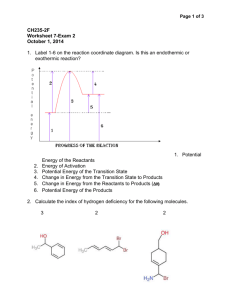
Organic Chemisty Ahmad Mahareeq 1 Review ⑳ Bonds ⑳ : Chemical · · - - · the within ionic ionic cation covalent overlapping · no . · or no . orbitals 8-bond = unpaired H I - C H - H = properties : Boiling point i in in 4 + 4x atom electronegativity = 2 Solubility .... Dipole-Dipole London force (P-P) it-bond of - · : valence H atomic difference to structure CHy : Physical -Melting point nonpolar covalent according Lewis : molecules between - theory by side = · anion - end of bond · coordinate covalent between to side polar , Bond : send · molecule covalent , : · Physical , H-bond Theory USEPR : molecular structure polarity > - M > M Symmetrical- domain Electron C H - 0 > - nonpolar triple bond , H ↑ - = > - o Fo London nonpolar polar Corces : double bond H M > = tetrahedral > - domain I = , 109 . 5: H Hybridization new energy Why ? 1 . . 2 and no of atomic orbitals to mixing : new shape . actual electron domain angle > - I > sp > 3 - sp2 > > Sp + one . . one hybridization Y 2 expected expected bond of actual . give & tetrahedral[109 5 " . trigonal Linear planar 120 ° 180 new orbitals with HCN 1 4 + + 5 = -r H CO2 10 M-10 = = : ! - - 2x6 + 20 : - 16 - - H-CEN 4 : I :C : = 16 4 = 2 1 + O = EO : linear + c Sp > - > - Sp : ff If H C OC O C 12 S O S/I Pz Bond order C-N 2-H : : sig 1 · P2 Py - O triple 3 single I O O : 0= C = . 0 > most stable : sp CO : : CEO : Py CO2 : I o= C - is because more it stable than CO has more resonance Resonance than more - lone lewis structure one i2 pair or , sp" sp or · stability increase atom Delocalization of electrons > - : Stable Lewis structure Formal Stability 1 2 zero . no negative charge . valence E's - around atom : more . charge positive charge high electronegativity low electronegativity on on O O atom . atom . O O O O G E C stable more - - (equal C O G in stability ( O & Resonance Bond order q hybride = = It Itz movement of by using electrons rich in i to poor :: ↑ , CH Ch t start from arrows : Fede : ,CH C , CH , Acid Base proton donor proton acceptor conjugate conjugate electron pk , base acceptor electron acidity equilibrium toward donor pk , the weakest acid acid and base basicity ↑ in e. Kinetici of Rate & [P K n is . is m = rate chemical 1 elementary. K [A] " = constant order of reactio n. CB . reaction equal to coefficient if reaction 2 3 : Alkanes ⑳ Hydrocarbons Saturated and Cycloalkanes of consist Unsaturated bond double : bond triple Aromatic · benzene contain : Alkane structural formula type Expanded Cormula - number : H H H & H- C i condensed formula : H : , C I H CHzCH If I C - - - ↑ CH , in molecule . connected with each other are I CHg atoms molecule. CzHf - of Lewis structure : H ↑ C and : how atoms : in H their derivatives. or their derivatives. or formula molecular · : benzene : Cutentz CHy alkyne doesn't contain : . alkene > - > cycloalkane and their derivatives. benzene Aliphatic hydrogen. and carbon bond s alkane and single : ⑳ H - H CHy Lewis : USEPR H in ↑ H - the away C - H plane of H I * H III H tetrahedral H viewer 1 C . 109 As H X out of plane toward 3D structural formula viewer : Ball and stick saw Cyttz horse formula H : HI, . C ⑭ H Line angle H C / ↑ Cormula : bond-line carbon = other atom angle than C and I appear H . 