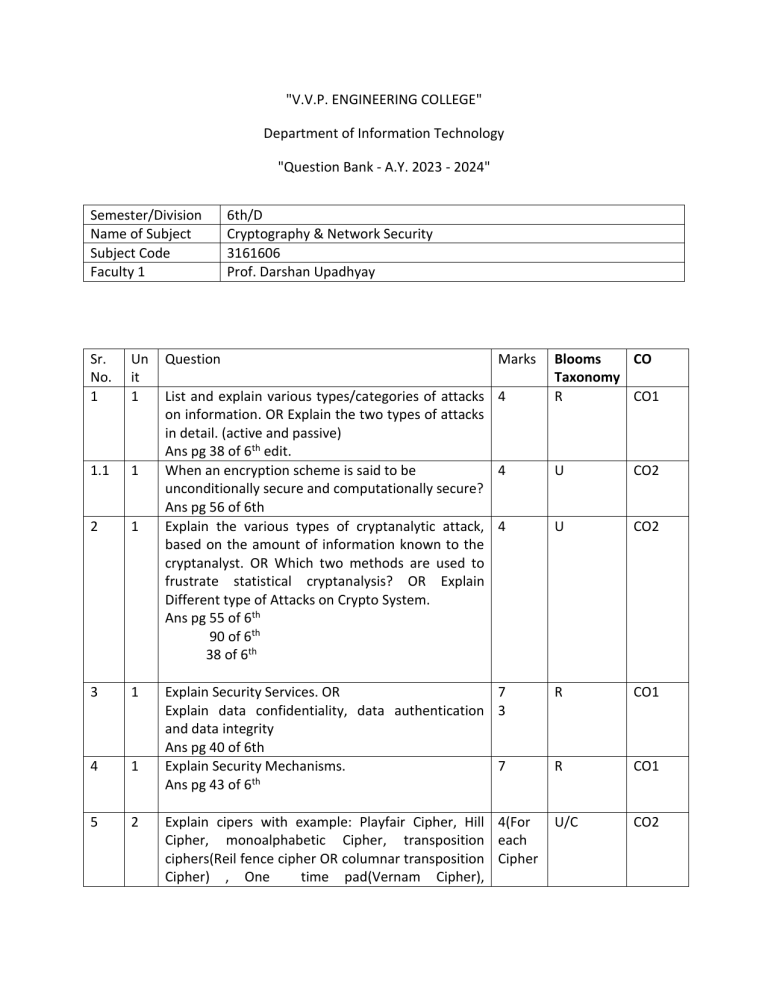
"V.V.P. ENGINEERING COLLEGE" Department of Information Technology "Question Bank - A.Y. 2023 - 2024" Semester/Division Name of Subject Subject Code Faculty 1 Sr. No. 1 Un it 1 1.1 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 2 Question 6th/D Cryptography & Network Security 3161606 Prof. Darshan Upadhyay Marks List and explain various types/categories of attacks 4 on information. OR Explain the two types of attacks in detail. (active and passive) Ans pg 38 of 6th edit. When an encryption scheme is said to be 4 unconditionally secure and computationally secure? Ans pg 56 of 6th Explain the various types of cryptanalytic attack, 4 based on the amount of information known to the cryptanalyst. OR Which two methods are used to frustrate statistical cryptanalysis? OR Explain Different type of Attacks on Crypto System. Ans pg 55 of 6th 90 of 6th 38 of 6th Blooms CO Taxonomy R CO1 U CO2 U CO2 Explain Security Services. OR 7 Explain data confidentiality, data authentication 3 and data integrity Ans pg 40 of 6th Explain Security Mechanisms. 7 th Ans pg 43 of 6 R CO1 R CO1 Explain cipers with example: Playfair Cipher, Hill 4(For Cipher, monoalphabetic Cipher, transposition each ciphers(Reil fence cipher OR columnar transposition Cipher Cipher) , One time pad(Vernam Cipher), U/C CO2 Polyalphabetic cipher(Vigenere Cipher) Ans pg 62 64 6 2 7 2 8 2 9 2 10 What is Avalanche Effect? What is diffusion and confusion? Differentiate confusion and diffusion. Pg 98 Draw and explain Feistel’s structure for encryption and decryption. The exact realization of Feistel network depends on the choice of which parameters? Pg 91 Explain Sbox in DES. what is the role of sbox in DES. OR Explain how DES(Data Encryption standard) algorithm observes Fiestel structure. Explain key generation and use of S-box in DES algorithm. Pg 95 Explain single round function of DES with suitable diagram. Pg 82 5th ed Pg 120 4th 4 U CO2 7 U CO2 4 U CO2 7 R CO2 2 Explain the triple DES scheme with two keys and 7 write about proposed attacks on 3DES. Ans pg 200 6th Pg 198 6th U CO2 11 2 Explain Double DES. Explain meet in-the middle 4/7 attack in DES. Pg 198 6th U CO2 12 2 R CO2 13 3 Explain AES or Explain the four function of AES 7 th Pg 179 5 Why mode of operation is defined? List various 7 modes of operations of block cipher. Explain them briefly. Pg 204 6th 4 OR Explain working of ECB.Why ECB (Electronic code book) is rarely used to encrypt message? 4 th Pg 205 6 E CO2 OR Why CFB(Cipher feedback mode) encrypted messages are less subject to tampering than OFB(Output feedback mode)? Pg 208 cfb Pg 210 ofb One advantage of the OFB method is that bit errors in transmission do not propagate. For example, if a bit error occurs in C1, only the recovered value of P1 is affected; subsequent plaintext units are not corrupted. With CFB, C1 also serves as input to the shift register and therefore causes additional corruption downstream. The disadvantage of OFB is that it is more vulnerable to a message stream modification attack than is CFB. Consider that complementing a bit in the ciphertext complements the corresponding bit in the recovered plaintext. Thus, controlled changes to the recovered plaintext can be made. This may make it possible for an opponent, by making the necessary changes to the checksum portion of the message as well as to the data portion, to alter the ciphertext in such a way that it is not detected by an error-correcting code. For a further discussion, see [VOYD83]. OFB has the structure of a typical stream cipher, because the cipher generates a stream of bits as a function of an initial value and a key, and that stream of bits is XORed with the plaintext bits (see Figure 3.1). The generated stream that is XORed with the plaintext is itself independent of the plaintext; this is highlighted by dashed boxes in Figure 6.6. One distinction from the stream ciphers we discuss in Chapter 7 is that OFB encrypts plaintext a full block at a time, where typically a block is 64 or 128 bits. Many stream ciphers encrypt one byte at a time 14 4 Differentiate Symmetric and Asymmetric key cryptography. OR Compare conventional encryption with public key encryption. E CO2