A Dedicated Institute for Nursing Competitive Exam
ENT
Ist portion of ear to develop – internal ear, begins 22 days after fertilization from ectoderm called
placodes.
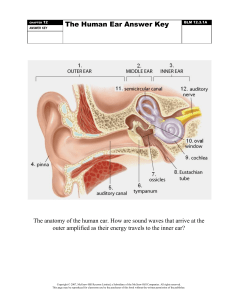
3 Parts:(1) External Ear – Outer Ear
(A) Pinna or Auricle
(B) External ear canal
(C) Tympanic membrane (Ear drum)
(2) Middle Ear – Also called tympanic cavity or tymparum.
(A) Tympanic Cavity
(B) Ear ossicles, auditory ossicles – Malleus, Incus Stapes
- Stapes – Shortest and smallest bone in human body.
(3) Inner Ear- Also called labyrinth.
- Semicirculas canals
- Utricle and saccule
- Cochlea
FUNCTION OF EAR
External Ear:
(A) Pinna or Auricle
– Collect sound waves.
(B) External Ear Canal – Direct sound waves to eardrum.
(C) Tympanic membrane – Transmit sound from air to the ossicles inside the middle ear.
Middle Ear –
(A) Ear Ossicles – Transmit and amplify vibrations from tympanic membrane to oval window.
(B) Auditory tube – Also called as Eustachian tube. Equalize air pressure on both sides tympanic
membrane.
Inner Ear –
(A) Cochlea – It play key role in sense of hearing.
(B) Utricle and Saccule – Maintain Body position
(C) Semicirculas Canal – Maintaining Balance
(D) Route of sound wave
(E) Route of vestibular pathways.
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
1
ENT
SOUND WAVES:
It travels at speed of 332 meter per second.
Characteristics of sound waves
Pitch: frequency. It is measured in Hertz.
Volume : amplitude, intensity, loudness. It is measured in decibel.
Resonance : prolonging of sound.
Audible range of human ear :20 – 20000 Hertz
Sounds from a jet plane several miles away :20-100 hertz.
Hearing threshold is 0 dB at 1000 Hz.
Most of common sound that we hear have frequency between 200 and 4500.
Ear are sensitive to 500 – 3500 Hz.
Sr no
1
2
3
4
5
6
Feature
Rusting leaves of a plant
Whispering in ear
Normal conversation
Shouting
Uncomfortable to normal ear
Painful to ear
Decible (dB)
15
30
60
80
120
140 or above
Sometime above 120 dB is considered as painful to ear.
Noise pollution occurs above 85 decibel.
EYE
- Eye is a sensory organ.
- Organ of sense of sight.
- Optic nerve (Cranial nerve) that transmits visual information from the retina to brain.
Structure of Eye –
(A) Outer Layer1. Sclera – Also known as ‘white part of the eye’.
- It is white outer cavity of eye
- It covers entire eye ball except – cornea
- It cover 5/6 part of Eye ball.
Function- Provide shape and protects inner parts.
2. Cornea – It is transparent centre and front past of eye that covers iris pupil.
- It form 1/6 part of eye ball.
- Cornea is avascular part.
- Central part of Cornea receives oxygen from the outside air.
Function – Admits and refracts (Bends) light.
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
2
ENT
(B) Middle layer –
1. Iris: - Colored portion of eye ball.
- It situated between cornea and lens.
- Eye color determine by the amount of melanin in iris.
Function – Regular the amount of light entering the eye ball through pupil.
- Absorbs the extra amount of light.
2. Pupil – The round opening in the centre of iris.
3. Choroid- A high vascularised middle layer of eye.
- It lies between sclera and retina.
Function – It provide nutrition to posterior surfaced retina.
4. Ciliary Body – Anterior portion of choroid.
(c) Inner layer
1. Retina – Inner visual receptive layer of eye.
- It is continuously posteriorly with optic nerve.
- Retina contains nerve cell and nerve fibres which contains. Photoreceptors.
2 TYPES PHOTO RECEPTORS(i) Rods – 120 million rods.
- It responsible to see in dim light (moon light).
(ii) Cones – 6 million
- It responsible to see in bright light and color vision.
Optic disc – Round spot on the retina formed by the passage of axons of the retrial ganglion cells.
- It is also called blind spot.
2. Lens – It is situated behind the pupil and Iris in eye ball. It is Biconvex.
Function – It help focus images on the retina to facilitate clear vision.