5 CHu Cotte Cate CaHsO Cuttio C · O of Shapes · · · oragnic compounds OH : open chain ring , cycle branched Alkane Alk = no of . carbons an en yn = = = single bond double bond triple bond · e = no functional group CHu methane : CH , CH , ethane : CHsCHCHs CHs(CH2l CHs , CH (CH2) , CHs , · propane : butane : : pentane CHs (CH2uCH : hexane CH , (CH2)5CHs CHs (CH2) , CH CHs (CH2) CHz CH, (CH2) & CH3 Cultio : relationship heptane : Octane : nonane : decane : Chain is : : constitutional branched isomers : isomer : molecules but 1 differ . differ in . differ same in isomer order of formula molecular formula . structural in constituent of constitutional 2 with the connectivity : . atoms in space connectivity : Stereoisomer which of the following are constitutional isomers ? O OH CH , O Cuttio CyHz CH , O CH ~ ,2 Cult same molecular Cormula ~ the same s Cat CsHiz ,2 molecular same butane : Cormula ? , - 20 o 36 > isobutan V V yes o 2 jo no o ↑ CHsCCHe CH , (CH3) , CH Cormula ? isomers d yes : no N * not constitutional constitutional isomers zo isomers · CHs(CH2) isopentane y , CH , CH CH , , CH(CHs) · , (CHs) hexane constitutional , X pentane not same structural : , neopentance C isohexane 1 20 o yo CHy (CHeSyCHg 2 y CCHelzCH(CHz) , CH CH CHCH , CH CHs , , , (CHCH2) CHCHs , zo (CH3) CHCH(CHz) CH , CHzCH C(CH )s , , order of carbon methyl : secondary tertiary * quaternary : : : order of * * primary carbons. carbon connect with carbon connect with three carbons . 3 carbon connect with one carbon . two carbons . : It connect with primary carbon - following from condensed to line formula ? CH , CH2C(CH3)2CH2CH(CH2CHs)2 CH3 CH2CH · , CHz CH CCH CH , CH2CH , CHzCH(CH(CH3)2) (CH2)>CH CCH , . . : CH , 2 4 carbons . four : CHs . . connect with with secondary carbon secondary It connect tertiary It connect with tertiary carbon e CH3 to carbon order. : Convert the CHs no carbon hydrogen according * connect with Carbon : primary * : CH2CH2CHs z Nomenclature of alkane IUPAC · Common · systemic # order alphabetically substituent-A-parent-suffix (functional group position of substituent - # before . parent Alkyl group CH3CH - , , - CH CH ,CH , propyl isopropyl (CH3) , CH- , alkane ethy) - , CH , CH CH (CH = : methyl CHz- CH , position of functional group > - of substituent name 1 name name name : #- : CH2-butyl , ICHCH-isobutyl CHaCHCHs d (CH3)s C- Sec-butyl tert-butyl It (R) 3 . 2 Cycloalkyl ex : cyclopropyl alkene . 3 : : methylene vinyl Phenyl benzyl halo flouro 8 . 9 lo : : OXO . = - z X- amino . CH2 CHCH2- GHsCH : hydroxy . CH- Colts- : 6. nitro 7 = : : bromo = , CH2 : benzene . 5 CH : · allyl . 4 cyclobutyl , mercapto BrF - : NO , : OH : NH2- - O : - - = SH- , ... Naming Rules : prefix 1 Parent . parent : suffix the longest attached carbons atom continuously with each other2 . numbering the carbons of parent. Starts from the give the carbon that connect with substituent nearest substituent the smallest number. 5 G 4 7 f X I 3 I 5 > substituent 4 6 2 3 I 2 7 I f U 3 6 55 4 7 G 2 3 4-methyl octane E I X (methyl) 2-methyl 2-methyl . 3 if there .1 3 are 2-methyl pentane propane 3-methyl pentane butane more than one identical substituents . > - the add · prefix di : tri , 2 2 2 . the same : carbon multiplication separated by number with same in substituent tetra , before substituent -dimethyl comma name . propane 31 .2 3 identical . > - number · add substituent : di , different carbons. separated by of carbons prefix on tri , tetra comma before substituent I 3 42 2 , 3-dimethy butane name . different substituents .3 3 . start > - from the numbering according name to nearest alphabetical one , then order g 54 3 I 6 2 2 & Y 5 3 I 6 : 3-ethyl-4-methyl 4 hexane 5-ethyl-2-methyl heptane 7 2 3 7 3-ethyl-2 6-dimethyl heptane I , O 7 ... ↓ 54 2 ,5 . 5-trimethyl heptane I I 3 7 5 3 3 6 Y 5 . 5-trimethyl heptane 6 &" & , , 3 . 