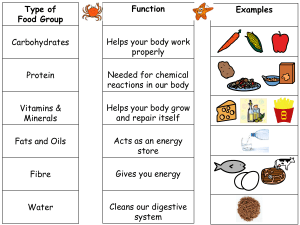
Small studies support that consumption of low GI meals can have up to a 20% lowering effect on post prandial glucose levels, with variables such as dietary fat and protein intake to also have some impact on post prandial blood glucose (just be aware that protein and fats could cause a delay in post-prandial hyperglycaemia). Dietary fibre (of any type) is associated with lower HbA1c levels, with the additional benefit of reduced risk of severe ketoacidosis (high levels of ketones in blood). Essentially aim for 30g per day minimum, it is suggested that higher intakes will be beneficial especially soluble fibre. Total Fat Intake - Studies recommend up to 40% of energy from fat (majority unsaturated fats). Salt - Less than 6g per day, less than 3g per day has been shown to be more beneficial.