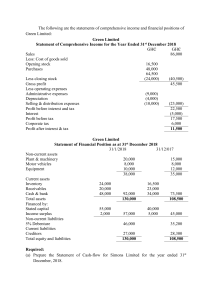
ACCOUNTS PROJECT - 1 ‘Financial statement analysis of Ultra Tech Cements Ltd by using Comparative and Common size statements’ ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I, -------- of grade 12-- would like to express my sincere gratitude to my Accounts teacher Mr/Ms---- for his/her guidance and continuous support in completing my ISC project. I would also like to extend sincere gratitude to my Parents for providing me all the facilities for completing the project. INDEX SL No 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Topic About the Company Introduction to Financial Statement Analysis Comparative Balance sheet and analysis Common size Balance sheet and analysis Comparative Statement of Profit and Loss and analysis Common size Statement of Profit and Loss and analysis Findings and Conclusions Bibliography Appendix Page No. 01-03 04-05 06-09 10-13 14-17 18-21 22 23 24-26 ULTRATECH CEMENT LIMITED ABOUT THE COMPANY UltraTech Cement Limited is the cement flagship company of the Aditya Birla Group. A $ 5.9 billion building solutions powerhouse, UltraTech is the largest manufacturer of grey cement and ready mix concrete and one of the largest manufacturers of white cement in India. It is the third largest cement producer in the world, excluding China. UltraTech is the only cement company globally to have 100+ MTPA of cement manufacturing capacity in a single country. The Company’s business operations span UAE, Bahrain, Sri Lanka and India. UltraTech pioneered the UltraTech Building Solutions concept to provide individual home builders with a one-stop-shop solution for building their homes. This is the first pan-India multi-category retail chain catering to the needs of individual home builders. The purpose of this initiative is to engage with home builders at all stages of the construction cycle, empower them with quality construction products and services, and assist in the completion of their dream homes. Today, UBS is the largest single brand retail chain with over 2500 stores across India. UltraTech is a founding member of Global Cement and Concrete Association. It is a signatory to the GCCA Climate Ambition 2050 and has committed to the Net Zero Concrete Roadmap announced by GCCA. UltraTech is focused on accelerating the decarbonisation of its operations. It has adopted new age tools like the Science Based Targets Initiative and Internal Carbon Price as well as set ambitious environmental targets through both EP100 and RE100. UltraTech is the first company in India and the second company in Asia to issue dollar-based sustainability linked bonds. UltraTech works to actively contribute to the social and economic development of the communities in which it operates in. The Company’s social initiatives focus on education, healthcare, sustainable livelihoods, community infrastructure and social causes. UltraTech reaches out to more than 2.1 million beneficiaries in over 500 villages in 16 states across India. Their Vision: To be the leader in Building Solutions Their mission: To deliver superior value to stakeholders on the four pillars of Sustainability Innovation Customer Centricity Team Empowerment Page: 01 HISTORY UltraTech Cement's top competitors include Heidelberg Cement, CEMEX, ASSA ABLOY Door Security Solutions and Carborundum Universal. UltraTech Cement Ltd. is the largest manufacturer of grey cement, Ready Mix Concrete (RMC) and white cement in India. Heidelberg Cement is a global manufacturer of building materials. Ultratech Cement was incorporated in 2000 as Larsen & Toubro. Later it was demerged and acquired by Grasim and was renamed as Ultra Tech Cement in 2004. Today Ultatech cement a part of Aditya Birla group, is the country’s largest exporter of cement clinker. UltraTech Cement Limited has an annual capacity of 52 million tonnes. It manufactures and markets Ordinary Portland Cement, Portland Blast Furnace Slag Cement and Portland Pozzalana Cement. It also manufactures ready mix concrete (RMC). All the plants have