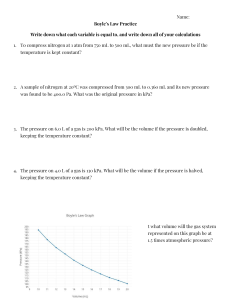
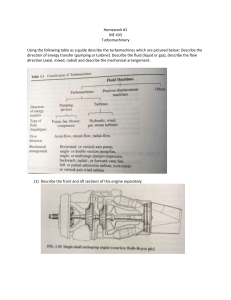
GEOTECH PREBOARD 1 A stratified soil deposit consists of four layers. The thickness of the second, third and fourth layers are equal to half, one-third and one-fourth, respectively, the thickness of the top layer, while their coefficients of permeability are respectively twice, thrice and four times that of the top layer. Determine: 1. Equivalent horizontal coefficient of permeability A. 1.46 k1 C. 1.92 k1 B. 1.03 k1 D. 1.32 k1 2. Equivalent vertical coefficient of permeability A. 1.03 k1 C. 1.32 k1 B. 1.46 k1 D. 1.92 k1 3. Ratio of equivalent coefficient of permeability A. 1.32 C. 1.92 B. 1.46 D. 1.03 Solution: 1 h1 2 k2 2k1 1 h3 h1 3 k3 3k1 h2 1 25 h1 H T h1 4 12 k4 4k1 h4 H T K eq / / hk 25 1 1 1 h1 ( K eq / / ) h1 k1 h1 (2k1 ) h1 (3k1 ) h1 (4k1 ) 12 2 3 4 K eq / / 1.92k1 HT h K eq k 25 h1 /12 K eq h1 k1 h1 / 2 2k1 h1 / 3 3k1 h1 / 4 4k1 K eq 1.46k1 ratio K eq / / K eq 1.92 k 1 1.32 1.46 k1 The in-site density of a soil mass is to be determined by the core-cutter method. The height and diameter of the core are 13 cm and 10 cm respectively. The core, when full of soil, weighs 3155 gm, while the selfweight of the empty core is 1250 gm. The natural moisture content and specific gravity of solids are 12% and 2.66 respectively. Determine the following: 4. Bulk Density in gm/cc A. 1.87 B. 1.95 5. Dry Density in gm/cc A. 1.67 B. 1.75 6. Void ratio A. 0.69 B. 0.59 C. 1.67 D. 1.75 C. 1.87 D. 1.95 C. 0.79 D. 0.89 Solution: Wt 3155 1250 1.87 gm / cc Vol (10) 2 (13) 4 1.87 d 1.67 gm / cc 1 w 1 0.12 G 2.66(1) d s w 1.67 e 0.59 1 e 1 e A sand sample is 50% saturated and has bulk density of 1.75 t/m 3. The specific gravity of solids is 2.65. Determine the following: 7. Void ratio of the soil A. 0.85 C. 0.96 B. 0.72 D. 0.65 8. Determine the critical hydraulic gradient A. 0.85 C. 0.96 B. 0.72 D. 0.65 9. How will the critical hydraulic gradient of the soil change if the soil is compacted to increase bulk density by 10% when the degree of saturation remains constant. A. 13.8% increase C. 16.3% increase B. 13.8% decrease D. 16.3% decrease Solution: Gs Se 2.65 0.5(e) w 1.75 (1) e 0.72 1 e 1 e G 1 2.65 1 icr s 0.96 1 e 1 0.72 G Se ' 2.65 0.5(e ') ' s w 1.75(1.1) (1) e 0.51 1 e ' 1 e ' G 1 2.65 1 icr ' s 1.09 1 e 1 0.51 1.09 % 1.135 13.5% increase 0.96 A layer of sand 5 meters deep overlies a 4 m thick bed of clay. Assume sand has saturated unit weight & dry unit weight of 20.9 kN/m3& 17.4 kN/m3 respectively, while the clay has saturated unit weight of 17.8 kN/m3. Determine the effective stress 9 m below the ground surface if: 10. The water table is at the ground level. A. 118.96 kPa C. 87.41 kPa B. 88.29 kPa D. 107. 03 kPa 11. The water table is at 2 meters below ground level and the sand above remains saturated with capillary moisture. A. 118.96 kPa C. 87.41 kPa B. 88.29 kPa D. 107. 03 kPa 12. If the water table is at the top of the clay. A. 118.96 kPa C. 87.41 kPa B. 88.29 kPa D. 107. 03 kPa Solution: Pe ' h Water table is at ground level : Pe (20.9 9.81)(5) (17.8 9.81)(4) 87.41 kPa 2 m below ground level : Pe 20.9(2) (20.9 9.81)(3) (17.8 9.81)(4) 107.03 kPa Top of Clay : Pe 17.4(5) (17.8 9.81)(4) 118.96 kPa From the figure below: Assume: 3K1=K2=1.5K3=2K4 and that layer 2 & 3 are of equal height. AB = 6 cm, BC = 10 cm and CD = 8 cm 13. Find the pressure head at point B A. 19.3 cm C. 16.2 cm B. 24.0 cm D. 12.0 cm 14. Find the pressure head at point C A. 19.3 C. 16.2 B. 24.0 D. 12.0 2 15. Find the rate of flow if K1= 3.5 x 10- cm/sec A. 0.11 cm3/sec C. 0.08 cm3/sec 3 B. 0.15 cm /sec D. 0.18 cm3/sec Solution: From 3K1 K 2 1.5 K 3 2 K 4 K 2 3K1 K 3 2 K1 K 4 1.5K1 HK eq hk 4( K 23 ) 2(3K1 ) 2(2 K1 ) K 23 2.5 K1 H h K eq k 24 6 10 8 K eq K1 2.5 K1 1.5 K1 K eq 1.565 K1 QT keq iA 1.565 K1 ( 12 )(4)(1) 3.130 K1 24 QT Q1 3.130 K 1 K1 ( 24 hb )(4)(1) hb 19.305 m 6 QT Q4 3.130 K1 1.5 K1 ( hc 12 )( 4)(1) hc 16.173 m 8 QT 3.130 K1 3.130(3.5 x 102 0.11 cm3 / s