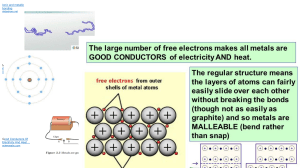
MATL 260/360 HOMEWORK #1 1. Table salt (NaCl) exhibits predominantly ionic bonding. The Na+ and Cl- ions have electron structures that are identical to which two inert gases? Na+ loses an electron, so it is identical to Ne. Whereas, Cl- gains an electron, so Ar. 2. Write the electron configurations for the following ions: Fe2+, and O2- . Fe2+ => 1s22s22p63s23p63d6 O2- => 1s22s22p6 3. For a Na+-Cl- ion pair, attractive and repulsive energies EA and ER are EA = -1.436/r and ER = 7.32(10)-6/r8 (a) Plot En, EA and ER on a single plot from r=0 to r=1.0 nm. Use a graphing program such as Excel or Origin. Each student must generate and print their own graph. sharing of graphs will result in a zero score for the entire homework #1. (b) From this plot, determine ro (the equilibrium spacing) between Na+ and Cl-. R = 0.18 (c) From this plot, determine the bond energy between Na+ and Cl-. -5.3 (d) Mathematically determine ro and compare this with your answer in (b). (7.32(10)-6)/r8 = 1.436/r => r = 1.754 4. What type(s) of bonding would be expected for each of the following materials: brass (a copper-zinc alloy), Metallic liquid Cl2, Covalent Bonding barium sulfide (BaS), Ionic Bonding solid xenon, Vander waals bonding polypropylene covalent w/ vander walls bonding 5. Compute the percentage ionic character for GaP and MgO. (Note: Consult equation in book). %IC = (1-e-.25(X1-X2)^2) x100 => Xgap = 2.1-1.6 = 0.5 AND XMgo = 3.5-1.2 = 2.3 => %IC = 55.5% 6. What is the main difference between chemical and physical bonding? Chemical bonding changes the e- configuration while physical bonding does not. 7. List the three types of chemical bonds in the following order: from having more restrictions to having less restrictions. List what those restrictions (and lack of restrictions) are for each one of them. 1. Covalent Bonds: Restrictions – Directional, bonding only besides specific atoms, more difficult to form crystals, and complex structures. Lack of Restrictions – more open structures 2. Ionic Bonds: Restrictions – must be opposite charges to bond, different size of ions Lack of Restrictions – non-directional, stoichiometry 3. Metallic bonds Restrictions – only uses metallic ions Lack of Restrictions – non-directional, easy to find structure that minimizes energy, easier to form crystalline structures