4-diethyl-2-methyl hexane 3-ethyl-4-isopropyl hexane writing the 7 9 56 4-isopropyl-4-propyl & I 3 2 · O C Cyclic Compounds carbon atoms · · · nonane saturated connected with each other to form unsaturated aromatic ring. , , carbons homocycle heterocycle - Cycloalkane : : carbons homocycle and other saturated atoms 0, N , P ... ring Enten CH2 600 CHz CH CH2 CH2 , cyclopropane cyclobutane Che CH2 T /smallest ring) cyclopentane cyclohexane substituent parent cycloalkyl : . cycloalkane : numbering start from the nearest substituent. methyl cyclopropane I 2 3 1-ethyl-1-methyl cyclopropane I 32 2 I Y 3 5 3-cyclopropyl pentane ↑ 2 3 I 2 1-ethyl-3-isopropyl cyclohexane 2-ethyl-1 4-dimethyl cyclohexane , U isobutyl cyclopentane 1-tert-butyl-3 5-diethyl cyclohexane . 4 conformation of alkane and conformation due cycloalkane arrangement of atom is : of (C-C) to rotation bond & : molecule in in . start from two carbons. types result to rotation of result from H H H of conformer ki C ↓ C carbon " 11434 ↳ 600 H H : # kill H H carbon H rotate C I H H eclipsed front carbon bond stable staggered projectionformula back carbon staggered. H C more Newman and eclipsed : = = : Circle dot - torsional o (eclipsed) strain HH - H H H H Eclipsed . space ↑ H o # O- / H staggered more Conformation of ethane stable : CH, CHz H HH I I 60s d - " 3 H ↑ O- / H "O / # 60 HH ° & - - H H H H ↑ 2 H H H H H # 3 60 60 - H H H 2 HH H H H ↑ O- / H # 60 - N HH HH HH "Eclipsed · it · H Hp H m PE . - - - n staggered - · ·· H If H 6 120 300 240 188 ethane ° ° s CHCCH2CI Y H a # Y H Cl & Q - H Cl T I > - gauch staggered anti staggered CIH CICI as stability I : I - H H H H HH Cl # IV eclipsed The most The eclipsed stable highest conformer energy : #I in 1 . 2-dichloroethane is : I IN II Which of the Y following the is H CH CHE Q , most stable CHz - H CH3 HH CH ,CH , CHs H CHs CHz - HA CH /CH , , Name H H CHE H steric strain result the following : from CH2CH3 " CH Q / , CH3 3 . 4-dimethyl hexane bulkiness of CH2CHz group conformer ? 2 . following of the which 3-dimethyl butane ? H CHE the most stable conformer of is ↑ CH , -O CHs & H CH c I , - CH H CHE in - cit cha CH , , , cycloalkanes H T 2-dimethyl : cyclopropane cyclobutane cyclopentane cyclohexane , 60° 1 - angle , , 109 5 . strain H . H 2 H --- i C H "4H C I Eclipsed arrangement torsional strain Ring H & / 2, Conformation c strain butane 90° 109 50 . ) 2) angle strain Ring forsional strain strain > 108" - 109 50 envelope . cyclohexane : The most stable - 1) 2 Stable cycloalkane Chair 109 5 . staggered arrangement axial up equatorial Flip down H H - Boat & 1 . 4-diaxial interaction (Hagpole interaction) Steric strain Monosubstituted cyclohexane 5 : methylcyclohexane H Hill 1111111111 . H - C - H H H CH3 more Steric * interaction between C , and C diaxial interaction , The most stable conformer is when the substituent CH , more stable on the Cels stable bulkiness felts more than Cis > decrease stability equatorial bond . Disubstituted geometrical connectivity cycloalkane isomer Two substituents Cis trans they up up : , different cis-1 · , of atoms in in , or in in , out physical properties : B . pt . M . pt 2-dimethylcyclopropane trans-1 , isomers 2-dimethylcyclopropane = · . space out out or , geometric => and the different carbons . , or Cormula molecular same arrangement down down or , are in two on up down : the : differ but : trans-1 , 3-dimethylcyclobutane constitutional cis-1 , ht h b 2-dimethyl cyclobutane trans-1-ethyl-2-methylcyclopentane e isomers same " 1 Disubstituted 1 the on . , cyclohexane same if there carbon are equatorial -dimethylcyclopentance where two substituents groups , the largest . .1 2 different carbons . on position trans (I) according to one equatorial. should be on I more on one C Cl . is . I 2 on : different bond the most stable conformer : 1 2 . : : trans Cis (I) (I) stability stable : I < IV - IT Cis (IV) I - if similar > if not groups similar , the bigger group on equatorial 22 . . position 1, 3 : Cis (I) Cis trans trans (I) (II) (IV) most stable .3 2 . Position 1, 4 trans (I) : trans Cis cis (IV) (H) (I) most stable Which of the following is the most stable Lis-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclohexane ? more stable than the last one / trans , most stable I-4 trans X Cis ? Cis Physical alkanes nonpolar are force (the weight Boiling point low is in the than and , insoluble . 