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
3
ENT
OTHER STRUCTURE OF EYE
Eye brow
Eyelids (palpebrae)
Palpebral fissures
Lateral commissure
Medial commissure
Lacrimal caruncle
Tarsal gland or Meibomian gland.
Eyelashes
Conjunctiva
Statified columnar epithelium ls cuh gksrh gSA
Palpebral conjunctive: inner lining of eye lids.
Bulbar conjunctiva.: around sclera & Chornea
Lacrimal apparatus
One lacrimal gland & its duct:- Almond shape
Two lacrimal Canaliculi
1 lacrimal sac.
1 nasolacrimal duct (2cm length):- ;g Inferior concha ij [kqyrh gSA
Conjunctiva – Thin protective mucus membrane that lines the inside of eyelid and cover the sclera.
Composed – Non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Eye lids – It is a fold & skin that closes over the eye to protect it.
CAVITY OF EYE BALL
(1) Anterior Cavity – The space anterior to lens. It consists of 2 chambers.
(A) Anterior Chamber – It lies between the cornea and Iris.
(B) Posterior Chamber – It lies behind the Iris and lens.
- Both chamber of anterior cavity are filled with aqueous humour.
Aqueous Humour – A transparent watery fluid that nourishes the lens and cornea.
- Normally aqueous humour is completely replaced about every 90 minutes.
(2) Posterior Cavity – It is also called viscous chamber.
- It lies between the lens and retina.
- Vitreous chamber contain vitreous body.
- Vitreous body – A transparent jelly like substance that holds the retina.
- It is formed during embryonic life.
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
4
ENT
DISORDERS OF EYE , EAR , NOSE AND THROAT
Epistaxis(NoseBleeding)
Epistaxis refers to nose bleed or hemorrhage from the nose .A hemorrhage from the nose, referred to
asepistaxis, is caused by the rupture of tiny, distended vessels in the mucous membrane ofany area of
the nose.Its most commonly originates in the anterior nasal cavity.
Little area:
It is situated in the anterior part of nasal septum, just above the vestibule.
Four arteries- anterior ethmoidal, septal branch of superior labial, septal branch of
sphenopalatine and the greater palatine, anastomose here to form a vascular plexus called
"Kiesselbach's plexus".
Sphenopalatine artery is also known as “Artery of epistaxis.”
Types :
Anteriorbleeds–fromanteriorpartofnasalseptum,morecommon
Posteriorbleeds–fromposteriorpartofnasalseptum,moreserious
AnteriorEpistaxis:
1) Morecommon
2) Fromanteriornosevessels
3) Seeninchildren
4) Commoncause-fingernailtrauma,drynose
Posterior Epistaxis:
1) Lesscommon
2) Fromposteriornosevessels
3) Seeninadultsusuallywithhypertension
4) Commoncause–trauma,uncontrolledhypertension.
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
5
ENT
Anterior
Epistaxis
Posterior
Epistaxis
Incidence
Morecommon
Lesscommon
Commonsite
Little'sarea
Woodruffplexus
Age
<18yr.
>40yr.
CommonCause
Trauma
Hypertension
Treatment
Anteriorpack
Posteriorpack
Causes:
Thesecanbedividedinto:
Local
General
Local Causes Nose
1)Trauma:Fingernailtrauma,directinjurytonose,nosesurgery,facialfractures
2) Infections: sinusitis , rhinitis
3) ForeignBodies
4) Cancers of Nose
5) DNS(DeviatedNasalSeptum)
GeneralCauses
1) Hypertension,pregnancy
2) Aplasticanamia,leukemia , plateletdisorders ,vitaminKdeficiency,haemophilia
3) Chronicliverandkidneydisease
4) Anticoagulanttherapy(bloodthinners)
Diagnostic evaluation
History - amount of blood loss, duration of blood loss , medications history.
Careful inspection with nasal speculum to determine site of bleeding (its very important to
determine which site of bleed first.)
Blood investigation - PT and INR , bleeding time , clotting time.
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
6
ENT
FIRST AID MANAGEMENT
Little's area- pinching the nose with thumb and index finger for about 5-10 minutescompression of vessels.
Trotter's method- patient is made to sit, leaning a little forward over a basin to spit any blood,
and breathe quietly from mouth-cold compresses should be applied to nose to cause
reflex vasoconstriction.
Medical management
Tranexaminicacid500mgstatdose,toarrestbleeding.