received ISO 9001 certification. The company has 11 integrated plants, one white cement plant, one clinkerisation plant in UAE, 15 grinding units 11 in India, 2 in UAE, one in Bahrain and Bangladesh each and five terminals, four in India and one in Sri Lanka. The export markets span countries around the Indian Ocean, Africa, Europe and the Middle East. Narmada Cement Company Limited was amalgamated with UltraTech in May 2006, while Samruddhi Cement Limited was amalgamated with UltraTech Cement Limited in July 2010. UltraTech Cement Middle East Investments Limited, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company acquired management control of ETA Star Cement together with its operations in the UAE, Bahrain and Bangladesh in September, 2010 UltraTech's other subsidiaries are Dakshin Cements, Harish Cements, UltraTech Ceylinco (P) and UltraTech Cement Middle East Investments. Page: 02 PRODUCTS It manufactures ordinary portland cement commonly used in dry–lean mixes, general– purpose ready–mixes, and even high strength pre–cast and pre–stressed concrete. It produces Portland blast furnace that has features like lighter colour, better concrete workability, easier finishability, higher compressive and flexural strength, improved resistance to aggressive chemicals and more consistent plastic and hardened consistency. It also manufactures portland pozzolana cement. Ultratech cement exports over 2.5 million tonnes per annum which accounts for 30% of country’s total exports. It exports to countries like Africa, Europe and the Middle East. COMPETITORS There are several brands in the market which are competing for the same set of customers. Below are the top 5 competitors of UltraTech Cements: 1. Ambuja Cement 2. ACC Limited 3. Shree Cement 4. The Indian Cement 5. JK Cements Page: 03 FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS Meaning It is a systematic process of critical examination of the financial information in the financial statements to understand and to make decisions regarding the operations of the enterprise. the term financial analysis includes both analysis and interpretation. a delicious beat simplify get classified the data in the financial statements and interpretation means understanding and interpreting the result of analysis. Tools/Techniques of Financial Statement Analysis Comparative statement: it means a comparative study of individual items or components of financial statement example balance sheet and statement of profited loss of two or more years of the enterprise itself. in this boat profit and loss and balance sheet are prepared in the form of comparative statements or comparative financial statements the amounts of current year are placed first and that of previous year later. this analysis is also known as horizontal analysis. Common size statements: these are the statements which shows the relationship of different items of financial statements with some common item by expressing each item as a percentage of that common base. common base in general are taken as a total asset value as hundred in case of common size balance sheet and revenue from operations in case of common size statement of profit and loss. this analysis is also known as vertical analysis. Objectives Assessing the earning capacity or profitability- on basis of financial analysis earning capacity of the enterprise can be assessed or computed and in addition the earning capacity of the enterprise in the coming years may also be forecasted all external users of financial statement especially the investors and potential investors are interested in earning capacity and forecast. Inter-firm comparison- it becomes easy with the help of financial analysis and it helps an enterprise in assessing its own performance as well as that of others if mergers and acquisitions are to be considered. Financial statement analysis help in assessing developments in future especially in the next year it may be possible to forecast the next year profit on the basis of earning capacity shown in the past and