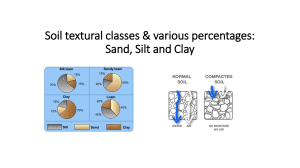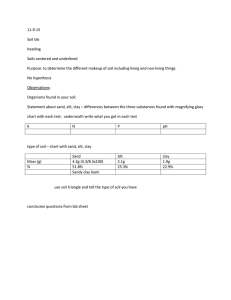
Subject: Grade 4 Science I. Procedures Teacher’s Activity 1. Daily Routine A. Prayer Class, before we start our discussionlet’s start our day with a prayer. Kindly bow your head and say this with me Student’s Activity Dear God, Thank you for our teachers, our school and our families. As we gather together this morning, we invite Your Holy Spirit to inspire us, guide us and teach us in everything that we have today. We give you our anxious thoughts and receive your peace. Thank you that You promise to be with us always. Amen. A. Greetings Good morning my dear students! How are you today? We’re good Ma’am That’s good. Have you enjoyed you weekend bonding with your family? Yes Ma’am! I’m glad to hear that! For this morning, our discussion for today is about soil and water. Are you ready class? Yes, Ma’am! B. Putting in Class <A reminder for everyone. Always mute your microphone. If you have any clarification, questions, or want to answer you can use the raise hand button or just say permission to speak to be acknowledged. Okay?= C. Attendance <Before we begin, I will be keeping track of 0 0 your attendance for today. When I call your name, unmute your mic and say present.= 2. Priming Activity A. Review of the Past Lessons Class did you still remember your past lesson? Yes Ma’am Can you tell the class about what you learned inprevious lessons?= (Student Answered) <Our previous lesson is about types ofsoil and the use of water.= Very good! It appears that you fully comprehend and recall our previous lesson. I hope everyone learned something about our past discussion.= Are you ready my dear students for new learnings? Yes, we are 3. Lesson Proper <Before we start our lesson, let’s have some mini games.= A. Activity Motivation <I'll show you some photographs and you'll have to guess what they are. If you want to answer, you can click the raise hand button or you can just type your answer in the comment section. Do I make myself clear class?= <Let’s get started! Who can answer number 1?= 1. (The student clicks the raise handbutton) C__Y <Very good . Who can guess the second picture?= 0 <Ma’am, that is a Clay.= 0 2. _OA_ (The student clicks the raise hand button) <You got it right 3?= . How about number <Ma’am, that’s a Loam.= 3. S_N_ <Good job . Next picture. Can someone answer number 4? (The student clicks the raise handbutton) <Ma’am, the answer is Sand.= 4. __T_R <That’s correct can guess it right? . Last picture. Who (The student clicks the raise handbutton) <Ma’am, that is water.= 5. W__E_ _YC_E (The student clicks the raise handbutton) Brilliant. Ok class, thank you for participating. That’s the end of our motivational activity and I hope you enjoy it. 0 <Ma’am, the picture shows the water cycle.= 0 B. Analysis If you notice our motivational activity, everything is related to our lesson for this day. The characteristics of various soil types and the different sources of water suitable for human consumption, as well as the importance of water cycle. We can now proceed to our discussion for today. Is my screen visible? Ok thank you. Now, can someone read the definition of what soil is? Yes Ma’am. (The student clicks the raise hand button) <Thank you. So, soil is the thin layer of material covering the earth's surface and is formed from the weathering of rocks. It is made up mainly of mineral particles, organic materials, air, water, and living organisms4 all of which interact slowly yet constantly. In addition, soil have different types and their characteristics. Can someone give me at least 3 examples of soil types?= Excellent. Soils vary enormously in characteristics, but the size of the particles that make up a soil defines its gardening characteristics. So, today, I am going to discuss 6 types of soil and their characteristics. The loose upper layer of the Earth's surface where plants grow is known as soil. Soil is made up of organic matter (dead plants and animals) as well as shattered rocks and minerals. (The student clicks the raise hand button) <Ma’am, loam, sand, and clay.= First is clay soil. Clay soil is a heavy soil type that benefits from high nutrients. Clay soils remain wet and cold in winter and dry out in summer. These soils are made of over 25 percent clay, and because of the spaces found between clay particles, clay soils hold 0 0 a high amount of water. Second is sandy soil. Sandy Soil is light, warm, and dry and tends to be acidic and low in nutrients. Sandysoils are often known as light soils due to their high proportion of sand and little clay (clay weighs more than sand). These soils have quick water drainage and are easy to work with. Third is silt soils. Silty soil is slippery when wet, not grainy, or rocky. The soil itself can be called silt if its silt content is greater than 80 percent. When deposits of silt are compressed and the grains are pressed together, rocks such as siltstone form. Silt is created when rock is eroded, or worn away, by water and ice. Do you have question class? Fourth is loam soil. Loam soils contain sand, silt and clay in such proportions that stickiness and non- adhesiveness are in balance - so the soils are moldable but not sticky. Loams are the "friendliest" soils to cultivate. Clays can absorb and hold onto large amounts of water because of their sheet structure and large surface area. <No Ma’am.= Fifth is the peat soil. Peat soils are mainly organic matter and are usually very fertile and hold much moisture. They are seldom found in gardens. And last is chalky or lime-rich soils. It is Chalky soil is comprised mostly of calcium carbonate from sediment that has built up over time. It is usually shallow, stony, and dries out quickly. This soil is alkaline with pH levels between 7.1 and 10. In areas with large deposits of chalk, well water will be hard water. Now, did you understand the different types of soil as well as their characteristics? 0 0 I’m glad to hear that all of you understand the lesson. Now, we are going to discuss the use of water in our daily living and the importance of water cycle. <Yes Ma’am= In your own opinion, how do we use (The student clicks the raise handbutton) water? Yes ___ ?= <Very well said Ma’am, water can be used drinking. .= for Water can be used for direct and indirect purposes. Direct purposes include bathing, drinking, and cooking, while examples of indirect purposes are the use of water in processing wood to make paper and in producing steel for automobiles. The bulk of the world’s water use is for agriculture, industry, and electricity.