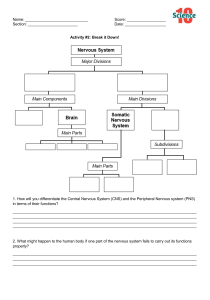
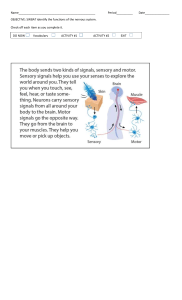
Name: ___________________________ General & Health Science Lesson Objectives: • • • Grade:___ Nervous System Date:______________________ Q.C. Science Department Review the nervous system and its components. Discuss the functions of the nervous system. Explain the different parts of the brain and what they are responsible for. What is the function of the nervous system? The function of the nervous system is to transmit ___________________________________(impulses) around the body. What are its component parts? Central Nervous system: _________________________________________________ Peripheral Nervous system: ________________________________________________ What does it do? • • • • • Gives you ____________________________ about the _______________________around you Enables you to______________________ your _____________________ The central nervous system consists of the Brain and the spinal cord. The brain is protected by the __________________________ or ______________________ The spinal cord is protected by the _______________________ or _________________________ The brain Name: ___________________________ General & Health Science Roles of the cerebrum • • • • • • • Grade:___ Nervous System Date:______________________ Q.C. Science Department The cerebrum is involved in _______________________________ and ___________________ (particularly the arms and legs). It also helps us to register __________________________ And to make _______________________ _______________________ portion of the brain Consists of 2_____________________________ (left and right) Responsible for intelligence, memory, consciousness, reasoning, acquired skills (mathematics, speech, playing music) It is this part that is also thought to be responsible for our ________________________________. Roles of the cerebellum • • Dark ridged structure at the back of the brain beneath the __________________________ Controls _____________________, ___________________________ and coordination of _________________. Roles of the medulla oblongata • • • Controls _________________________involuntary responses. e.g. Heartbeat and breathing. ________________________________ center of the brain. Controls _________________________________, coughing, swallowing, yawning, sneezing and vomiting. The Hypothalamus and the pituitary gland • • Hypothalamus- Controls ___________________________. The hypothalamus monitors blood-sugar levels, temperature control, water balance and carbon dioxide levels in the blood. The pituitary gland ( _______________________________) produces hormones in response to this. Controls growth and the other endocrine glands. • Nerves that run from our sense organs (RECEPTORS) to our CNS (carrying information about the environment). Nerves that run from our CNS to our effectors (either _____________ or __________) Lesson #2 Lesson Objectives: 1. Differentiate between neurons of the nervous system 2. Describe how reflex actions help protect the body from damage. 3. Explain the route through a reflex arc. There are three types of neuron: ____________________________ neurons- detect changes in the environment, send signals to CNS. ______________________________ neurons- Pass signals from the sensory to the motor neuron. ______________________________neurons- send signals to muscles and glands. Name: ___________________________ Grade:___ Date:______________________ General & Health Science Nervous System Q.C. Science Department Sensory neurons carry impulses from the receptor to the CNS. Receptors detect stimuli and convert them to an electrical impulse. Sense organs are receptors. Associate/Intermediate/Relay/ Connector neuron forms a link between sensory and motor neuron. They are located in the brain and spinal cord. They also run throughout the CNS connecting the brain and spinal cord. Motor neuron carry nerve impulse from the CNS to effectors. Effectors bring about a response to stimuli. Muscles and glands are effectors Grey matter is made up of __________________________ (and nuclei). White matter is made up of ______________________________ When a _____________________________ is stimulated, it sends a signal to the _________________________ nervous system, where the brain co-ordinates the_______________________________. Sometimes a very quick response is needed, one that does not need the involvement of the brain. This is a reflex action. An _______________________ response to a stimulus Reflex actions are involuntary quick responses to a stimulus. • • • • Innate _____________________________ _____________________________ Done in response to an environmental stimulus. Reflex actions are part of the autonomic system. This is the _________________________________ part of the body that also controls heart rate, breathing rate, digestion and sexual arousal. Name: ___________________________ General & Health Science Types of Reflexes Grade:___ Nervous System Date:______________________ Q.C. Science Department ____________________________ reflexes are inherited and do not have to be learnt. Examples: knee-jerk reflex Pupil reflex ____________________ _______________________ Producing saliva Response to pain _________________________reflexes are actions which have to be learnt before they become automatic. Examples: Talking reading ___________________ playing an instrument driving a car ____________________________ Conditioned reflex This is a type of learnt reflex where the response has no natural relationship to the stimulus. Example: Pavlov’s dog producing saliva in response to a bell. Lesson 3: Nervous system Disorders Objectives: • • Review the parts of the spinal cord Describe various disorders of The Nervous System. Nervous system disorders • • • • • • Huntington's disease. Parkinson's disease Alzheimer's disease Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Multiple sclerosis (MS). Peripheral neuropathies. dancing