the analysis thus helps in forecasting and preparing the budgets. Financial analysis helps the users of financial statement to understand the complicated matter in the simplified manner and financial data can be made more comprehensive by charts, graphs and diagrams which can be easily explained and understood. Page: 04 Limitations Historical analysis: Financial statement analysis is an analysis of historical or past data and it analyzes what has happened in the past and does not reflect the future and people like shareholders, investors, etc. Arbor interested in knowing the likely position in the future. Ignores price level changes: Price level changes and purchasing power of money are inversely related and change in the price level makes analysis of financial statements of different accounting years invalid because accounting records ignored changes in value of money. Variation in accounting practices: For interfirm comparison it is desirable that accounting practices followed by the firms do not vary significantly as there maybe variations in accounting practices followed by different firms a meaningful comparison of their financial statement is not possible. Window dressing: It is the presentation of a better financial position than what it is by manipulating the books of accounts and on account of such a situation financial analysis may give false information to the users Page: 05 COMPARATIVE BALANCE SHEET COMPARATIVE BALANCE SHEET as at 31st March 2021 Absolute 31st Change NOTE march 31st march (Increase/ PARTICULARS NO. 2021 2020 Decrease) ₹ ₹ ₹ I. EQUITY AND LIABILITIES 1. Shareholder's Funds (a) Share Capital 27673.08 25648.41 2024.67 (b) Reserve and Surplus 274.64 274.61 0.03 Percentage Change (Increase/ Decrease) % 7.89 0.01 2. Non-Current Liabilities (a) Long term borrowings (b) Long Term Provisions (c ) Defered tax liabilities (d) Other non current liabilities 14939.28 135.58 3544.35 6.27 13906.63 136.78 3174.05 6.57 1032.65 -1.20 370.30 -0.30 7.43 -0.88 11.67 -4.57 3. Current Liabilities (a) Short term borrowings (b) Trade Payables (c ) Other Current Liabilities (d) Short term Provisions TOTAL 2642.74 2653.74 5672.16 894.61 58436.45 2687.83 2224.16 5386.89 927.07 54373 -45.09 429.58 285.27 -32.46 4063.45 -1.68 19.31 5.30 -3.50 7.47 34365.67 2929.72 1075.85 34218.98 2991.86 1472.97 146.69 -62.14 -397.12 0.43 -2.08 -26.96 3.8 5549.66 127.18 0.91 2214.19 140.33 2.89 3335.47 -13.15 317.58 150.64 -9.37 147.71 132.99 14.72 11.07 II. ASSETS 1. Non Current Assets (a) Property, plant, equipment and intangible assets i) property, plant and equipment ii) Intangible assets iii) Capital Work in progress iv) Intangible assets under development (b) Non Current Investments (C ) Deffered tax assets (d ) Long term Loans and Advances (e ) Other non current assets 2. Current Assets (a) Current Investments (b) Inventories (c ) Trade Receivables (d) Cash and Bank Balances (e ) Short term Loans and Advances (f) Other Current Assets TOTAL 2758.14 2615.16 142.98 5.47 1514.85 3273.62 2097.59 623.96 3948.71 3101.5 1714.2 199.32 -2433.86 172.12 383.39 424.64 -61.64 5.55 22.37 213.04 1919.49 2049.21 58436.45 111.02 1510.86 54373 1808.47 538.35 4063.45 1628.96 35.63 7.47 Page: 07 GRAPHS COMPARATIVE BALANCE SHEET ABSOLUTE CHANGES IN EQUITY AND LIABILITIES Share Capital Reserve and Surplus Long term borrowings Long Term Provisions Defered tax liabilities Other non current liabilities Short term borrowings Trade Payables Other Current Liabilities Short term Provisions ABSOLUTE CHANGES IN NON CURRENT AND CURRENT ASSETS property, plant and equipment Intangible assets Capital Work in progress Intangible assets under development Non Current Investments Deffered tax assets Long term Loans and Advances Other non current assets Current Investments Inventories Trade Receivables Cash and Bank Balances Short term Loans and Advances Other Current Assets Page: 08 PERCENTAGE CHANGES IN EQUITY AND LIABILITIES Share Capital Reserve and Surplus Long term borrowings Long Term Provisions Defered tax liabilities Other non