= Is there anyone in this class who knows where we can get water? Give me at (The student clicks the raise handbutton) least one.= <Very good Ma’am, in the river. .= <All of the water that we use comes from local lakes, rivers, streams, or underground aquifers, depending on your city and state. How we use water depends onthe purpose at hand.= Water can be used in various ways, such as in household water uses. Common household uses consume a lot of water. It may take between 30 and 40 gallons for one bath while the average toilet uses about 5 gallons of water per flush. Much of our residential freshwater resources are also used for watering lawns, flower beds, and vegetable gardens, as well as washing cars, etc. 0 0 Next is communities. Cities use water for firefighting, street cleaning, and watering public areas such as parks, grass, trees, shrubs, and flowers. Water is also used to fill public drinking fountains, including those at schools and libraries. All of the different businesses in your community also use large amounts of water. Another example is farming. The amount of water needed to run a farm is tremendous. When we think of water on a farm, we think of watering crops; but the amount of water needed on a dairy farm is just as large. Chickens, pigs, sheep, and all the other animals in a farmyard need drinking water to stay alive. Food must be grown for them to eat, and water is also required in the cooling systems used to keep the production of meat fresh. Most of the water used on farms is used for irrigation. Moreover, water is also essential in industry, as it is heated and the steam is used to run machinery. Water is used to cool hot metal such as in the production of steel. Water is also an important element in many products like chemicals, drugs, lotions, shampoos, cosmetics, cleaners, andbeverages. Water is used in processing food and in innumerable factories and industrial processes including the manufacturing of paper. Water used in processing foods and beverages must be absolutely clean, while other industries such as a manufacturing plant may use a lower quality of water. Water plays a significant role in our daily life. So, we should conserve water. Failing to conserve water caneventually lead to a lack of an adequate, healthywater supply, which can have drastic consequences in rising costs, reduced food supplies, health hazards, and political conflict. Did you understand my dear students? <Yes teacher.= Moving on to our next lesson. The 0 0 importance of water cycle. But before that, can someone explain what a water cycle is? Just a brief or simple explanation. (The student clicks the raise hand button) That’s correct. Thank you so much . <Ma’am, the water cycle is simple circular cycle of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.= The water cycle is an extremely important process because it enables the availability of water for all living organisms and regulates weather patterns on our planet. If water didn’t naturally recycle itself, we would run out of clean water, which is essential to life.= Water is necessary for sustaining life on Earth, and helps tie together the Earth's lands, oceans, and atmosphere into an integrated system. Precipitation, evaporation, freezing and melting, and condensation are all part of the hydrological cycle - a never-ending global process of water circulation from clouds to land, to the ocean, and back to the clouds. This cyclingof water is intimately linked with energy exchanges among the atmosphere, ocean, and land that determine the Earth's climate and cause much natural climate variability. The impacts of climate change and variability on the quality of human life occur primarily through changes in the water cycle.= <The major physical components of the global water cycle include the evaporation from the ocean and land surfaces, the transport of water vapor by the atmosphere, precipitation onto the ocean and land surfaces, the net atmospheric transport of water from land areas to ocean, and the return flow of fresh water from the land back into the ocean. The additional components of oceanic water transport are few, including the mixing of fresh water through the oceanic boundary layer, transport by ocean currents, and sea ice processes. On land, the 0 0 situation is considerably more complex and includes the deposition of rain and snow on land; water flow in runoff; infiltration of water into the soil and groundwater; storage of water in the soil, lakes, and streams, and groundwater; polar and glacial ice; and use of water in vegetation and human activities. Illustration of the water cycle showing the ocean, land, mountains, and rivers returning to the ocean. Processes labeled include precipitation, condensation, evaporation, evapotranspiration (from the tree into the atmosphere), radiative exchange, surface runoff, groundwater, stream flow, infiltration, percolation, and soil moisture.= <Alright! Do you have questions my dear <Nothing Ma’am.= students?= < That’s great. We just learned a lot about the various types of soil and its characteristics, the use of water, and the importance of water cycle in our lives. C. Abstraction I'm presuming you understood our lesson because no one else in our class has asked any questions. Now, I'll give you 10 mins to write a reflection on what you have learned in our discussion today. Write it on one whole sheet of pad paper. Your timer starts now. 4. Evaluation Directions: Type in the comment section <green= ifthe statement is TRUE and comment <red= if the statement is FALSE. Let’s begin. 0 0 1. Clay soil is light, warm, and dry and tends tobe acidic and low in nutrients. Why did you answer red? May I call That’s correct! Very good The student commented RED.) (The . student unmutes his/her mic.) <Ma’am, the correct answer in number 1 is sandy soil.= . 2. Peat soils are seldom found in gardens. (The student commented GREEN.) (The Good job class! student commented RED.) 3. Water is not important. Since everybody answered red, what is the importance of water? <Wow! You have a great answer That’s impressive.= . (The student clicks the raise handbutton) <Ma’am, water is the basic necessity for the functioning of all life forms that exist on earth. It is safe to say that water is the reason behind earth beingthe only planet to support life. Thisuniversal solvent is one of the major resources we have on this planet. It is impossible for life to function without water.= 5. Assignment I. Directions: Make a digital art showing the importance of water and the water cycle ineveryday life. II. Directions: Make a photo collage of differenttypes of soil and label it. 0 0