Other management
Cauterization
Anterior Nasal Packing
Posterior Nasal Packing
TESPAL- Trans-Nasal Endoscopic Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
7
ENT
Rhinitis
Inflammation of the nasal mucosa.Rhinitis is a group of disorders characterized by inflammation and
irritation of the mucous membranes of the nose.
Classification:
Acute rhinitis – Viral- Most commonest cause of acute rhinitis
Bacterial
Chemical
Allergic
Chronic rhinitis – Drug induce rhinitis , chronic disease induce rhinitis
Clinical symptoms:
1. Stage of invasion (few hours):
• Sneezing, burning sensation in the nasopharynx, nasal obstruction, and headache.
2. Stage of secretion (few days):
•Low grade fever, malaise, arthralgia
• Profuse watery rhinorrhea.
3. Stage of resolution: Resolution within5-7 days is thenatural course of an uncomplicated disease.
• Symptoms lasting beyond 7 days, or worsening
Management :
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Anti-histamin drugs (levocetrazine )
Tablet Paracetamol
Stem Inhalation therapy
Tablet Decongestants
Maintain proper hygiene to avoid infections
Bed rest
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of pharyngeal mucuosa . It is also called sore throat.
Etiology :
-
Viral –Most common cause
a) Adenovirus
b) Epstein-Barr virus
c) Influenza virus
-
Bacterial-Mixed infection common
-beta-hemolytic streptococci
-H. influenza
-staphylococcus aureus
-diphtheria
-gonococcus
- Fungal - Candida albicans.
- Other risk factor : Cold , smoking , allergy
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
8
ENT
Sign and symptoms:
Discomfort in throat (sore throat)
Fever
Headache
Joint pain
Enlarge lymph nodes
Dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing )
Loss of appetite
Investigations :
Physical examination
Throat culture
Blood test
Management :
NSAID- acetaminophen , aspirin (children under 19 should not take aspirin)
Antibiotics – amoxicillin
Bed rest
Avoid smoking and alcohol
Drink warm liquids
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
9
ENT
Acute Suppurative Otitis Media (ASOM)
It is an acute inflammation of middle ear cleft by pyogenic organism . Middle era cleft includes
Eustachian middle ear and mastoid air cells .It is very common in infants and children.
Etiology:
a) Viral– RSV ,Rhino virus , Adeno virus
b) Bacteria - Streptococcus pneumonia – most commonest bacteria
c) Haemophilus influenza – 2ndmost commonest bacteria
d) Common cold
e) Allergy
f) Sinusitis (inflammation of the paranasalsinus )
g) Rhinitis (inflammation of nasal mucus membrane )
h) Cleft plate
Sign and symptoms :
a) Decrease hearing
b) Pus discharge from ear
c) Irritability
d) Fever
e) Disturb sleeping pattern
Management :
a) Antibacterial therapy : ampicillin , amoxicillin , erythromycin
b) Eartoilet:Ifeardischarge thenmoppedgentlywithcottonbuds.
c) Analgesics and antipyretics :Paracetamol , ibuprofen syrup
d) Dry local heat : help to relive pain
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
10
ENT
Conjunctivitis
Definition:
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation or infection of the transparent membrane (conjunctiva) that lines
the eyelid and covers the white part of the eyeball. When small blood vessels in the conjunctiva
become inflamed, they're more visible. This causes the white of the eyes to appear reddish or pink.
Also known as "PINK EYE"
Types of conjunctivitis :
1. Viral conjunctivitis : Viral conjunctivitis most commonest conjunctivitis
Adeno virus(most commonest cause of viral conjunctivitis ) , picona
virus
2. Bacterial conjunctivitis : Staphylococcal:mostcommoncauseofbacterialconjunctivitis
Streptococcal:producespseudomembranousconjunctivitis
3. Chemical conjunctivitis: exposure to acid or alkaline chemical.
4. Allergic conjunctivitis :Pollen , perfumes , cosmetics , smoke and dust.
Giantpapillaryconjunctivitis :Itisatypeofallergicconjunctivitiscausedbythe chronic presence of
a foreign body in the eye.
