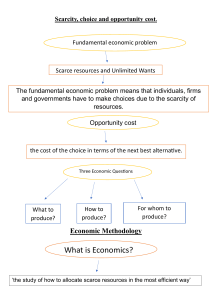
NEW PICTURE TO COME Module 1 The Study of Economics KRUGMAN'S MACROECONOMICS for AP* Margaret Ray and David Anderson What you will learn in this Module: • How scarcity and choice are central to the study of economics • The importance of opportunity cost in individual choice and decision making • The difference between positive economics and normative economics • When economists agree and why sometimes disagree • What makes macroeconomics different from microeconomics Individual Choice: The Core of Economics • Economics: •the study of choices individuals make about how to use their scarce resources • Choices: •decisions about what and what not to do • Scarce: •not available in sufficient quantities to satisfy unlimited wants Opportunity Cost: The Real Cost of Something Is What You Must Give Up to Get It • Opportunity Cost • Why all costs are opportunity costs •with every choice, an alternative is foregone - money or time spent on one thing can’t be spent on another Basketball star LeBron James chose to skip college and go straight to the NBA from high school when offered a $13 million contract. Individual Choice: The Core of Economics • Economy: •a system for coordinating a society’s productive and consumptive activities • Market Economy: •system in the U.S.; producers and consumers determine what, how and for whom to produce, with little government interference Resources Are Scarce • Resources (Factors of Production) • Land - • Labor • Capital - • Entrepreneurship • Scarcity and society: •societal decisions can be the result of individual choices or they may be better made through community-wide representation Microeconomics Versus Macroeconomics • Microeconomics • Macroeconomics • Economic Aggregates •Unemployment data, inflation data, gross domestic product Table 1.1 Microeconomic Versus Macroeconomic Questions Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Macroeconomics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers Macro or Micro? A family’s decision about how much income to save. The effect of government regulations on auto emissions. The impact of higher national savings on economic growth. ? A firm’s decision about how many workers to hire. ? Positive Versus Normative Economics • Positive economics 1. How much revenue will the tolls yield? 2. How much more revenue would be collected if the toll were raised from $1.00 to $1.50? • Normative economics 1. Should the toll be raised? Positive or Normative Statements? A reduction in the rate of growth of money will reduce the rate of inflation. ? Society faces a short run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. ? The Federal Reserve should reduce the rate of growth of money. Society ought to require welfare recipients to look for jobs. Lower tax rate encourage more work and more saving. When and Why Economists Disagree • Economists may disagree because they have different values or opinions • Economists may disagree because they use different models or methods to conduct their analysis • Over time, disputes in economics are resolved by the accumulation of evidence (but this can sometimes take a long time!)