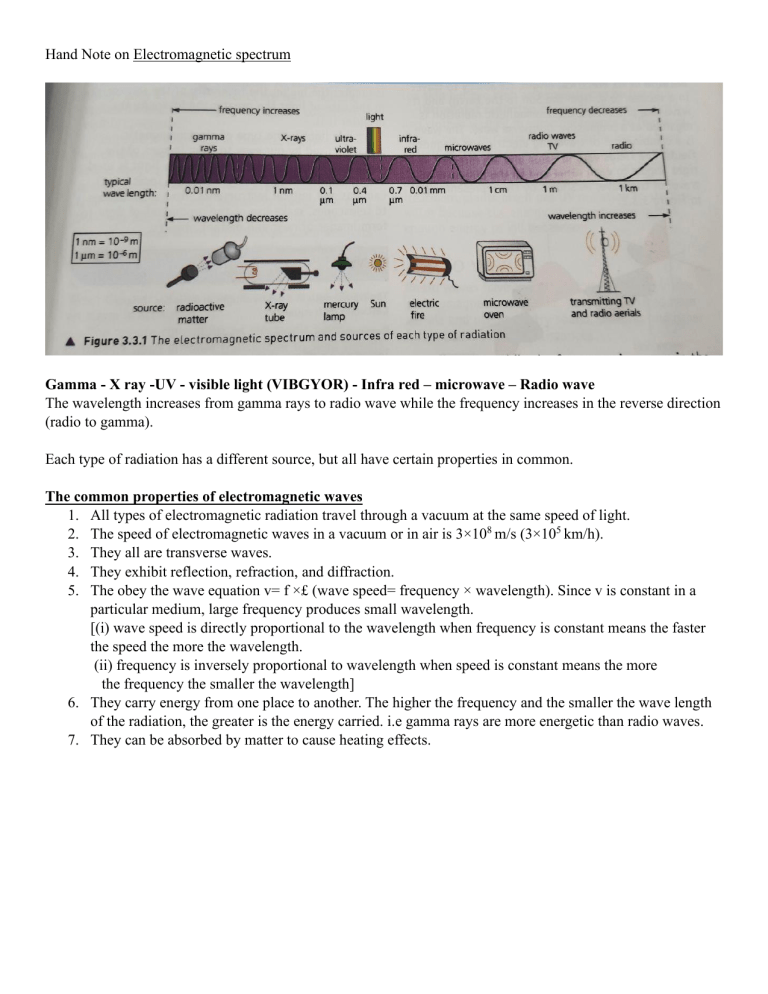
Hand Note on Electromagnetic spectrum Gamma - X ray -UV - visible light (VIBGYOR) - Infra red – microwave – Radio wave The wavelength increases from gamma rays to radio wave while the frequency increases in the reverse direction (radio to gamma). Each type of radiation has a different source, but all have certain properties in common. The common properties of electromagnetic waves 1. All types of electromagnetic radiation travel through a vacuum at the same speed of light. 2. The speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum or in air is 3×108 m/s (3×105 km/h). 3. They all are transverse waves. 4. They exhibit reflection, refraction, and diffraction. 5. The obey the wave equation v= f ×£ (wave speed= frequency × wavelength). Since v is constant in a particular medium, large frequency produces small wavelength. [(i) wave speed is directly proportional to the wavelength when frequency is constant means the faster the speed the more the wavelength. (ii) frequency is inversely proportional to wavelength when speed is constant means the more the frequency the smaller the wavelength] 6. They carry energy from one place to another. The higher the frequency and the smaller the wave length of the radiation, the greater is the energy carried. i.e gamma rays are more energetic than radio waves. 7. They can be absorbed by matter to cause heating effects. Dangers of electromagnetic radiation High exposures to electromagnetic radiation can cause harmful effects. Microwaves Microwaves produce heating of soft tissue in the body when they are absorbed by the water in living cells. This can damage or kill the cells. Infra-red Infra-red radiation transfers thermal energy, so when of high intensity can cause burns to the skin. Ultraviolet Ultraviolet radiation causes ionisation, so when absorbed in high doses it can cause skin cancer and eye damage including cataracts. X rays and Gamma rays: X rays and gamma rays also cause ionisation of atoms in cells and cause mutation or damage to cells in the body which can lead to cancer. Gamma Rays: Gamma rays are high frequency rays, so they have high penetrating power. They are more penetrating and dangerous than X-rays. Uses: 1. They are used to both diagnose and treat cancer. 2. They are also used to kill harmful bacteria in food and on surgical instruments. 3. In engineering applications , gamma-ray photography is used to detect cracks and flaws in metals. X rays: X rays are produced when high speed electrons are stopped by a metal target in an X -ray tube. The wave length of X -rays are smaller than UV-ray and longer than Gamma -ray. The X-ray can penetrate certain solid objects and affect a photographic film. They can not pass through bones, teeth ,so shadow pictures can be taken. Uses: 1. They are widely used in dentistry and in medicine for example to detect broken bones and in radiotherapy to kill cancerous cells. 2. X-rays are also used in security machines at airports for scanning luggage, screening passengers. 3. X- ray imaging is used to inspect welded joints and detect cracks in metal parts . Ultraviolet radiation: UV rays have shorter wavelengths than light. They cause suntan and produce vitamins in the skin but too high an exposer can be harmful. Uses: 1. UV radiation causes fluorescent paints and clothes washed in some detergents to fluoresce. [they glow by re-radiating as light ,the energy they absorb as UV.] 2. It is also used in security marking to verify invisible signatures on bank documents and to detect fake bank notes. 3. Water treatment plants use UV radiation to sterilize water because the energy of UV radiation is high enough energy to kill bacteria. Infra red radiation: Our bodies detect infra-red radiation by its heating effect on the skin. Infra-red ration can cause burns to the skin and eye damage if the intensity is high. Uses 1. It is used in heating elements such as electric fire, a toaster or an electric grill . 2. It is also used in thermal imaging cameras ,which shows hot spots and allow images to be taken in the dark. 3. Infra-red sensors are used on satellites and aircrafts for weather forecasting 4. It is also used in monitoring of land use by the people , assessing energy loss from buildings and locating victims of earthquakes. 5. One type of intruder alarm activates an alarm when its sensor detects the infrared radiation emitted by a near by moving body. 6. The remote control for an electric device contains a small infrared transmitter to send signals to the device such as television or DVD player. 7. It is also used to carry data in long range optical fibre communication system. Micro wave: Uses 1. They are used for international telecommunications and direct broadcast satellite television relay via geostationary satellites. 2. They are used for mobile phone networks via microwave aerial towers. 3. They are also used in wireless applications ,such as Bluetooth. 4. It can be used for cooking in a microwave oven . Radio Wave: Radio Waves have the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum.They are radiated from the aerials and used to carry sound, pictures and other information over long distances.