solutions-manual-mechanics-of-materials-9th-edition-russell-c-hibbeler
advertisement
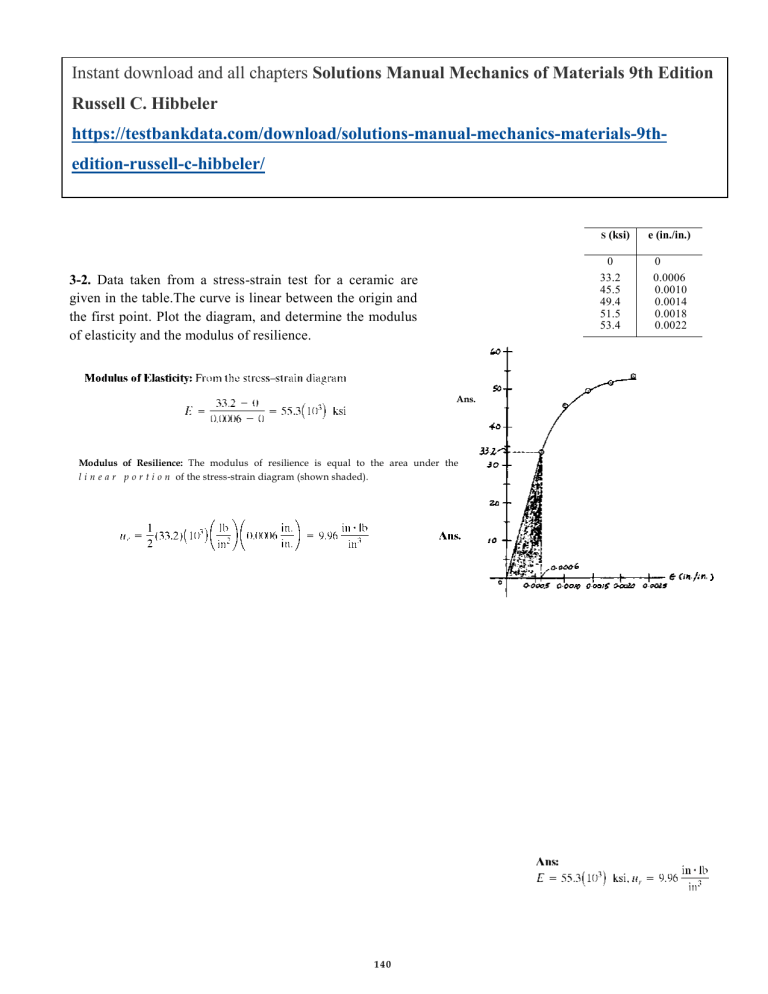
Instant download and all chapters Solutions Manual Mechanics of Materials 9th Edition Russell C. Hibbeler https://testbankdata.com/download/solutions-manual-mechanics-materials-9thedition-russell-c-hibbeler/ S 0 33.2 45.5 49.4 51.5 53.4 3-2. Data taken from a stress-strain test for a ceramic are given in the table.The curve is linear between the origin and the first point. Plot the diagram, and determine the modulus of elasticity and the modulus of resilience. Ans. Modulus of Resilience: The modulus of resilience is equal to the area under the l i n e a r p o r t i o n of the stress-strain diagram (shown shaded). 140 (ksi) e (in./in.) 0 0.0006 0.0010 0.0014 0.0018 0.0022 3-3. Data taken from a stress-strain test for a ceramic are given in the table.The curve is linear between the origin and the first point. Plot the diagram, and determine approximately the modulus of toughness. The rupture stress is sr = 53.4 ksi. S Modulus of Toughness: The modulus of toughness is equal to the area under the stress-strain diagram (shown shaded). 141 (ksi) 0 33.2 45.5 49.4 51.5 53.4 e (in./in.) 0 0.0006 0.0010 0.0014 0.0018 0.0022 Load (kip) 0 2.50 142 Elongation (in.) 0 0.0009 6.50 0.0025 8.50 0.0040 9.20 0.0065 9.80 0.0098 12.0 0.0400 14.0 0.1200 14.5 0.2500 14.0 0.3500 13.2 0.4700 3-5. A tension test was performed on a steel specimen having an original diameter of 0.503 in. and gauge length of 2.0 in. Using the data listed in the table, plot the stress-strain diagram and determine approximately the modulus of toughness. 143 Load (kip) Elongation (in.) 0 2.50 6.50 8.50 9.20 9.80 12.0 14.0 14.5 14.0 13.2 0 0.0009 0.0025 0.0040 0.0065 0.0098 0.0400 0.1200 0.2500 0.3500 0.4700 3-6. A specimen is originally 1 ft long, has a diameter of 0.5 in., and is subjected to a force of 500 lb. When the force is increased from 500 lb to 1800 lb, the specimen elongates 0.009 in. Determine the modulus of elasticity for the material if it remains linear elastic. Ans: E= 144 8.83 (10 3) ksi Ans: A = 0.209 in2, P = 1.62 kip 145 * 3-8. The strut is supported by a pin at C and an A-36 steel guy wire AB. If the wire has a diameter of 0.2 in., determine how much it stretches when the distributed load acts on the strut. B 146 3-9. The s—e diagram for elastic fibers that make up human skin and muscle is shown. Determine the modulus of elasticity of the fibers and estimate their modulus of toughness and modulus of resilience. Ans: E = 5.5 psi, u t = 19.25 psi, u r = 11 psi 147 s (ksi) 3-10. The stress-strain diagram for a metal alloy having an original diameter of 0.5 in. and a gauge length of 2 in. is given in the figure. Determine approximately the modulus of elasticity for the material, the load on the specimen that causes yielding, and the ultimate load the specimen will support. -e 0 0.001 0.002 0.003 0.004 0.005 0.006 0.007 Ans: E — 30.0(103) ksi, PY — 11.8 kip, Pult — 19.6 kip 148 (in./in.)