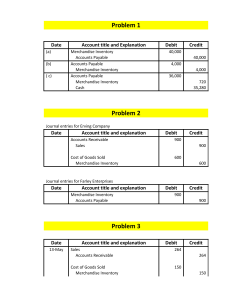
ACCOUNTING FOR MERCHANDISING ACTIVITIES Item 1 Merchandise inventory is classified on balance sheet as a a. Current liability b. Current asset c. Long – term asset d. Long – term liability Item 1 Merchandise inventory is classified on balance sheet as a a. Current liability b. Current asset c. Long – term asset d. Long – term liability Item 2 The inventory system employing accounting records that continuously disclose the amount of inventory is called • retail • periodic • physical • perpetual Item 2 The inventory system employing accounting records that continuously disclose the amount of inventory is called • retail • periodic • physical • perpetual Item 3 Assuming that net purchase was P 900,000 during the year and that ending merchandise inventory was P 20,000 less than the beginning merchandise inventory of P 250,000, how much was cost of goods sold? a. P 1,130,000 b. P 670,000 c. P 920,000 d. P 1,170,000 Item 3 Assuming that net purchase was P 900,000 during the year and that ending merchandise inventory was P 20,000 less than the beginning merchandise inventory of P 250,000, how much was cost of goods sold? a. P 1,130,000 SOLUTION: b. P 670,000 Beg. 250,000 c. P 920,000 Add:Purchases 900,000 d. P 1,170,000 Total goods for sale 1,150,000 Less: Inv, end 230,000 COGS 920,000 Item 4 The December 31, 2018 trial balance for Aileen Maglana Company included the following: purchases, P 40,000; purchases returns and allowances, P 2,000; transportation in, P 3,000; ending inventory was P 8,000. What was the cost of goods sold for 2018? a. P 39,000 b. P 33,000 c. P 38,000 d. None of the above Item 4 The December 31, 2018 trial balance for Aileen Maglana Company included the following: purchases, P 40,000; purchases returns and allowances, P 2,000; transportation in, P 3,000; ending inventory was P 8,000. What was the cost of goods sold for 2018? a. P 39,000 SOLUTION: b. P 33,000 =40,000-2,000+3,000-8,000 c. P 38,000 d. None of the above Item 5 On February 3, Smart Company sold merchandise in the amount of 4,300 to Truman Company, with credit terms of 3/10, n/30. The cost of the items sold is 2,970. Smart uses the perpetual inventory system and the gross method. Truman pays the invoice on February 8, and takes the appropriate discount. The journal entry that Smart makes on February 8 is: a. Cash 2,970 Accounts receivable 2,970 b. Cash 4,300 Accounts receivable 4,300 c. Cash 4,220 Sales discounts 89 Credit Accounts receivable 4,309 d. Cash 2,890 Accounts receivable 2,890 e. Cash 4,171 Sales discounts 129 Credit Accounts receivable 4,300 Item 5 On February 3, Smart Company sold merchandise in the amount of $4,300 to Truman Company, with credit terms of 3/10, n/30. The cost of the items sold is $2,970. Smart uses the perpetual inventory system and the gross method. Truman pays the invoice on February 8, and takes the appropriate discount. The journal entry that Smart makes on February 8 is: a. Cash 2,970 Accounts receivable 2,970 b. Cash 4,300 Accounts receivable 4,300 c. Cash 4,220 Sales discounts 89 Accounts receivable 4,309 d. Cash 2,890 Accounts receivable 2,890 e. Cash 4,171 Sales discounts 129 Accounts receivable 4,300 Item 6 On September 12, Vander Company sold merchandise in the amount of $7,400 to Jepson Company, with credit terms of 3/10, n/30. The cost of the items sold is $4,800. Jepson uses the periodic inventory system and the gross method of accounting for purchases. Jepson pays the invoice on September 18, and takes the appropriate discount. The journal entry that Jepson makes on September 18 is: a. Purchases 7,178 Cash 7,178 b. Accounts payable 7,400 Merchandise inventory 222 Cash 7,178 c. Accounts payable 7,400 Purchases discounts 222 Cash 7,178 d. Cash 7,178 Accounts receivable 7,178 e. Cash 7,178 Purchases discounts 222 Credit Accounts payable 7,400 Item 6 On September 12, Vander Company sold merchandise in the amount of $7,400 to Jepson Company, with credit terms of 3/10, n/30. The cost of the items sold is $4,800. Jepson uses the periodic inventory system and the gross method of accounting for purchases. Jepson pays the invoice on September 18, and takes the appropriate discount. The journal entry that Jepson makes on September 18 is: a. Purchases 7,178 Cash 7,178 b. Accounts payable 7,400 Merchandise inventory 222 Cash 7,178 c. Accounts payable 7,400 Purchases discounts 222 Cash 7,178 d. Cash 7,178 Accounts receivable 7,178 e. Cash 7,178 Purchases discounts 222 Credit Accounts payable 7,400 Item 7 A company purchased 3,700 of merchandise on July 5 with terms 2/10, n/30. On July 7, it returned 850 worth of merchandise. On July 12, it paid the full amount due. Assuming the company uses a perpetual inventory system, and records purchases using the gross method, the correct journal entry to record