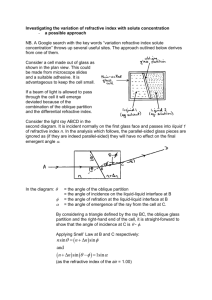
Lab Title: Practical Guide to Determine the Refractive Index of Glass Using Snell's Law Introduction: Understanding the refractive index of a material is crucial in various fields such as optics, physics, and material science. Snell's Law provides a fundamental relationship between angles of incidence and refraction and the refractive indices of the materials involved. This practical guide will help you determine the refractive index of glass using Snell's Law. Materials Needed: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Rectangular glass prism Protractor White sheet of paper Pencil Light source (e.g., laser pointer or torch) Ruler or measuring tape Table or flat surface Procedure: 1. Setup: Choose a well-lit area with a flat surface. Place the white sheet of paper on the table. Ensure the glass prism is clean. 2. Incident Ray: Place the glass prism on the paper. Measure and mark the angle of incidence (θâ‚). Direct the light source towards the marked angle. 3. Refracted Ray: Observe and mark the direction of the refracted ray inside the prism. Measure and record the angle of refraction (θ₂). 4. Calculation: Use Snell's Law: nâ‚ * sin(θâ‚) = nâ‚‚ * sin(θ₂). nâ‚ is the refractive index of the medium outside the prism, usually air. nâ‚‚ is the refractive index of the glass. Calculate the refractive index of the glass prism using the formula. 5. Determination of Refractive Index: Calculate nâ‚‚: nâ‚‚ = nâ‚ * sin(θâ‚) / sin(θ₂). Substitute the known values and calculate nâ‚‚. 6. Repeat: Repeat the experiment for accuracy. Average the calculated refractive indices. Conclusion: By following these steps and Snell's Law, you can determine the refractive index of glass accurately. This experiment reinforces optics principles and light behavior in different mediums. Reflection Questions: 1. What factors could introduce errors in your measurements? 2. How does changing the angle of incidence affect the refracted ray? 3. Why is it important to repeat the experiment multiple times? Assessment: Students will be assessed based on the accuracy of their calculated refractive indices. Written reflections on the experiment and its application in real-world scenarios will be graded. Relevant Standards: 1. NGSS Standard HS-PS4-1: Use mathematical representations to support a claim regarding relationships among the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction, and the refractive index of materials. 2. NGSS Standard HS-PS4-2: Evaluate the validity and reliability of claims in published materials of the effects that different frequencies of electromagnetic radiation have when absorbed by matter. Data Collection Table: Trial Angle of Incidence (θâ‚) Angle of Refraction (θ₂) Refractive Index (nâ‚‚) Calculation 1 2 3 4 5 Feel free to use this table to record your data during the experiment. Be sure to fill in the angles of incidence and refraction for each trial and calculate the refractive index accordingly. Graphs for Data Analysis: 1. Scatter Plot: Create a scatter plot with the angle of incidence (x-axis) against the angle of refraction (y-axis) for all trials. This will help visualize the relationship between the two angles. 2. Line Graph: Plot a line graph showing the refractive index (nâ‚‚) calculated for each trial. This graph will demonstrate any trends or patterns in the refractive index values obtained. 3. Bar Graph: Use a bar graph to compare the average refractive index calculated from all trials. This will provide a clear comparison of the refractive index values. These graphs will aid in analyzing the data collected during the experiment and identifying any patterns or discrepancies. Feel free to create these graphs using a graphing tool or software for a more visual representation of your results.