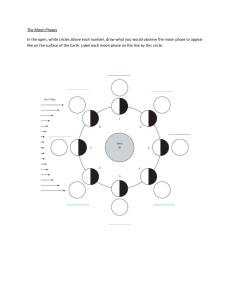
How Earths gravitational force keeps the Moon in orbit? The Earth has a gravitational force on the Moon, and the Moon has a gravitational pull on the Earth that is equal and opposing. The Moon is kept in orbit around us by the gravity of the Earth. It constantly shifting the Moon's velocity direction. This means that, despite its constant speed, gravity causes the Moon to accelerate all the time. The Moon revolves around the Earth in a circular motion due to the centripetal gravitational force of the Earth. The centripetal force acting on the moon tries to move it outwards and the gravitational force pulls it towards earth .So this two forces balance the moon to be fixed it on its own circular orbit and thus the moon moves in a circular motion around the earth . The moon is revolving around the earth. In this process the work done by the gravitational force is zero because the displacement of the moon is at right angle to the gravitational force. In this process the work done by the gravitational force is zero because the displacement of the moon is at right angle to the gravitational force. Centripetal force always acts perpendicular to the direction of motion. Hence no work is done. Why the moon doesn’t fall into the Earth? The Earth's and Moon's gravitational pulls are a pair of Newton's Third Laws. Newton's First Law of Motion (Inertia) An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion at constant speed and in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. The Earth's gravitational pull is what keeps the Moon from flying off into space. However, the Moon also has inertia, which is why it does not fall to Earth. The moon's velocity and distance from Earth allow it to make a perfect balance between fall and escape. In case the velocity of rotation of the moon was a little bit faster, it would have escaped the Earth's Gravity. On the other hand, if it's a little bit slower, it would have fallen on Earth.