • Diploma (C3,P4,A3) • Undergraduate (C4, P4, A3) • Masters (C5, P5, A4) • PhD (C6, P6, A5) • General Rule of Thumb –at least 5% of total no.of courses for the program must achieve proposed BLOOM'S level E.g. • For Undergraduate program with total no.of courses = 40 courses/subject • Hence, at least 2 courses must achieve C4, at least 2 courses must achieve P4, and at least 2 courses must achieve A3. Note for writing CO • It is NOT compulsory for every CO to have all 3 learning domains (C,A,P) • It is NOT compulsory for every CO to have all 3 components (i.e. V+C+S) • But must have at least V+C or V+S • CANNOT have 2 “verbs” in the same domain (e.g. state and explain the basic principles.....), use the highest level of taxonomy only (i.e. explain the basic principles....) • Can have 2 “verbs” in different domains (e.g. explain and display the standard procedure........), BUT must measure both (i.e. there must be assessments for both outcomes) • CO can have sub outcomes (e.g. Topic Outcomes, Lesson Outcomes) which might be more detail and can have ALL 3 components to ensure the attainment of the CO. PROGRAM LEARNING OUTCOMES (PLO) At the end of this programme, students will be able to: LO1 PLO1: Acquire and apply knowledge of sciences and engineering fundamentals to civil engineering field. LO2 PLO2: Demonstrate comprehensive technical expertise in civil engineering. LO3 PLO3: Identify, formulate and provide creative, innovative and effective solution to civil engineering problems. LO4 PLO4: Communicate effectively both in written and spoken form with engineers, other professionals and community. LO5 PLO5: Function individually or in teams, effectively, with a capability to be a leader. LO6 PLO6: Understand and commit professionally, ethically and with humane responsibility, in line with the engineer's code of conduct. LO7 PLO7: Recognize the need for and to engage in life-long learning and professional development. LO8 PLO8: Self motivate and enhance entrepreneurship skills for career development. LO9 PLO9: Realize and demonstrate effective leadership responsibility. MAPPING PLO to PEO √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ MAPPING PLO to MOE LO √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ MAPPING CLO to PLO CLO1: Propose solution to manufacturing and operation problems using related theory and analytical methods (C6,A5, PLO3) VERB Propose (C6) CONDITION STANDARD BLOOM’S LEARNING OUTCOMES solution to manufacturing and operation problems using related theory and analytical methods C6 A5 PLO3 (PLO3) PROPOSE (A5) C6 Use components concepts to solve problems A3 Ability to solve problem A5 Use objective approaches in problem solving CLO1: Propose solution to manufacturing and operation problems using related theory and analytical methods (C6,A5, PLO3) PLO1 CLO1 PLO2 PLO3 √ PLO4 PLO5 PLO6 PLO7 PLO8 PLO9 CLO2: Organise in groups to study and present the application of advanced manufacturing and operation analysis methods based on a given topics (C6,A4,P5, PLO3, PLO4, PLO5) VERB Organise CONDITION (C6) in groups; STANDARD (PLO5) based on a given topics to study; the application of advanced manufacturing and operation analysis methods (A4) (PLO3) and present; ORGANISE BLOOM’S LEARNING OUTCOMES C6 A4 P5 PLO3 PLO4 PLO5 (P5) (PLO4) C1 Recalling information C6 Put parts together to form a whole; Use concepts to solve problem A4 Explain role of systematic planning in problem solving P4 Perform with some confidence P5 Perform without hesitation CLO1: Propose solution to manufacturing and operation problems using related theory and analytical methods (C6,A5, PLO3) CLO2: Organise in groups to study and present the application of advanced manufacturing and operation analysis methods based on a given topics (C6,A4,P5, PLO3, PLO4, PLO5) PLO1 PLO2 PLO3 CLO1 √ CLO2 √ PLO4 PLO5 √ √ PLO6 PLO7 PLO8 PLO9 CLO3: Explain the main concepts and methods obtained from literatures to professionally analyse the manufacturing and operation system (C5,A4, PLO1, PLO3, PLO7) VERB Explain (C5) CONDITION STANDARD BLOOM’S LEARNING OUTCOMES the main concepts and methods; the manufacturing and operation system (A4) C5 A4 (PLO1) PLO1 PLO3 PLO7 obtained from literatures; (PLO7) to professionally analyse; (PLO3) EXPLAIN C2 Paraphrase; Use one’s own words C5 Evaluate by comparing to standards; Make judgements about ideas or materials C6 Put parts together to form a whole; Use concepts to solve problem A3 Ability to solve problem A4 Explain role of systematic planning in problem solving P2 Readiness to act; Accepts responsibilities for one’s behaviour CLO1: Propose solution to manufacturing and operation problems using related theory and analytical methods (C6,A5, PLO3) CLO2: Organise in groups to study and present the application of advanced manufacturing and operation analysis methods based on a given topics (C6,A4,P5, PLO3, PLO4, PLO5) CLO3: Explain the main concepts and methods obtained from literatures to professionally analyse the manufacturing and operation system (C5,A4, PLO1, PLO3, PLO7) PLO1 PLO2 PLO3 CLO1 √ CLO2 √ CLO3 √ √ √ √ PLO4 PLO5 √ √ PLO6 PLO7 √ √ √ √ PLO8 PLO9