current liabilities Short term borrowings Trade Payables Other Current Liabilities Short term Provisions PERCENTAGE CHANGES IN NON-CURRENT AND CURRENT ASSETS property, plant and equipment Intangible assets Capital Work in progress Intangible assets under development Non Current Investments Deffered tax assets Long term Loans and Advances Other non current assets Current Investments Inventories Trade Receivables Cash and Bank Balances Short term Loans and Advances Other Current Assets Page: 09 COMMON-SIZE BALANCE SHEET ULTR TECH CEMENT Ltd COMMON-SIZE BALANCE SHEET as at 31st March 2021 Absolute amounts % of Balance sheet total NOTE 31st PARTICULARS NO. March 31st March 31st March 2021 2020 2021 31st March 2020 ₹ ₹ % % I. EQUITY AND LIABILITIES 1. Shareholder's Funds (a) Share Capital 27673.08 25648.41 47.36 47.17 (b) Reserve and Surplus 274.64 274.61 0.47 0.51 2. Non-Current Liabilities (a) Long term borrowings (b) Long Term Provisions (c ) Defered tax liabilities (d) Other non current liabilities 14939.28 135.58 3544.35 6.27 13906.63 136.78 3174.05 6.57 25.57 0.23 6.07 0.01 25.58 0.25 5.84 0.01 3. Current Liabilities (a) Short term borrowings (b) Trade Payables (c ) Other Current Liabilities (d) Short term Provisions TOTAL 2642.74 2653.74 5672.16 894.61 58436.45 2687.83 2224.16 5386.89 927.07 54373 4.52 4.54 9.71 1.53 100.00 4.94 4.09 9.91 1.71 100.00 34365.67 2929.72 1075.85 34218.98 2991.86 1472.97 58.81 5.01 1.84 62.93 5.50 2.71 3.8 5549.66 127.18 0.91 2214.19 140.33 0.01 9.50 0.22 0.00 4.07 0.26 147.71 2758.14 132.99 2615.16 0.25 4.72 0.24 4.81 II. ASSETS 1. Non Current Assets (a) Property, plant, equipment and intangible assets i) property, plant and equipment ii) Intangible assets iii) Capital Work in progress iv) Intangible assets under development (b) Non Current Investments (C ) Deffered tax assets (d ) Long term Loans and Advances (e ) Other non current assets 2. Current Assets (a) Current Investments (b) Inventories (c ) Trade Receivables (d) Cash and Bank Balances (e ) Short term Loans and Advances (f) Other Current Assets TOTAL 1514.85 3273.62 2097.59 623.96 3948.71 3101.5 1714.2 199.32 2.59 5.60 3.59 1.07 7.26 5.70 3.15 0.37 1919.49 2049.21 58436.45 111.02 1510.86 54373 3.28 3.51 100.00 0.20 2.78 100.00 Page: 11 GRAPHS COMMON-SIZE BALANCE SHEET EQUITY AND LIABILITIES - PERCENTAGE ON BALANCE SHEET TOTAL( 31.3.2019) Share Capital Reserve and Surplus Long term borrowings Long Term Provisions Defered tax liabilities Other non current liabilities Short term borrowings Trade Payables Other Current Liabilities Short term Provisions ASSETS- PERCENTAGE ON BALANCE SHEET TOTAL( 31.3.2019) property, plant and equipment Intangible assets Capital Work in progress Intangible assets under development Non Current Investments Deffered tax assets Long term Loans and Advances Other non current assets Current Investments Inventories Trade Receivables Cash and Bank Balances Short term Loans and Advances Other Current Assets EQUITY AND LIABILITIES - PERCENTAGE ON BALANCE SHEET TOTAL( 31.3.2018) Share Capital Reserve and Surplus Long term borrowings Long Term Provisions Defered tax liabilities Other non current liabilities Short term borrowings Trade Payables Other Current Liabilities Short term Provisions ASSETS- PERCENTAGE ON BALANCE SHEET TOTAL( 31.3.2019) property, plant and equipment Intangible assets Capital Work in progress Intangible assets under development Non Current Investments Deffered tax assets Long term Loans and Advances Other non current assets Current Investments Inventories Trade Receivables Cash and Bank Balances Short term Loans and Advances Other Current Assets Page: 13 COMPARATIVE STATEMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS ULTR TECH CEMENT Ltd COMPARATIVE STATEMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS as at 31st March 2021 Absolute Percentage 31st Change Change NOTE March 31st March (Increase/ (Increase/ PARTICULARS NO. 2021 2020 Decrease) Decrease) ₹ ₹ ₹ % I. Revenue from Operations 35703.50 30251.75 5451.75 18.02 II. Other Income 471.45 599.55 -128.10 -21.37 36174.95 30851.30 5323.65 17.26 III. Total Revenue (I+II) IV. Expenses Cost of Materials Consumed Purchase of Stock In Trade Changes in inventories Employees benefit expenses Finance costs Depreciation and amortisation expense Other expenses Total Expenses 4737.22 1582.35 -103.86 1926.01 1419.15 3978.36 814.37 -113.08 1706.24 1191.15 758.86 767.98 9.22 219.77 228.00 19.07 94.30 -8.15 12.88 19.14 2010.27 21065.66 32636.80 1763.56 18020.92 27361.52 246.71 3044.74 5275.28 13.99 16.90 19.28 V. Profit before tax (III-IV) VI. Less Tax 3538.15 736.12 3489.78 712.00 48.37 24.12 1.39 3.39 VII. Profit after tax (V-VI) 2802.03 2777.78 24.25 0.87 Page: 14 GRAPHS COMPARATIVE STATEMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS ABSOLUTE CHANGES IN EXPENSES 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 Cost of Purchase of Changes in Materials Stock In Trade inventories Consumed Employees benefit expenses Finance costs Depreciation and amortisation expense Other expenses ABSOLUTE CHANGES IN PROFIT 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Profit before tax Tax Paid Profit after tax PERCENTAGE CHANGE IN REVENUE 20 15 10 5 0 Revenue from Operations -5 -10 -15 -20 -25 Other Income Total Revenue PERCENTAGE CHANGE IN EXPENSES 100 80 60 40 20 0 -20 Cost of Materials Consumed Purchase of Stock In Trade Changes in inventories Employees benefit expenses Finance costs Depreciation and amortisation expense Other expenses PERCENTAGE CHANGE IN PROFIT 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 Profit before tax Tax Paid Profit after tax Page: 17 COMMON SIZE STATEMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS ULTR TECH CEMENT Ltd COMMON SIZE STATEMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS as at 31st March 2021 % of Revenue from Absolute amounts Operations NOTE PARTICULARS 31st NO. March 31st March 31st March 31st March 2021 2020 2021 2020 ₹ ₹ % % I. Revenue from Operations 35703.50 30251.75 100.00 100.00 II. Other Income 471.45 599.55 1.32 1.98 36174.95 30851.30 101.32 101.98 III. Total Revenue (I+II) IV. Expenses Cost of Materials Consumed Purchase of Stock In Trade Changes in inventories Employees benefit expenses Finance costs Depreciation and amortisation expense Other expenses Total Expenses 4737.22 1582.35 -103.86 1926.01 1419.15 3978.36 814.37 -113.08 1706.24 1191.15 13.27 4.43 -0.29 5.39 3.97 13.15 2.69 -0.37 5.64 3.94 2010.27 21065.66 32636.80 1763.56 18020.92 27361.52 5.63 59.00 91.41 5.83 59.57 90.45 V. Profit before tax (III-IV) VI. Less Tax VII. Profit after tax (V-VI) 3538.15 736.12 2802.03 3489.78 712.00 2777.78 9.91 2.06 7.85 11.54 2.35 9.18 Page: 18 GRAPHS COMMON SIZE STATEMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS PERCENTAGE OF REVENUE TO REVENUE FROM OPERATIONS (31.03.2019) 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Revenue from Operations Other Income Total Revenue PERCENTAGE OF EXPENSES TO REVENUE FROM OPERATIONS (31.03.2019) 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 -10 Cost of Materials Consumed Purchase of Stock In Trade Changes in inventories Employees benefit expenses Finance costs Depreciation and amortisation expense Other expenses PERCENTAGE OF EXPENSES TO REVENUE FROM OPERATIONS (31.03.2019) 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Profit before tax Tax paid Profit after tax PERCENTAGE OF REVENUE TO REVENUE FROM OPERATIONS (31.03.2018) 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Revenue from Operations Other Income Total Revenue PERCENTAGE OF EXPENSES TO REVENUE FROM OPERATIONS (31.03.2018) 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 -10 Cost of Materials Consumed Purchase of Stock In Trade Changes in inventories Employees benefit expenses Finance costs Depreciation and amortisation expense Other expenses PERCENTAGE OF EXPENSES TO REVENUE FROM OPERATIONS (31.03.2018) 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Profit before tax Tax paid Profit after tax Page: 21 FINDINGS and CONCLUSIONS From the analysis of comparative balance sheet, it