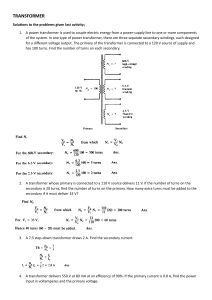
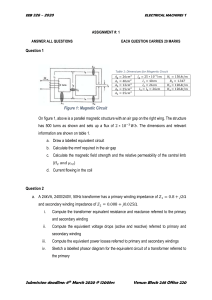
What is ampere turn balance in transformer? In a transformer, the ampere-turn balance refers to the principle that the product of the number of turns in the primary winding and the current flowing through it is equal to the product of the number of turns in the secondary winding and the current flowing through it. This principle is based on the conservation of energy in an ideal transformer. Mathematically, the ampere-turn balance in a transformer can be expressed as N1 is the number of turns in the primary winding, I1 is the current flowing through the primary winding, N2 is the number of turns in the secondary winding, I2 is the current flowing through the secondary winding, This equation implies that the product of the current and the number of turns remains constant in an ideal transformer, neglecting losses such as resistance and leakage flux. Practically, the ampere-turn balance is crucial for ensuring that the transformer operates efficiently and delivers the desired voltage transformation. It's also important for designing transformers to meet specific voltage and current requirements in various applications, such as power distribution, electrical appliances, and industrial machinery.