Sign and symptoms:
1. Redness of eye
2. Discharge from eye
3. Tenderness and pain of the eye
4. Photophobia – eye discomfort in bright light
5. Infection usually begins with one eye but can quickly spread to the other eye.
6. Blepharitis
- inflammation of eye lid
Management :
Bacterial conjunctivitis : Antibiotic eye drop , Antibiotic eye ointment
Viral conjunctivitis : No treatment for most cases of viral conjunctivitis , usually self limiting
supportive treatment – dark goggles , cold compress
Allergy conjunctivitis : Avoid the irritant
NSAID and anti Histaminic medication
Topical steroid eye drops
Cold compress
Chemical conjunctivitis: Flushing of the eye with saline
Topical steroid eye drop
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
11
ENT
Trachoma
It is a disease of the eyes caused by infection with bacteria chlamydia trachomatis.
Mode of transmission :-5F’s of transmission
A. Finger
B. Flies
C. Face
D. Feces
E. Fomites
Risk factors : - Crowded living condition
Poor sanitation
Venereal transmission
Dirt and dust
Clinical manifestation :-conjunctivitis
Eye pain
Eye swelling
Photophobia
Mucopurulentoccular discharge
WHO classification of trachoma
1. Trachomatous inflammation, follicular (TF)-Five or more follicles of >0.5 mm on the upper
conjunctiva
2. Trachomatous inflammation, intense (TI)-hypertrophy and inflammatory thickening of the
upper conjunctiva with the presence of follicles
3. Trachomatous scarring (TS)-Presence of scarring in conjunctiva.
4. Trachomatoustrichiasis (TT)-At least one ingrown eyelash touching the globe.
5. Corneal opacity (CO)-Corneal opacity or blurring part of the pupil margin
Management :1. Antibiotics : Azithromycin (single dose oral)
2. Eye ointment : 1% tetracycline
3. WHO recommended – “SAFE” strategy
S – Surgical care
A – Antibiotics
F – Facial cleanliness
E -Environment improvement
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
12
ENT
Cataract
It is an opacity of lens.
Etiology :1. Age : Most commonest cause
Age related cataract also known as senile cataract
2. Eye injury
3. Radiation or UV light
4. Drugs : Corticosteroid
5. Disease : Diabetes mellitus (most commonest disease)
Risk factors :1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Smoking
Obesity
High BP
Excessive alcohol
Vitamin-C deficiency
Types of cataract :
1. Nuclear cataract
2. Cortical cataract
3. Posterior subcapsular cataract
4. Congenital cataract
Clinical manifestation :
o Decrease in vision (blurred vision) and decreased color perception
o Diplopia – Double vision
o White pupil
o Photophobia
o Halos around light
o Difficulty seeing at night
Investigation :
History and physical examination
Ophthalmoscopy – examination of eye
Slit lamp examination
Visual acuity test – most commonest test for vision
Surgical management :
Extra capsular cataract extraction
Intra capsular cataract extraction
Nursing management cataract:
1. Ensure room environment is safe and proper lighting
2. Wear sunglasses
3. Regular eye checkup
4. Avoid smoking and alcohol
5. After surgery position – Non operative side or fowler position
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
13
ENT
Refractive error
Refraction : It is a process of focusing of light rays on Retina , result vision.
Refractive power :- It is the degree to which the eye is able to refract the light rays.
Refractive Error : When light rays are not proper focused on retina.
The shape of eye does not bend light correcting resulting blurred vision.
Types of refractive error –
1. Myopia :It is also known as short sightedness and near sightedness. In this condition light rays
are focused in front of the retina.
Distant vision: Blurred vision
Closed vision : Clear
Management :Concave lens used for this refractive error.
2. Hypermetropia :It is also known as far sightedness , long sightedness .
In this condition light rays focus on back on retina.
Distant vision :Clear
Near vision : Blurred
Management :Convex lens used for this refractive error.
3. Pressbyopia : It is a related condition in which eye loss the ability to focus clearly on close
object.
It is a condition of far sightedness.
Management :Convex lens used for this refractive error.
4. Astigmatism : It occurs when the cornea has abnormal shape.
In this condition light rays focused on two points of retina Instead one point.
Management :Cylindrical lens used for this refractive error.
Deafness
Deafness hearing impairment or hearing loss refer to total or partial inability to hear.
It is also called “Unseen Handicap”
1. Conductive hearing loss : It occurs when conditions in the outer or middle ear impair the
transmission of sound through air to inner ear.