the payment on July 12 is: a. Debit Merchandise Inventory 2,850; credit Cash 2,850. b. Debit Cash 2,850; credit Accounts Payable 2,850. c. Debit Accounts Payable 2,850; credit Merchandise Inventory 57; credit Cash 2,793. d. Debit Accounts Payable 3,700; credit Cash 3,700. e. Debit Accounts Payable 2,850; credit Cash 2,850. Item 7 A company purchased 3,700 of merchandise on July 5 with terms 2/10, n/30. On July 7, it returned 850 worth of merchandise. On July 12, it paid the full amount due. Assuming the company uses a perpetual inventory system, and records purchases using the gross method, the correct journal entry to record the payment on July 12 is: a. Debit Merchandise Inventory 2,850; credit Cash 2,850. b. Debit Cash 2,850; credit Accounts Payable 2,850. c. Debit Accounts Payable 2,850; credit Merchandise Inventory 57; credit Cash 2,793. d. Debit Accounts Payable 3,700; credit Cash 3,700. e. Debit Accounts Payable 2,850; credit Cash 2,850. Item 8 If title to merchandise purchases passes to the buyer when the goods are shipped from the seller, the terms are a. n/30 b. FOB shipping point c. FOB destination d. consigned Item 8 If title to merchandise purchases passes to the buyer when the goods are shipped from the seller, the terms are a. n/30 b. FOB shipping point c. FOB destination d. consigned Item 9 Question Which of the following accounts should be closed to Income Summary at the end of the fiscal year? a. Merchandise Inventory b. Accumulated Depreciation c. Dividends d. Cost of Merchandise Sold Item 9 Question Which of the following accounts should be closed to Income Summary at the end of the fiscal year? a. Merchandise Inventory b. Accumulated Depreciation c. Dividends d. Cost of Merchandise Sold Item 10 Question In credit terms of 3/15, n/45, the "3" represents the a. number of days in the discount period b. full amount of the invoice c. number of days when the entire amount is due d. percent of the cash discount Item 10 Question In credit terms of 3/15, n/45, the "3" represents the a. number of days in the discount period b. full amount of the invoice c. number of days when the entire amount is due d. percent of the cash discount Item 11 For a merchandising firm, product cost includes all of the following items except: a. Freight – in cost b. Merchandising packaging c. Advertising expenses d. The cost of merchandise itself Item 11 For a merchandising firm, product cost includes all of the following items except: a. Freight – in cost b. Merchandising packaging c. Advertising expenses d. The cost of merchandise itself ACCOUNTING FOR MANUFACTURING ACTIVITIES Item 12 Work in process is a. Sales less cost of goods sold b. Sales plus cost of goods sold c. Value of finished goods on hand d. Value of partly finished goods Item 12 Work in process is a. Sales less cost of goods sold b. Sales plus cost of goods sold c. Value of finished goods on hand d. Value of partly finished goods Item 13 The items, raw materials inventory, work in process, and finished goods inventory are MOST likely seen together on a balance sheet of a a. Garage b. Shoe factory c. Supermarket d. Bus Company Item 13 The items, raw materials inventory, work in process, and finished goods inventory are MOST likely seen together on a balance sheet of a a. Garage b. Shoe factory c. Supermarket d. Bus Company Item 14 • • • • • Work in progress as at January 1 1 600 Work in progress as at December 31 700 Cost of materials used 3 000 Indirect expenses 3 200 Factory wages 5 000 What is the cost of goods produced? A. 8 000 B. 8 700 C. 11 100 D. 11 200 Item 14 • • • • • Work in progress as at January 1 1 600 Work in progress as at December 31 1 700 Cost of materials used 3 000 Indirect expenses 3 200 Factory wages 5 000 What is the cost of goods produced? A. 8 000 B. 8 700 C. 11 100 D. 11 200 Item 15 Which of the following may be used to calculate the cost of production? A. Prime cost + factory overheads - opening work in progress + closing work in progress. B. Prime cost - factory overheads - opening work in progress + closing work in progress. C. Prime cost + factory overheads - opening work in progress - closing work in progress. D. Prime cost + factory overheads + opening work in progress - closing work in progress. Item 15 Which of the following may be used to calculate the cost of production? A. Prime cost + factory overheads - opening work in progress + closing work in progress. B. Prime cost - factory overheads - opening work in progress + closing work in progress. C. Prime cost + factory overheads - opening work in progress - closing work in progress. D. Prime cost + factory overheads + opening work in progress - closing work in progress. Item 16 What is a prime cost? a. The total of direct materials cost, all of the direct labor and all direct expenses. b. The total cost of all