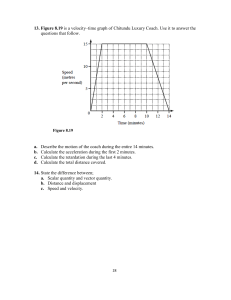
Princeton International School École Internationale Princeton Physics Revision Worksheet Name:................................................. Date:.................................................. Grade 12:........................................... PROBLEM SOLVING 1. A rock is thrown downward from the top of a cliff with an initial speed of 12 m/s. If the rock hits the ground after 2.0 s, what is the height of the cliff? (Disregard air resistance. a = g = 9.81 m/s2.) …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… 2. A horse trots past a fencepost located 12 m to the left of a gatepost. It then passes another fencepost located 24 m to the right of the gatepost 11 s later. What is the average velocity of the horse? 20. A rock is thrown downward from the top of a cliff with an initial speed of 12 m/s. …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… 1| Page Princeton International School École Internationale Princeton 3. A person pushing a wagon starts from rest, uniformaly accelerating at a rate of 0.500 m/s2. What is the velocity of the wagon after it has traveled 4.75 m? ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… 4. A car with an initial speed of 4.30 m/s accelerates uniformaly at the rate of 3.00 m/s2 . Find the final speed and the displacement after 5.00 s. ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………. 2| Page Princeton International School École Internationale Princeton 5. Mathew was traveling initially at +7.0 m/s accelerates uniformaly at the rate of +0.80 m/s2 for a distance of 245 m. a. What is its velocity at the end of the acceleration? b. What is its velocity after it accelerates for 125 m? ………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………... ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………. 6. A book falls from a lbrary shelf 25.0 m above the ground floor. a. How fast is the book moving when it strikes the ground? b. How much time does a person below have to move out of the way before the book hits the ground? ……………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………… …………… Complete the following sentences with the suitable terms: 3| Page Princeton International School École Internationale Princeton 1. A vector that represents the sum of two or more vectors …………………………… 2. Rate of change of displacement ………………………… 3. Rate of change of velocity ……………………………….. 4. Chang in position ………………………………………… 5. Free falling objects always have the same downward acceleration …………………………………….. 6. The position of an object at rest doesn’t change with respect to a fixed ………………………………….. 7. A system for specifying the precise location of objects in space and time ………………………………….. 8. The SI unit of displacement ………………………………. 9. The SI unit of velocity …………………………………… 10. The SI unit of acceleration ………………………………… 11. Physical quantities that have magnitude only ……………………… 12. Examples of Physical quantities that have magnitude only………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………… 13.Physical quantities that have magnitude and direction …………………………………. 14.Examples of physical quantities that have magnitude and direction …………………………………. 15. The slope of a line drawn tangent to a point on the curve of a position versus time graph describes what concept? ………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………… 16. When there is no air resistance, objects of different masses dropped from rest fall with equal ………………….. and different …………………………… 17. x = xf - xi is the equation of ……………………………………………….. 18. is the equation of………………………………………………… 19. is the equation of…………………………………………………. 20. The slope of a line drawn tangent to a point on the curve of a position versus time graph describes ………………………………………………… 21. Acceleration due to gravity ………………………………………………… 4| Page Princeton International School École Internationale Princeton 22. The name of the length of the straight line drawn from an object’s initial position to the object’s final position…………………………………………. Choose the correct answer 1. In free fall towards Earth, objects move …… a. slower then faster. b. slower and slower. c. at a constant velocity. d. faster and faster. 1. A cotton ball or a tennis ball which one of them will hit the ground first in free-fall in vacuum? a. the cotton ball b. the tennis ball c. They would hit the ground at the same time. d. They would be suspended in a vacuum. 3. What is the speed of an object at rest? a. 0.0 m/s b. 1.0 m/s c. 9.8 m/s d. 9.81 m/s 4. Which of the following situations represents a positive displacement? (Assume positive position is measured vertically upward along a y-axis.) a. A squirrel stands on a tree limb. b. A squirrel jumps from the ground onto a tree limb. c. A squirrel jumps from a lower tree limb to a higher one. d. A squirrel jumps from a tree limb to the ground. 