Causes
Any obstruction in the ear canal – foreign body
Benign or malignant tumor in external ear and middle ear
Otitis Media
Perforation of tympanic membrane
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
14
ENT
2. Sensorineural hearing loss : It is caused by impairment of function of the inner ear or the
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
Causes:
Presbycusis – hearing loss caused by aging process
Noise trauma
Ototoxic drugs – Aspirin , aminoglycosides , vincristine
Systemic disorders : Diabetes mellitus , autoimmune disorders
3. Mixed hearing loss : Mixed hearing loss occurs due to a combination of conductive
sensorineural cause.
4. Central hearing loss : When central nervous system cannot interpret normal auditory signals.
Cerebrovascular accidents , brain tumor
5. Psychogenic hearing loss : It is a hearing loss for which no organic cause or lesion can be
found
It is also called psychogenic hearing loss
It percipitated by emotional stress
6. Malingering : It is a type of psychogenic hearing loss
Classification of hearing loss
Meaning
Normal
Mild
Moderate
Moderate severe
Severe
Profound
Decibel (db)loss
0-15
26-40
41-55
56-70
71-90
More than 90
Decibel : The intensity or strength of a sound wave is expressed in terms – decibel (Db)
Normal :Adult hear frequency – 20 Hz to 20000 Hz
Normal speech conversation – 60 db
Clinical manifestation :
Hearing loss
Difficult in conversations
Ear discharge
Tinnitus (Ringing in the ear)
Excessively loud speech
Constant need for classification of conversation
Strained facial expression
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
15
ENT
Investigations: History taking
Physical examination
Rinne’s test
Webber’s test
Audiometry
BERA (Brain stem-evoked response audiometry)test :It is best audiometric test to confirm
hearing loss in neonates and infants.
Medical management: Antibiotics : to treat infections
Ceruminolytics : for impacted wax
Corticosteriods : for reduce inflammation
Assist hearing: Hearing aids
Hearing device implantation in middle ear
Cochlear implants Minimum age 1 year for implantation
Sign language
Nursing Management: Inspect ear canal for obstruction
Allow patient to verbalize feelings
Environment noise control
Monitoring oto toxic drugs
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
16
ENT
Glaucoma
It is a condition when intraocular pressure increased due to inadequate drainage of
acqueoushumor . Increase intraocular pressure damage optic nerve , cause blindness .
In India –Glaucoma is the third leading cause of blindness.
In India Istcause of blindness is cataract .
In India 2ndcause of blindness is refractory error.
Types :
Primary angle closer glaucoma :It occurs due to a reduction in the outflow of aqueous
humor that results from angle closure.
II.
Primary open angle glaucoma : most commonest type of glaucoma
It occurs due to obstruction of outflow of aqueous humor
and over production
III.
Secondary glaucoma : It occurs as a result of other disorder
IV.
Congenital glaucoma : It occurs when a congenital defect in angle of anterior chamber
obstruct the outflow of aqueous humor
I.
Risk factor of glaucoma :
High internal high pressure
Age over 50 years
Certain medical condition – hypertension , diabetes mellitus
Refractory errors
Medications – steroids drug
Injury of eyes
Clinical Manifestation:
Diminishedaccommodation – early sign of glaucoma
Pain in eye
Blurred vision
Photophobia
Lacrimation
Morning headache
Investigation :
Tonometry :IOP measurement
Ophthalmoscopy
Gonioscopy
Visual field perimetry
Medical management :
Miotics or cholinergic agents – pilocarpine
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors – acetazolamide
Surgical management :
Trabeculectomy
Trabeculoplasty
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
17
ENT
Nursing Management: Eye medication should have to use in entire life
Teach the patient and caregivers about the risk of glaucoma.
The current recommendation is for an ophthalmologic examination :
Every 2-4 years for people between age 40 and 64 years
Every 1-2 years for people age 65 years or older
The patient with acute angle closure glaucoma requires immediate medication to lower the
IOP
Advice the patient eye examination 1 week and again 4 to 6 weeks after surgery.
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
18
Nursing Coaching for
AIIMS, DSSB, ESIC, PGIMER, RPSC,
RAILWAY, CHO, STAFF NURSE AND NUSRING TUTOR
A Dedicated Institute for Nursing Competitive Exam
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar,
Near Gyan Ashram School/
Sanskriti College, Jaipur (Raj. )
www. conceptrna.com
concept.rna@gmail.com
info@conceptrna.com
7426955591
7426955593
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593
19
ENT
MCQ {CHO}
MCQs
Q.1
Q.2
Q.3
Q.4
Q.5
Q.6
Q.7
Q.8
Q.9
The part of the ear which the
responsible for maintaining balance of
the body:
(a) Semi- circular canals
(b) Tympanic membrane
(c) Cochlea
(d) Ossicles
The organ which is responsible for the
body balance is:
(a) Eye
(b) Ear
(c) Mouth
(d)Tongue
Infection of middle ear is called:
(a) Sinusitis
(b) Mastoiditis
(c) Otitis media
(d) Labyrinthitis
The equipment used in the examination
of ear is:
(a) Laryngoscope
(b) Ophtthalmoscope
(c) Otoscope
(d) Proctoscope
What is the meaning of otitis media?