3 increase Melting increase packness H no chain Solubility 2 . are : > - form London . gases as no of carbons . , density is . low of . > - carbon increase branched alkanes and soluble water in point weight molecular as in nonpolar increase but M = 0 > London H HI , , , force 2 H H according to B pt . : I I T > - Y2 . solvent irregular effect. h I . : Hill Order B : 1 he lower . H/ 1 1 [ H dispersion : same open molecules weakest bond) low molecular I. of alkanes properties 62 62 #I , due to pt Chemical they properties are . 2 + 202 : > - CO , + 2 H 20 Free radical substitution R-H Cl = : saturated unreactive 1. combustion CHy of alkanes R-C + + energy reaction : H UV Cl ↓ CI . .. C1- radical ↓ Cancer Quiz > Homolysis 4: ⑳ Alkenes Alkene and Alkyne unsaturated molecule that consist of are : double bonds if alkene consist * * cycloalkene with The smallest is alkene bond, double one Cntan or more general CnHanz. two carbons s ethene is the - double bond one one . of molecular formula * ⑳ . H H c C = IπT H H 58 sp2 · trigonal planar bond C P-C , P , bonds Yc 1 - C - Hsp2- S sp-sp C 120 Alkynes : are unsaturated molecular formula of * General * The smallest H - C = C - H is 180 alkyne with one triple bond ethyne (acetylene) 2π 36 sp linear alkyne , triple bond molecule with bonds bonds - - 1 sp-sp 2 sp-S 2 is bonds . Cnten- 6 Naming: 1 2 Select the . start . from the numbering unsaturated bond unsaturated . 3 chain that contain longest when bond write the suffix > - = : => Y > take two s name position . yne - pentene or I 5 3 ( 5-methyl-1-hexene I . 5 pent-1-ene 2 U 4433 3 2 2-ethyl-3-methyl-1-pentene . of unsaturated bond ene 1 3 nearest to sequence number I 5 6 is . . the smallest bond using end that unsaturated bond by methylene = vinyl allyl - - CH2 CH = CH2 CH2CH CH2 = CH2 methylenecyclohexane allylcyclopentane 3 2 3-methylcyclohexene I ↑ Y 2 3 1-isopropyl-4-methylcyclohexen 4-methylene cyclohexene CH2 180 3 2 I-propyne I I Y 3-methyl-1-butyne 2 3 I 2 3 45 6-dimethyl-3-heptyne 6 7 Geometrical cis/trans CH2 CH2 = ethene isomers in alkene : EIZ CH , CH = propene CH2 CHsCH2CHICH CH3CH CHCHz = , I-butene constitutional 2 - butene isomers CHyCH H = CHCH , CH, H C = C C CH, CHE B pf . I Geometrical = C H isomers CHE B pt IC 4 co . trans-2-butene cis-2-butene London force ↓. molecular 2 . surface : weight area more surface bigger which of the 1. CHs CH = ((CH3)2 . CH , CH2CH 2 . 3 . 4 . 5 following = CHCHs (CH3)C C(CHz) = , (CH3)CHCH CHCH2CH , = Coltio molecules exhibit Cis C Cla stable cis/trans area isomer ? = H H , Rules for 1 . Double cis trans : bond . Each carbon of 2 double bond attach with two different groups => on the => on the same side cis opposite side trans Name the following : (CH3)CHCH-CHCH2CH , 2-methyl-3-hexene trans-2-pentene 6 -" 7 9 2 Do 7 2 3 · cycloalkenes From 3-7 · 2 trans I Y , 4 trans-2 . 4- heptadiene 2 3 exhibit only is I cis/trans 3 trans 7 cis-1 3 7-nonatriene , . , isomerism ? isomer cis/trans 1 , 2-dimethylcyclopropene 1 , 2-dimethylcyclohexene transcyclooctene ciscyclooctene El2 1 . system groups : that attached classified into higher priority direction of (1) 2 . . (1) at the C 2 = C C 1 H - 2 - - , H , 2) if there . 