7. A squash ball rolls from +7 m to +10 m. Which of the following statements is true? a. xf = +7m c. x = +3 m b. xi = +7 m d. vavg = 10m 8. If you know an object’s acceleration, the information you must have to determine if the car’s velocity is increasing is the a. direction of the objects initial velocity. b. direction of the object’s acceleration. c. initial speed of the object. d. final velocity of the object. 7. If you know the acceleration of an object and its initial velocity, you can predict which of the following? a. the direction of the object’s final velocity b. the magnitude of the object’s final velocity c. the displacement of the object 5| Page Princeton International School École Internationale Princeton d. all of the above 8. When an object’s velocity is positive and its acceleration is negative, what is happening to the object’s motion? a. The object slows down. b. The object speeds up. c. The object travels at constant speed. d. The object remains at rest. 9. At which of the labeled points is the velocity zero? a. C, E b. A c. B d. D, E 10. In the graph below, what is the displacement of the object the graph represents? a. Zero b. 10 m b. 20 m d. 20 m 11. The graph at right describes the motion of a toy car . At what point 6| Page Princeton International School École Internationale Princeton does the ball have an instantaneous velocity of zero? a. A b. B c. C d. D 12. The motion of an object described by the equation x = ½ Vf t. This statement implies which of the following quantities has a value of zero? a. xi c. vi b. xf d. tf 13. Two balls of different masses dropped from rest knowing that there isn’t air resistance a. fall with equal accelerations and with equal displacements. b. fall with different accelerations and with different displacements. c. fall with equal accelerations and with different displacements. d. fall with different accelerations and with equal displacements. 14. The position-time graph represents part of a car trip along a straight road. 7| Page Princeton International School École Internationale Princeton What is the average velocity of the car for the first 6.0 s? a. 15 m/s c. 20 m/s b. 10 m/s d. 12 m/s Use the following graph to solve the 15 to 17 15. During which interval is the object is at rest? a. 0.0 b. 30.0 to 50.0 s c. 50.0 to 70.0 s d. 15.0 20.0 s 16. The oject has the fastest speed during which interval? a. 0.0 5.0 s c. 50.0 to 70.0 s b. 0.0 to 30.0 s d. 15.0 20.0 s 17. During which interval does the object have the greatest positive velocity? a. 0.0 30.0 s c. 10.0 15.0 s b. 5o.o to 70.0 s d. 15.0 20.0 s 18. Which graph might represent the acceleration of a jet plane moving down a runway from a rest position? 8| Page Princeton International School École Internationale Princeton 19. At what point in an object which is thrown upward path does it experience zero velocity and nonzero acceleration at the same time? a. midway on the way up b. at the top of its path c. the instant it leaves the catcher’s hand d. the instant before it arrives in the catcher’s mitt 20 . John drives his car with an average velocity of 50.0 Km/h to the east. How long will it take him to drive 150 Km/h to the east? a. 3:00 h b. 2.75 h c. 4:00 h d. 4: __ 21. The graph shows the velocity of a car as the rider moves away from a roadway. 9| Page Princeton International School École Internationale Princeton Based on the slope of the graph, what is the average acceleration of the car? 22.. a. 6.00 m/s2 c. 1.33 m/s2 b. 3.00 m/s2 d. 0.750 m/s2 Which of the following statements applies to the motion of an object rising and then falling in free fall? I. The ball has constant acceleration as it moves upward. II. The ball has constant acceleration at the top of its path. III. The ball has constant acceleration as it moves downward. a. I only b. III only c. I and III d. I, II, and III 23. Multiplying or dividing vectors by scalars results in a. vectors. b. scalars. c. vectors if multiplied or scalars if divided. d. scalars if multiplied or vectors if divided. 24. How many displacement vectors shown in the figure above have horizontal components? a. 2 c. 4 b. 3 d. 5 10 | P a g e Princeton International School École Internationale Princeton SHORT ANSWER 1. The figure below represents the motion of a squirrel in woods for certain intervals of time. (Questions from a to d ) a. The slope in this graph represents which physical quantity? ………………………………… b. During which time interval the dog has the highest speed? ………………………………….. 11 | P a g e Princeton International School École Internationale Princeton c. During which interval(s) the dog was not moving? ………………………………………. d. What is the displacement of the dog? ……………………………………………………………………… 3. How an object that has moved can have a displacement of zero. ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… 4. Explain the direction of free-fall acceleration usually negative ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… 5. For the graphs shown below, determine which graph(s) represents an object that is slowing down …………………………………………………………………………………………………… 12 | P a g e