(a) Inflammation of the tonsils
(b) Inflammation of the sinus cavity
(c) Inflammation the middle ear
(d) Inflammation of the kidneys
What do you mean by sinuses
(a) Space between two bones
(b) Cavities in the bones
(c) Space between two tissue layers
(d) Space between two lungs
In following which is a function of
nose in human being
(a) Filtering the inspired air
(b) Humadification of inspired air
(c) Sense of smell
(d) All
Length of pharynx in an adult is about
(a) 6-8 cm
(b) 12-14 cm
(c) 20-25 cm
(d) 50-54 cm
Opening of the auditory tube found in
(a) Nasopharynx
(b) Oropharynx
(c) Laryngophaynx
(d) Oesophagus
Q.10
Q.11
Q.12
Q.13
Q.14
Q.15
Q.16
Q.17
Q.18
Q.19
Q.20
Q.21
Which structure is known as voice box
(a) Pharynx
(b) Larynx
(c) Oesophagus
(d) Intercostal muscles
Adam‟s apple is more prominent in
(a) Adult male
(b) Adult female
(c) Male child
(d) Female child
The space between the vocal cords is
known as
(a) Epiglottis
(b) Glottis
(c) Adam‟s apple
(d) Vermis
The organ which plays an important
role in production of sound is known
as
(a) Mouth
(b) Larynx
(c) Pharynx
(d) Teeth
In following which organ is known as
a windpipe
(a) Larynx
(b) Trachea
(c) Lung
(d) Bronchi
Length of trachea is about
(a) 10-12 cm
(b) 25-30 cm
(c) 40 - 45 cm
(d) 2 - 4 cm
Number of incomplete rings found in
trachea are
(a) 2 - 4
(b) 10 - 12
(c) 16 - 20
(d) 30 - 35
In following which is not a auditory
ossicle
(a) Malleus
(b) Incus
(c) Stapes
(d) Vomar
Which part of ear is also known as
labyrinth
(a) Outer ear
(b) Middle ear
(c) Inner ear
(d) Lateral ear
Semicircular canals are found in
(a) Outer ear
(b) Middle ear
(c) Inner ear
(d) Lateral ear
Auditory ossicles are the part of
(a) Outer ear
(b) Middle ear
(c) Inner ear
(d) All
Total number of auditory ossicles are
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593 19
MCQs
Q.22
Q.23
Q.24
Q.25
Q.26
Q.27
Q.28
Q.29
Q.30
Q.31
The eustachian tube is also known as
(a) Auditory tube
(b) Tympanic tube
(c) Pharyngotympanic tube
(d) Both I and III
Sound waves are measured in
(a) Pound
(b) Decibles
o
(c) A
(d) Km
Utricle and saccule found in ear, are
the part of
(a) Cochlea
(b) Vestibule
(c) Semicircular canals
(d) Tympanic cavity
Tinnitus is a(a) Subjective symptom
(b) Objective symptom
(c) Prodromal symptom
(d) Functional
Ear pain is also known as(a) Labrynthritis
(b) Otosclerosis
(c) Tympanosclerosis (d) Otalgia
Difficulty in swallowing is known as(a) Aphagia
(b) Dysarthria
(c) Agnosia
(d) Dysphagia
Weber test is done to diagnose(a) Eye problem
(b) Hearing loss
(c) Respiratory problem
(d) Cardiac problem
Epistaxis means (PGI 2006)
(a) Bleeding from gums
(b) Bleeding from nose
(c) Bleeding from vagina
(d) Bleeding from ear
About 90% of nose bleed are(a) Anterior
(b) Posterior
(c) Lateral
(d) None of these
Sinusitis is the inflammation of
(a) Larynx
(b) Cavity found in nasal bones
(c) Cranial bones
(d) Cartilage
Q.32
Q.33
Q.34
Q.35
Q.36
Q.37
Q.38
Q.39
Q.40
Most common cause of Pharyngitis is(a) Pneumococci
(b) Beta-hemolytic streptococci
(c) Candida Albicans
(d) Malnutrition
In following which is not a clinical
