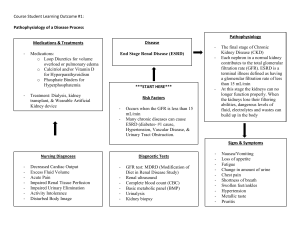
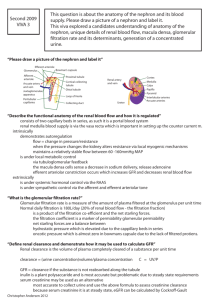
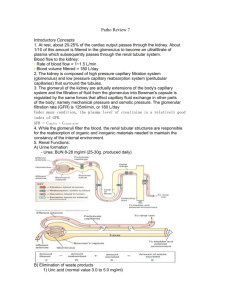
2024 Introduction: Renal Structure and Function Emily Nobles, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNE NURS 312 Pathophysiology University of South Carolina Aiken - Function of the Urinary System substances hormones finia - ? Kidneys – excretory and endocrine function • regulate water, electrolytes and acid-base balance • excrete foreign chemicals and metabolic waste materials • synthesis and activation of renin, erythropoietin, vitamin D and prostaglandins Temotology disorders • Gluconeogenesis (production Ureters, Bladder, Urethra of • Storage and transport of urine - - - I O . > - - - ( RAAS (maintains RBC) 1 2024 > I Erythropoietin - - that hormone Stimulates Stem cells 1m bore marrow ↑ RBC to Production Nephron • Functional unit of the kidney • Approx. 1.2 million/kidney (x2 • Don’t regenerate, number declines with age (10%/decade beginning at 40 yrs) • Parts: - L4 large Renal - Kidneys eletal Glomerulus citration) Bowman’s capsule Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle (ascending, descending) – Distal convoluted tubule – Collecting tubule – – – – textbook Kicheys) = - & ! Supplemental folder ↑ waste and out got reserve a re able Filter blood to · Toxins, waste i , nee wy S damage seven to Kidneys/Rephone, + > - ↑15- can louse 50 % 90 %or e age Kidne 2 2024 Nephron - Function • Filtration of water-soluble substances from blood • Reabsorption of filtered nutrients, water and electrolytes • Secretion of wastes or excess substances into the filtrate • Different segments specialize to accomplish these tasks. · Glomerulus as of filtration ↳ blood where it Glomerular > filtrate i lo starts similar - N To blood Plasma encastel Glomerulus & 3 Audio 2024 (lip 4 ④ moveisata substances ↑ ④ Hos) rzsof Karen space < perfra Glomerulus Layers D & layer ② single enothelial , 1. Capillary ① endothelium ① revent 2. Basement selective plasma membrane barter proties / WBC , 3. Outer capillary RB ,Cp [endothelium plateless podocytes inner Do ( ( gransing ↑ = ° through ( & foot processes - (surrund glomerous ④ spaces blu called silt 7 poles makeermciable > - blood Oseperates capillaries W) ④ - , from filtrate from bowmans in e of Protec is Slomeular/ss > - capsule Secretion/Reabsorption · tubular reapsorbtion ↳ removal filtrate w/in the of materials been thathas from the a develop s · tubular ↳ secretion fluids a re after : substances added it has to specialized that filtrate extracted been from glomerulus has the ; each section function 4 2024 and e page 847 Parts of the Nephron and Function - - - - L - - - - - - - - Glomerular Filtration i • Movement of fluids and solutes from blood in the Ira secof on · S glomerulus into Bowman’s capsule • Water and small solutes move through the glomerulus • Larger molecules, proteins and blood cells, unable to Injured move through unless glomerulas urin) • Resulting fluid -> glomerular filtrate (precurser • 125 ml of glomerular filtrate produced per minute = glomerular filtration rate (GFR) • 20-25% of normal cardiac output (1000ml – 1300 ml/min) of blood perfuses the kidney promotes glomerular filtration • Primary filtration pressures -> glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (2-3X higher than other capillary beds in the body) • Feedback mechanisms (intrarenal and extrarenal) help to maintain blood flow and GFR is to of filtration Pressures importance e · arterial Vasular system ( > - = nepon nee Tubularsystemof · G that for system Vascular good pressure (to supply blood and supply blood for filtration) · · blood adequate good pump adequate ( filtration driven by hydrastatic pressure pressure a dra throug blood circulate blood wase fluie against pushes and if - alt r promote needs - volume to to have Kidneys - Bp'fluid room i Perfusion : filtration Southe 02 (ful) (good (a) pressure , good resistance cul ar St /enoughthe (siltrati promote 5 2024 audio Clip b Regulation of Renal Blood Flow -GFR a co • Neural/Humoral Controls Vasoconstrictor - – Sympathetic stimulation ↑ HR 4 BP – Angiotensin II, ADH, prostaglandins , > - · Stimulates release of aldosterme Kidney - - - • Renin angiotensin system RASS – Control of blood pressure in & Bp 4.pPirtulate e , - 3 • Autoregulation hold on to fluid ↑ circulating blood volume a · blood supply e vasodilation & Renal blood flow ↑ glomerular filtration rate - – Maintain blood flow to provide a constant GFR that allows for solute and water excretion – Renal systems responds to arterial pressure