the most important cost c. The of all direct materials cost and all of the direct labor cost d. The total of all direct cost and all of the manufacturing overhead Item 16 What is a prime cost? a. The total of direct materials cost, all of the direct labor and all direct expenses. b. The total cost of all the most important cost c. The of all direct materials cost and all of the direct labor cost d. The total of all direct cost and all of the manufacturing overhead Item 17 Which of the following are part of manufacturing overhead a. Direct Labor b. Indirect Labor c. Office Depreciation Item 17 Which of the following are part of manufacturing overhead a. Direct Labor b. Indirect Labor c. Office Depreciation Item 18 The depreciation on the machines used on the manufacturing line is considered to be ____________a manufacturing cost. a. A Direct b. An Indirect Item 18 The depreciation on the machines used on the manufacturing line is considered to be ____________a manufacturing cost. a. A Direct b. An Indirect Item 19 Commissions paid to sell products are reported as part of cost of goods sold a. TRUE b. FALSE Item 19 Commissions paid to sell products are reported as part of cost of goods sold a. TRUE b. FALSE Item 20 For the year ended 31 December 2018, the prime cost was $80 000, factory overheads totalled 120 000, work in progress 1 January 2018 was 20 000 and at 31 December 2018 was 30 000. What was the cost of production of finished goods? A. 190 000 B. 200 000 C. 210 000 D. 220 000 Item 20 For the year ended 31 December 2018, the prime cost was $80 000, factory overheads totalled 120 000, work in progress 1 January 2018 was 20 000 and at 31 December 2018 was 30 000. What was the cost of production of finished goods? A. 190 000 B. 200 000 C. 210 000 D. 220 000 Item 21 The following figures have been taken from the accounts of a manufacturing organization: • • • • • Cost of raw materials used 90 000 Direct wages 50 000 Indirect wages 30 000 Direct expenses 40 000 Indirect expenses 20 000 • • • • • Which of the following figures represents the manufacturers' prime cost? A. 230 000 B. 180 000 C. 140 000 D. 90 000 Item 21 The following figures have been taken from the accounts of a manufacturing organization: • • • • • Cost of raw materials used 90 000 Direct wages 50 000 Indirect wages 30 000 Direct expenses 40 000 Indirect expenses 20 000 • • • • • Which of the following figures represents the manufacturers' prime cost? A. 230 000 B. 180 000 C. 140 000 D. 90 000 Item 22 Which of the following is a direct cost a. Factory rent b. Production workers’ wages c. Factory supervisor’s salary d. Factory machine maintenance Item 22 Which of the following is a direct cost a. Factory rent b. Production workers’ wages c. Factory supervisor’s salary d. Factory machine maintenance Item 23 In a manufacturing company, the costs debited to the Work in Process Inventory account represent: a. Direct materials used, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. b. Cost of finished goods manufactured. c. Period costs and products costs. d. None of the above; the types of costs debited to this account will depend upon the type of products being manufactured. Item 23 In a manufacturing company, the costs debited to the Work in Process Inventory account represent: a. Direct materials used, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. b. Cost of finished goods manufactured. c. Period costs and products costs. d. None of the above; the types of costs debited to this account will depend upon the type of products being manufactured. Item 24 The accounting records of Newport Mfg. Co. include the following information for 2000: Dec. 31 Jan. 1 Inventory of work in process $20,000 $10,000 Inventory of finished goods 80,000 60,000 Direct material used 200,000 Direct labour 120,000 Manufacturing overhead (150% of direct labour) 180,000 Selling expenses 150,000 Indicate which of the following are correct: (More than one answer may be correct.) a. Amount debited to the Work in Progress Inventory account during 2000, $500,000 b. Cost of finished goods manufactured, $490,000 c. Costs of goods sold, $470,000 d. Total manufacturing costs for the year, $650,000 Item 24 The accounting records of Newport Mfg. Co. include the following information for 2000: Dec. 31 Jan. 1 Inventory of work in process $20,000 $10,000 Inventory of finished goods 80,000 60,000 Direct material used 200,000 Direct labour 120,000 Manufacturing overhead (150% of direct labour) 180,000 Selling expenses 150,000 Indicate which of the following are correct: (More than one answer may be correct.) a. Amount debited to the Work in Progress Inventory account during 2000, $500,000 b. Cost of finished goods manufactured, $490,000 c. Costs of goods sold, $470,000 d. Total manufacturing costs for the year, $650,000