features of pharyngitis
(a) Dysphagia
(b) Sore throat
(c) Increased WBC
(d) Decreased WBC
Tonsilitis is the
(a) Carcinoma of tonsils
(b) Inflammation of tonsils
(c) Rupture of tonsils
(d) Removal of tonsils
Most common cause of tonsilitis is(a) Streptococci
(b) Pneumococci
(c) E. coli
(d) Staphylococci
Rhinitis is the inflammation of
(a) Nasal mucosa
(b) Gastric mucosa
(c) Lung parenchyma
(d) Brain parenchyma
Other name of common cold is(a) Pharyngitis
(b) Acute rhinitis
(c) Laryngitis
(d) Gingivitis
Outpouching of mucus membrane
lining of the nose or paranasal sinuses
is known as(a) Nasal polyp
(b) Nasal sputum
(c) Nasal mucosa
(d) Sinus mucosa
Otitis media is related to
(a) Eye
(b) Ear
(c) Respiratory infection
(d) GIT infection
Gradual sensorineural hearing loss that
occur with aging is known as(a) Presbycusis
(b) Hyperacusis
(c) Conductive hearing loss.
(d) None of these
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593 20
MCQs
Q.41
Q.42
Q.43
Q.44
Q.45
Otoscopy means(a) Examination of eye
(b) Examination of middle ear
(c) Examination of external ear and
tympanic membrane
(d) Examination of nasal cavity
Infection of the inner ear is called as(a) Labrynthritis
(b) Otosclerosis
(c) Tympanosclerosis
(d) Otagia
The following group of drugs cause
side effects of both ototoxicity and
nephrotoxicity(a) Aminoglycosides
(b) Penicillin
(c) Sulfonamides
(d) Erythromycin
“Bacterial sore throat”
Most common causative organism
(a) Streptococcus pyogenes
(b) Mycoplasma pneumonia
(c) Cornybacterium
(d) Mycobacterium
“Bleeding from the nose”
“Medical Term”
(a) Hyperemesis
(b) Haemoptysis
(c) Haematemesis
(d) Epistaxis
Q.46
Q.47
Q.48
Q.49
Q.50
Q.51
Q.52
Statement
“Dysphagia” Term
(Appropriate meaning)
(a) Difficulty in writing
(
)
(b) Difficulty in focusing
(
)
(c) Difficulty in understanding
(
)
(d) Difficulty in swallowing
(
)
Q.53
Larynx is the part of _____ System.
(a) Digestive
(b) Respiratory
(c) Circulatory
(d) Urinary
“Olfactory Nerve”
Cranial Nerve
(a) Ist Cranial Nerve
(b) IInd Cranial Nerve
(c) IIIrd Cranial Nerve
(d) IVth Cranial Nerve
Nerve
Infection
Injury
„Deafness‟
(a) Vagus nerve
(b) Trigeminal nerve
(c) Vestibular nerve
(d) Cochlear nerve
„Anotia‟ Term
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
The audible range of human ear is
between
(a) 50-5000 Hz
(b) 200-20,000 Hz
(c) 20-20000 Hz
(d) 20-2000 Hz
The refractive error caused by the
differences in the curvature if the
cornea and lens is called:(a) Emmetropia
(b) Astigmatism
(c) Myopia
(d) Hypermetropia
Profound hearing loss is described as
greater than
(a) 40 dB
(b) 20 dB
(c) 60 dB
(d) 80 Db
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593 21
MCQs
1
A
11
A
21
B
31
B
41
C
51
C
2
B
12
B
22
D
32
B
42
A
52
B
3
C
13
B
23
B
33
D
43
A
53
D
4
C
14
B
24
B
34
B
44
A
54
5
C
15
A
25
A
35
A
45
D
55
6
B
16
C
26
D
36
A
46
D
56
7
D
17
D
27
D
37
B
47
B
57
8
B
18
C
28
B
38
A
48
A
58
9
A
19
C
29
B
39
B
49
D
59
10
B
20
B
30
A
40
A
50
D
60
C-6, 80 Ft. Road, Shanti Nagar, Near Gyan Ashram School/Sankriti College, Jaipur. (Raj) Mo.7426955591, 7426955593 22