3 - C to atomic number CH (H , = CH2 C C) . atomic number C - atom C are - the -CHBr CHCI (H E 2 higher if the first . = 2 : atoms with . = (2) E PriorityI according Rules = I 2 Z side bond I 2 I priority lower different sides at I and (1) same : carbon that make double each with CH are , 0 - H , Br) CH, then same - is higher priority. = go CH to analyze CH , OH (H , H Of , - CECH (c , C, C) C CH2C , - C the other atoms. (H H Cl) multiple bond, repetition - - , , of atoms. E-3-methyl-2-pentene 'CH i > H , = CH H H) , , , c zH , HzCH , (C . H H) , ! CH H 21) H , , H HO E HO (H , HEN Cl # C) , I 2 HEN , CH , , H <K Cl E H HO H HO , (H , 0 0) , 2 Type number (, (C . C . H) (C , H H) , O (C HO O HO then (0 . 0 01 , Q O ② , C , E H) O (H , H H) , 7 Cl ~ -z Physical properties and alkene * * of alkene alkyne are force > dispersion insoluble in E and alkyne nonpolar molecule boiling point is : so water . . pt of of terminal that is alkyne B.pt of alkane Because Hydrogen London low . B Acidity form they molar mass is alkene bigger : attached with sp carbon acidic . is pka HO-H HCEC H2C = . - CH HzC- CH2 Acid 15 7 25 increase H 44 acidity H 5/ H - - : sp-more > - more acid . Sp > sp" > sp3 s % > - stable more anion electronegativity > - stronger HCEC-H +: H amide s pKa . acid s HC = Ci , alkynide anion base . W . C . z NH + anion base w . c. acid 25 = 38 Forward RCECH + sRCEC: Na NaNH2 very strong and CHICH + NaOH NH , + base Nucleophile CHEC Na : + H2O . 15 7 25 w . acid w . base s 2 . . base s c . . acid Backward 1-alkyne Quiz 1-alkyne alkene or +: + NH Of allane X +: NHS or OH X 5 : Reactions ⑳ free radical substitution reaction RH (2 Cli C Cl R : . of Alkene and R C s - . + Cl RH > R + Cl - RC + . : H initiation . + . + Alkyne HE propagation termination: Cl . R . R. + + + Organic 1 . Cl R CI - . - . reaction . 2 Elimination . 3 Addition Reduction : RR RCI types : substitution Oxidation Cl2 > . : : replacement removal unsaturated bond . convert to saturated bond ⑳ & , = I C s - unsaturated break C-CI - saturated I 28 sp3 sp2 Trigonal tetrahedral planar Addition reaction Addition : = & & C = C - / = C -= \ = E - - CHBr HI HCl) , + + HA H20 . = THF -2) NaOH H2O . c - GG Hydrohalogenation - C-d- o Hydrogenation - I CCls 2 1) BH, ↑ C-C I HX + , C ↑ Niorp He + I , reduction e Halogenation Acid Hydroboration catalyzed Hydration oxidation ↑ c-c / 1 1) BH . THF - - & C-C-OR 2) RONa H2O2 - I . Reaction properties 1 than other isomer 1. Addition of HX : HBr , oxidation that prefer one constitutional . reaction that : halide hydrogen HCI reaction : Stereoselective reaction . 2 Hydroboration : reaction regioselective . & prefer one stereoisomer than other . Hydrohalogenation : HI or regioselective - = c + HX / Ex : CHICH CH2 = 1- - CHsCHCHs propene connect with + CHgCH2CHL : addition of H20 (acid hydrogen - HC + Markovinkoves Rule In -C Hy s catalyzed) carbon that or has HX to greater , unsaturated bond no . of hydrogen . What is the product of following the HBr + : Br t & Br 2-bromopentane not 3-bromopentane regioselective I HI + Hol - regioselective & not & regioselective CI 2 Mechanism * Chlorobutane : elementary steps that describe bond breaking and forming in * movement of * of the movement arrow starts neutral anions : : represent by from molecule rich Cl , , the reaction H2O I' , , in HaS OH , , electrons RNH2 NH2 , , arrow , C C , = , , describe : Lewis Base ROH occur by representing electrons. electrons NHz reaction the how are RCEC' , ... ... (Nucleophile) : end to molecule * neutral cation BH : E Nu * Steps , in HC Fe Lewis acid , AlCIs , HsO", , E Nu two I's * Hydrogen , Carbocation : electrons in poor , SOs . . . . ... Free radical = (Electrophile) mechanism one reactants : mechanism diagram , activated complex intermediate , , product explained by diagram called potential energy represent the progress of chemical reaction can that be vs . potential energy. CHICH CH2 = Mechanism > CHzCH = + HCI CH, CHCHs d electrophilic : CH2 + H - C addition rxn CHzCH"CH : 2) C + : / CH : + 8: - . CHe H E