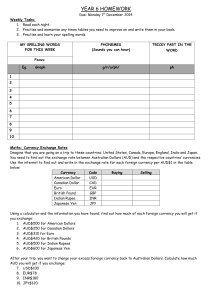
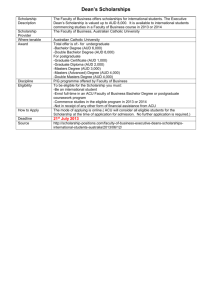
HSC ECONOMICS – AUSTRALIA’S PLACE IN THE GLOBAL ECONOMY – EXCHANGE RATES AUSTRALIA’S FLOATING EXCHANGE RATE SYSTEM Presented by Eva Spalj Syllabus dot point: Exchange rates • factors affecting the demand for and supply of Australian dollars © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 1 What’s in this lesson? What factors influence demand for the AUD? What factors influence supply of the AUD? © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 2 Floating Exchange Rate Where the value of the exchange rate is determined by the forces of demand and supply. Indirect Method of Quotation Refers to the rate of exchange between one unit of domestic currency and the equivalent amount of foreign currency. The Market for Australian Dollars Theory summary Where demand and supply intersect, we have our equilibrium price for AUD. This is called the exchange rate. Price of AUD$ in terms of USD$ When discussing the price of currency it must always be in terms of another currency (such as the US dollar). Supply of AUD$ 0.68 Note: The quantity of AUD traded is found on the horizontal axis. Demand for AUD$ Q © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 Quantity of AUD$ 3 Floating exchange rate Where the value of the exchange rate is determined by the forces of demand and supply. Appreciation An increase in the value of a currency in a floating exchange rate system. The Market for Australian Dollars Supply of AUD$ Appreciation © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 The A$ is demanded in the foreign exchange market to: • Buy exports of goods and services • Send income into Australia • Invest in Australia, capital inflow 4 Appreciation An increase in the value of a currency in a floating exchange rate system. What factors influence the demand for the AUD? The demand for Australian exports by foreigners: Supply of AUD$ Increased demand for Australian X à increase in demand for AUD (shift to the right) à appreciation of the AUD. Decreased demand for Australian X à decrease in demand for AUD (shift to the left) à depreciation of the AUD. Appreciation © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 5 Terms of Trade The ratio of export prices to import prices. What factors influence the demand for the AUD? Relative rates of domestic and world economic growth: Relatively strong world growth Increased demand for AUS exports Increased demand for AUD Terms of trade movements: Higher commodity prices Favorable terms of trade Higher export income Increased demand for AUD The demand for Australian assets such as shares, real estate, government bonds, and currency: Increased demand for AUS assets Capital inflow into AUS Foreigners convert their currency © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 Increased demand for AUD 6 Interest rates Annual percentage cost of borrowing funds or percentage return on a financial asset. Inflation rate The rate at which prices increase over time, resulting in a fall in the purchasing value of money. What factors influence the demand for the AUD? Australia’s relative interest rate (differential): Rise in relative interest rate differential Greater returns on investment Attracts Increased demand more FDI for AUD Australia relative inflation rate (differential): Rise in relative inflation rate differential Increased prices Decreased international competitiveness for exports Decreased demand for exports Exchange rate expectations: Expectation of future appreciation Expectation of future gain and profit © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 Increased demand for AUD Decreased demand for AUD International Competitiveness Refers to a country’s ability to compete with other countries on international markets. It takes into account both price and non-price factors. 7 Depreciation A fall in the value of a currency in a floating exchange rate system. What factors influence the supply of the AUD? The demand for foreign imports by Australians: Supply of AUD$ Price of AUD$ in terms of USD$ S2AUD$ Increased demand for foreign M à increase in supply of AUD (shift to the right) à depreciation of the AUD. Decreased demand for foreign M à decrease in supply of AUD (shift to the left) à appreciation of the AUD. 0.68 Depreciation 0.64 Demand for AUD$ Q Q2 © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 Quantity of AUD$ 8 Interest rates Annual percentage cost of borrowing funds or percentage return on a financial asset. What factors influence the supply of the AUD? The demand for foreign assets such as shares, real estate, government bonds, and currency: Increased demand for foreign assets Capital outflow from AUD Australians convert their currency Increased supply of AUD Australia’s relative interest rate (differential): Fall in relative interest rate differential Lower returns on investment Increased demand for foreign assets © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 Outflow of capital Increased supply from AUS of AUD 9 What factors influence the supply of the AUD? Exchange rate expectations: Expectation of future depreciation Expectation of future loss Increased supply of AUD Relative rates of domestic and world economic growth: Higher AUS growth Increased demand for imports © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 Increased supply of AUD 10 Balance of Payments The balance of payments (BoP) is a record of all transactions between residents of a country and the rest of the world over a given period. Link to the Balance of Payments Changes in the demand and supply of Australian dollars are influenced by transactions in the current account, and capital and financial accounts of the Balance of Payments. Factors affecting Demand and supply of AUD Balance of Payments Demand for AUS exports (X) Demand for AUD Credit on the BOGS – Current Account Demand for foreign imports (M) Supply of AUD Debit on the BOGS – Current Account Demand for Australian assets Demand for AUD Credit on the Financial Account Demand for foreign assets Supply of AUD Debit on the Financial Account © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 Influences • Interest rate differential • Terms of trade • Domestic and world economic growth rates • Interest rate differentials • Exchange rate expectations 11 Multiple choice activity Which of the following are the most likely effects of an increase in Australian interest rates relative to overseas interest rates? A. Decreased outflow of capital and an depreciation of the Australian dollar. B. Increased outflow of capital and a depreciation of the Australian dollar. C. Decreased inflow of capital and an appreciation of the Australian dollar. D. Increased inflow of capital and an appreciation of the Australian dollar. E. I don’t know. © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 (Written by the author) 12 Multiple choice – Response Which of the following are the most likely effects of an increase in Australian interest rates relative to overseas interest rates? A. Decreased outflow of capital and an depreciation of the Australian dollar. B. Increased outflow of capital and a depreciation of the Australian dollar. C. Decreased inflow of capital and an appreciation of the Australian dollar. D. Increased inflow of capital and an appreciation of the Australian dollar. E. I don’t know. © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 (Written by the author) 13 Multiple choice activity Which of the following would NOT account for the change shown in the diagram? A. Increased Australian economic growth B. More capital outflows C. Decreased imports D. Increased speculation E. I don’t know. Diagram from 2Z019 HSC Exam © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 (Written by the author) 14 Multiple choice – Response Which of the following would NOT account for the change shown in the diagram? A. Increased Australian economic growth B. More capital outflows C. Decreased imports D. Increased speculation E. I don’t know. Diagram from 2Z019 HSC Exam © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 (Written by the author) 15 The copyright in substantial portions of this material is owned by the NSW Education Standards Authority. Used with permission. The NESA does not endorse this product and makes no warranties regarding the correctness or accuracy of its content. To the extent permitted by law, the NESA excludes all liability for any loss or damage suffered or incurred as a result of accessing, using or relying on the content. Current and past NESA/BOSTES exams and related content can be accessed directly at http://educationstandards.nsw.edu.au. We do our best to make these slides comprehensive and up-to-date, however there may be errors. We'd appreciate it if you pointed these out to us! © Eva Spalj & Edrolo 2020 16