changes and like sodium chlorideFrom concentrations • Increased protein and glucose loads - – Increase GFR 80-180 systolic - Factors Effecting Glomerular Filtration Rate O • Glomerular filtration rate used to • • • • • • evaluate renal tissue function Decrease in B/P – decreases hydrostatic pressure that drives filtration – decrease GFR Increased protein and glucose - increase GFR trying to filter out 4 effecitivly Sympathetic nervous system – decrease GFR Hormones – angiotensin II – efferent ↳ arteriole vasoconstriction increases B/P increases GFR > Aging – loss of nephrons – decrease GFR Prostaglandins – increase GFR or other damage vasodilation ↑ Blood flow to glomeras 6 2024 Relationship of GFR to Functioning Nephrons ↓ GFR = ↓ functioning nephrons - Audio Clip 7 Indicators of Renal Function Normal serm- Elevation - - GFR down filtering as) profeffectively • Creatinine (0.6 –1.2 mg/dl –Adult) – Non-protein end product of skeletal muscle metabolism – Eliminated to the degree renal function will eliminate allow How body is able – Most specific indicator of renal function – estimates function capacity of the kidney = slowed - - much to (Normally I excretion = or than ( Urinary will be slightly amount produced in 7 2024 Renal Function/Creatinine ↑ Creatinine = ↓ Normal Renal function Indicators of Renal Function Blood urea Nitrogen level · • BUN (8-20 mg/dL – Adult) –⑤ Urea – byproduct of protein metabolism, accumulates as renal function declines – Eliminated entirely by the kidney – Can be elevated by causes other than renal disease (high protein diet, GI bleeding) - m C Notadequatrenal function it CAN by alone be other bc. elevated factors - ↓ renal function = 4 BUN (Not abletoend 8 2024 * 32-1 table Pg . Urinalysis na 857 • Urinalysis – gross and microscopic exam of urine to evaluate ph, specific gravity and presence of abnormal substances and formed elements • Gross exam – color, clarity, odor, sediment • Microscopic – RBC, WBC, epithelial cells, casts, crystals, bacteria, pH • Specific gravity – concentration of solutes, hydration status, functional ability of kidney (1.010-1.025) ↓ Renal function ↓ Concentrating ability specific Gravity • Urine protein - - ( - - - - : = Normal - > - - Color · negative for glucose n · yellow-amber · ·blood o · 4 5-8 . (around 16: 5-6) 45 ⑳ . . · -volu me to bilirubin bacteria · PH glomerulus Probl em/damage With Ei-cinalist Ketones - Clarity clear-slightly hazy Cass WB C-Commun idicator of UT I Crystal · 200-2500m)/day · · RBL The “Urias” Polyuria – increased volume of urine voided (diabetes diuretics) failure -acute/chronic Oliguria –↓urine output less than 400ml/day (dehydrate Anuria – urine output less than 50ml/day (completeObstruction Nocturia – excessive urination at night Hematuria – red blood cells in the urine (either microscopic/ gross) Proteinuria – abnormal amounts of protein in the urine • Dysuria – painful or difficult voiding • • • • • • , - , ~ - absence renal , Chronic Renal faliure) - - - - m - 9 2024 Other Terms • Frequency – frequent voiding, more than every three hours • Urgency – strong desire to void (emergency got • Hesitancy – delay, difficulty in initiating voiding • Enuresis – involuntary voiding during sleep - x - to go : got to go) , - - - - - Questions • What is the functional unit of the kidney called? nephron • What structure in the nephron filters blood? glomerulus • What percent of cardiac output do the kidneys (21000-1300 mL/min) receive under normal circumstances? 60) • What is a normal GFR? 125 mL/min (A (increase) • What forces drive glomerular filtration? Bp • What happens to urine output with &CO 4HR sympathetic nervous stimulation? Why? ↑ • What lab test is the most specific indicator of renal function? Creative 20-25 % of CO ~ (lecrease) & ↓ Stimulation , agirg Bp , SN) c , loss of nephrone is it <or > , 4 Protein 4 Glucose , RAAS , bC - , 10 2024 Questions (acid • • • • : In response to acidosis the kidneys will? Produce : Ha0 >↑ Circulating What is the action of aldosterone? Retain What action to natriuretic peptides have in the kidney? Promote Is it normal to find RBC and large amounts of protein in the urine? NO • What substance produced by the kidney will promote RBC production in the bone marrow? erythropoietin • What co-factor, synthesized by the kidney, is needed to promote the absorption of calcium in the GI tract? Vitamin D Conserve bicarb Na- Retain excrete buffer system) hydrogen acid BP - blood base volume Na excretion > - HpO excretion > - ↓ circulating blood volume and - ↑ urine output · (cangetun) or procee Kidneys 11