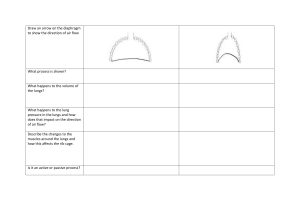
BOYLE’S LAW Gases expand spontaneously to fill any volume available to them. Consequently, the volume of a gas equals the internal volume of the container in which it is held. The volume of gases unlike those of solids and liquids is greatly affected by changes in pressure and temperature Objectives: 1. Relate the volume of a gas to its pressure; 2. Solve problems involving Boyle’s law I. DISCUSSIONS Boyle’s law states that the volume of a fixed quantity of gas maintained at constant temperature is inversely proportional to the pressure. 𝑷 ∝ 𝟏 𝑽 When two measurements are inversely proportional, one gets smaller as the other gets larger. Boyle’s law can be express in mathematical terms: 𝑷𝑽=𝒌 or 𝑷𝟏 𝑽𝟏 = 𝑷𝟐 𝑽𝟐 The value of the constant depends on the temperature and the amount of gas in the sample. II. WARMING UP A. Fill in the blanks. Choose from the given options in the box below. Boyle’s Law and Breathing Process Between breaths, the gas pressure inside the lungs equals the atmospheric pressure. The volume of the lungs is governed by the 1) _______________, which can expand and contract, and the 2) _______________, a muscle beneath the lungs. 3) _______________ occurs when the rib cage expands and the diaphragm moves downward. Both of these actions serve to 4) _______________ the volume of the lungs, thus decreasing the gas pressure inside the lungs. The atmospheric pressure then forces air in the lungs until the pressure in the lungs once again 5) _______________ atmospheric pressure. 6) _______________ involves the reverses of the process. The rib cage contracts and the diaphragm moves up, both of which 7) _______________ the volume of the lungs. Air is forces out of the lungs by the increase in 8) _______________ caused by this reduction in volume. Decrease Diaphragm Equals Exhalation Increase Inhalation Pressure Rib Cage B. Answer the following questions. 1. Gas cylinders, LPG tanks and oxygen tanks are made of very strong materials like steel. Why are plastic, glass, and ordinary tin cans not used as gas storage? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What basic assumption of the Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) explains Boyle’s Law? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ III. WORKING OUT Answer the following and show your complete solution by following GUSAO. 1. What volume will 50 mL of a gas at 725 Torrs occupy if the pressure is increased to 760 Torrs? 2. A gas occupies 250 mL when the barometer reads 720 mm. How many milliliters will it occupy when the barometer reads 740 mm? 3. Find the volume of a gas at standard pressure if its volume at 780 mm Hg is 80 mL? 4. If the volume of a gas, at constant temperature, changes from 200 ml to 500 mL, the pressure on the gas must have changed from 400 torr to ____________. 5. Boyle’s Law describes the relationship between ___________ and _____________, and they are ___________ proportional. The variables __________ and ___________ remain constant. 6. A balloon is filled with 73 L of air at 1.3 atm pressure. What pressure is needed to change the volume to 43 L? 7. If 50 mL of Oxygen gas is compressed from 20 atm of pressure to 40 atm of pressure, what is the new volume at constant temperature? 8. If a gas sample in a balloon had a volume of 100 mL and a pressure of 3 atm. It was then compressed to a pressure of 10 atm, what would be its volume? 9. At 0.75 atm, the volume of a gas is 300 mL. If the temperature remains constant and the pressure is changed to 456 torr, what is the new volume of the gas? IV. WRAPPING UP Create a concept map by using the following words inside the box. Link the words in the box with another word/phrase to show how these concepts are related to each other. Boyle’s Law Gas Volume Quantity of Gas Moles Temperature Gas Pressure Collision of Molecules Container