has been observed that there is a substantial increase in shareholders funds. Also, there is an increase in current assets and current liabilities. There is a high increase in its cash and bank balances that shows that the liquidity position of the company is good. Also, there is a substantial increase in its current investments, that shows company has utilized their extra cash in investments to generate revenue. Common size balance sheet shows that a major part of liability side consists of equity capital. Also, there is non-current tangible assets consists the major part of assets. This shows that company has made right investments in non-current assets from their equity capital. In other words long term sources of capital is used to finance long term assets. It is also noted that company is dependent on long term borrowing. Comparative income statement shows an increase in its revenue and total profit of the company. The increase in its revenue is 17.26%, however the increase in its profit is only 1.39%. the reason for the same is increase in expenses. It is advisable for the company to adopt cost control techniques to reduce its expenses, so that the increase in its revenue will reflect in its profit as well. It is also noted that there is a huge rise in cost of purchase of stock and trade. It is recommended to review the supplier. The common size statement of profit and loss shows percentage of net profit on its revenue from operations is 9.91% in the year 2021wherein it is 11.54% in the year 2020. It shows a dip in percentage of profit on its revenue from operations. The main reasons for the same are increase in its expense over a period of one year and a small dip in its other incomes. As stated above the management should take effective steps in cost sontrolling. Page: 22 BIBLIOGRAPHY https://www.ultratechcement.com/ https://www.moneycontrol.com/ Management accounting book – T.S. GREWAL Annual report of Ultratech cements limited Page: 23 APPENDIX BALANCE SHEET as at 31st March 2021 NOTE NO. PARTICULARS 31st march 2021 ₹ 31st march 2020 ₹ I. EQUITY AND LIABILITIES 1. Shareholder's Funds (a) Share Capital (b) Reserve and Surplus 27673.08 274.64 25648.41 274.61 2. Non-Current Liabilities (a) Long term borrowings (b) Long Term Provisions (c ) Defered tax liabilities (d) Other non current liabilities 14939.28 135.58 3544.35 6.27 13906.63 136.78 3174.05 6.57 2642.74 2653.74 5672.16 894.61 58436.45 2687.83 2224.16 5386.89 927.07 54373 34365.67 2929.72 1075.85 34218.98 2991.86 1472.97 3.8 5549.66 127.18 147.71 0.91 2214.19 140.33 132.99 3. Current Liabilities (a) Short term borrowings (b) Trade Payables (c ) Other Current Liabilities (d) Short term Provisions TOTAL II. ASSETS 1. Non Current Assets (a) Property, plant, equipment and intangible assets i) property, plant and equipment ii) Intangible assets iii) Capital Work in progress iv) Intangible assets under development (b) Non Current Investments (C ) Deffered tax assets (d ) Long term Loans and Advances (e ) Other non current assets 2758.14 2615.16 2. Current Assets (a) Current Investments (b) Inventories (c ) Trade Receivables (d) Cash and Bank Balances (e ) Short term Loans and Advances (f) Other Current Assets TOTAL 1514.85 3273.62 2097.59 623.96 1919.49 2049.21 58436.45 3948.71 3101.5 1714.2 199.32 111.02 1510.86 54373 Page: 25 STATEMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS as at 31st March 2021 PARTICULARS I. Revenue from Operations II. Other Income III. Total Revenue (I+II) NOTE NO. 31st march 2021 ₹ 35703.50 471.45 36174.95 31st march 2020 ₹ 30251.75 599.55 30851.30 IV. Expenses Cost of Materials Consumed Purchase of Stock In Trade Changes in inventories Employees benefit expenses Finance costs Depreciation and amortisation expense Other expenses Total Expenses 4737.22 1582.35 -103.86 1926.01 1419.15 3978.36 814.37 -113.08 1706.24 1191.15 2010.27 21065.66 32636.80 1763.56 18020.92 27361.52 V. Profit before tax (III-IV) VI. Less Tax VII. Profit after tax (V-VI) 3538.15 736.12 2802.03 3489.78 712.00 2777.78 Page: 26