Nu EAST m CH3 - +:: , Hs i H + . C + CHe OW R CHse , AC Cl E Nu activated complex . H intermediate carbocation H A C, . - CH, III C Ho CH, P Cl Potential A C . A C , . . Energy : ACC E R P exothermic D R endothern c M A C, . A PE . . "SH I P (Progress ratio between concentration concentration * the * * can of of reactant product disappear x + Y determined be the slowest step = appear time per to time . order of the reaction from the lowest step in mechanism . the rate of the slowest in is : K[R] "[Rc]" rate of reaction peak steps of Reaction) reaction = highest two - chemical rate Law the = O Rate of or peak C = Reaction Coordinate two electrophilic slowest rate of step so step = addition reaction , rate of overall reaction . carbocation formation is the : chemical reaction = K[alkene][HCI] order of rxn = 2 8 Stability of carbocation : RS H ! ↑ C C H'H carbocation R is group > - > called is donating 8 via more stable than form faster and stable more : t t yo O more stable t t * 2 R Co bond to O zo more stable charge . more S -x R ... positive carbon (delocalization) localized + o inductive effect * 2 S 20 distribution of positive ~ S + 2 , H 1 electron s Which + H H methyl * R + charge Cl Ex + : HCI & + Cl Mechanism major - n : H - HCI H-shifts 7 V t + zo carbocation : rearrangement Cl : - * * Cl Cl carbocation rearrangement convert carbocation 1. . 2 Hydride shift : : from 20 to H-shift methanide shift : ° 3 by : . CH- -shift . Note : Check : if carbon near sp" has one or two substituents. Br + HBr & + Br major - & ⑦ & t 2 : 3 G Br HBr + & Br + t Br major CH2 HC + 2 . produce * obey need so , catalyst use convert one with bond Hydration and forming H . . is poor concentrated acid to it : and other with OH because water H2O water by breaking Markovinkoves rule we > - alcohol bonds 2 Cl addition of catalyzed Acid * I HzO" . regioselective . electrophile H2SOn , HPOy or mix of them) OH + H2SOn H2O 2 : propano OH + H HeSOn O s + , major Mechanism electrophilic addition : 1) OH reaction . - H- + · - H it OH - * 2) + SLOW + H : H2O , OH H - ↳ - H 3) + * Corward * backward hydration and dehydration AGA, M + He catalyst produce and Hot alcohol s produce alkene increase , [Acid] decrease [Acid] , heat Halogenation . 3 anti is * Addition of Bre : addition (add Xc electrophilic addition * bridged reaction with bromonium X ↳ C- Ex + & Xc : Laboratory Mechanism - - 1) : C = C - - Br CCl , Bra 2 3 , dibromobutane double bond . identify test used to - Br(colorless) (orange) electrophilic intermediate C-C- ↓ + 2-butene * - ion stereoselective 11 c / Cl sides ( opposite on or addition . : Br-Br - - CI BO Bri d I - - - , & C-c- bridge ④ BrT 2) - , I ion Br Bri ~_ - - C-C- Br +: I I B bromonium intermediate CH2Cks Bry + Be Br Br BrBr Br stereoselective · Cla IIII/CI 7 CClu CC * Cl Methylcyclohexene . 4 Hydroboration * produce Without * * - oxidation alcohol rearrangement AntiMarkovinkoves It no . reaction: role : (It connect with sp2 carbon that has lowest ) * Syn addition * occur in CH and two steps OH : 1. are added from the Hydroboration : same side) electrophilic addition , add H, Br without carbocation. . 2 Oxidation : (replacement between OH and boron) 1) 1- BHz . OH THF 1 - propand 7 2) OH H2O propene , , Bets + s THE Mechanism H 1) CHC - , (tetrhydrofurane) B B - : CH2 · H a CHCHCH, Hydroboration CCHyCH2CHugB ECHsCH 2) BH : - = 2 oxidation : NaOH (CH3CH2CH2'zB Replace OH , H2O -OH , = CH > = CH CH CH2 zBH [CH , , , 3 CH H2O2 with CH CH B CH ,CHOH , + NaBOs , 1) BHz . THF H & "III I CH, = 2) NaOH H2O2 . => OH => OH trans-2-methylcyclohexane OH OH H2O + & H , SO4 OH OH 1) BHz . THF & 2) NaOH H2O2 . 1) BHz . THF & CHO: H2O2 2) OCHz - ether RONa sochium - C C - = / ~ 1) 2) alkoxide BHz THF . . RO H2O2 & - - - OR