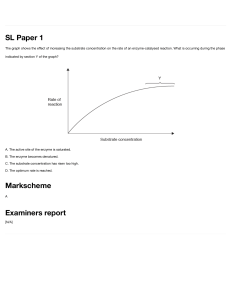
General1 [48 marks] 1. [Maximum mark: 1] 23M.1.HL.TZ2.37 Light of frequency f is incident on a metallic surface of work function W. Photoelectrons with a maximum kinetic energy Emax are emitted. The frequency of the incident light is changed to 2f . What is true about the maximum kinetic energy and the work function? Maximum kinetic energy Work function A. less than 2Emax unchanged B. less than 2Emax greater than W C. greater than 2Emax unchanged D. greater than 2Emax greater than W Markscheme C [1] 2. [Maximum mark: 1] A rectangular sheet of paper has dimensions of (30.0 ± 0.5) cm and (20.0 ± 0.5) cm. 22N.1.SL.TZ0.1 What is the percentage uncertainty of the perimeter of the paper? A. 1 % B. 2 % C. 2.5 % D. 4 % Markscheme B [1] 3. [Maximum mark: 1] Two forces, F and G, act on a system. 22N.1.SL.TZ0.2 F is reversed in direction and G is halved. Which vector correctly represents the new resultant force? [1] Markscheme D 4. [Maximum mark: 1] A projectile is launched with a velocity u at an angle θ to the horizontal. It reaches a maximum height s. What is the time taken to reach the maximum height? A. 22N.1.SL.TZ0.4 2s u cos θ B. 2s C. u cos θ D. u sin θ g g g Markscheme D [1] 5. [Maximum mark: 1] The diagram shows the trajectory of a projectile and the velocity v of the projectile at point P in its trajectory. P is located before the projectile reaches the peak altitude. Air resistance acts on the projectile. The acceleration of the projectile at P is a. 22N.1.HL.TZ0.5 What are the magnitudes of the horizontal component and the vertical component of the acceleration of the projectile at P? [1] Markscheme B 6. [Maximum mark: 1] What is the order of magnitude of the wavelength of visible light? 22M.1.SL.TZ1.1 A. 10−10 m B. 10−7 m C. 10−4 m D. 10−1 m [1] Markscheme B 7. [Maximum mark: 1] The magnitude of the resultant of two forces acting on a body is 12 N. Which pair of forces acting on the body can combine to produce this resultant? 22M.1.SL.TZ1.2 A. 1 N and 2 N B. 1 N and 14 N C. 5 N and 6 N D. 6 N and 7 N Markscheme D [1] 8. [Maximum mark: 1] A student measures the time for 20 oscillations of a pendulum. The experiment is repeated four times. The measurements are: 22M.1.SL.TZ1.3 10.45 s 10.30 s 10.70 s 10.55 s What is the best estimate of the uncertainty in the average time for 20 oscillations? A. 0.01 s B. 0.05 s C. 0.2 s D. 0.5 s Markscheme C [1] 9. [Maximum mark: 1] The radius of a circle is measured to be (10.0 ± 0.5) cm. What is the area of the circle? 22M.1.SL.TZ2.1 A. (314.2 ± 0.3) cm2 B. (314 ± 1) cm2 C. (314 ± 15) cm2 D. (314 ± 31) cm2 Markscheme D [1] 10. [Maximum mark: 1] Two different experiments, P and Q, generate two sets of data to confirm the proportionality of variables x and y. The graphs for the data from P and Q are shown. The maximum and minimum gradient lines are shown for both sets of data. 22M.1.SL.TZ2.2 What is true about the systematic error and the uncertainty of the gradient when P is compared to Q? [1] Markscheme C 11. [Maximum mark: 1] The intensity of a wave can be defined as the energy per unit area per unit time. What is the unit of intensity expressed in fundamental SI units? 22M.1.HL.TZ1.1 A. kg m−2 s−1 B. kg m2 s−3 C. kg s−2 D. kg s−3 [1] Markscheme D 12. [Maximum mark: 1] The uncertainty in reading a laboratory thermometer is 0.5 °C. The temperature of a liquid falls from 20 °C to 10 °C as measured by the thermometer. What is the percentage uncertainty in the change in temperature? 22M.1.HL.TZ1.3 A. 2.5 % B. 5 % C. 7.5 % D. 10 % Markscheme D [1] 13. [Maximum mark: 1] 22M.1.HL.TZ2.16 Four particles, two of charge +Q and two of charge −Q, are positioned on the x-axis as shown. A particle P with a positive charge is placed on the y-axis. What is the direction of the net electrostatic force on this particle? [1] Markscheme D 14. [Maximum mark: 1] Which is a vector quantity? 21N.1.SL.TZ0.1 A. Acceleration B. Energy C. Pressure D. Speed Markscheme A [1] 15. [Maximum mark: 1] A ball of mass (50 ± 1) g is moving with a speed of (25 ± 1) m s−1. What is the fractional uncertainty in the momentum of the ball? 21N.1.SL.TZ0.2 A. 0.02 B. 0.04 C. 0.06 D. 0.08 [1] Markscheme C 16. [Maximum mark: 1] Which lists one scalar and two vector quantities? 21M.1.SL.TZ1.1 A. Mass, momentum, potential difference B. Mass, power, velocity C. Power, intensity, velocity D. Power, momentum, velocity Markscheme D [1] 17. [Maximum mark: 1] 21M.1.SL.TZ1.2 Two sets of data, shown below with circles and squares, are obtained in two experiments. The size of the error bars is the same for all points. What is correct about the absolute uncertainty and the fractional uncertainty of the y intercept of the two lines of best fit? [1] Markscheme D 18. [Maximum mark: 1] A student measures the length l and width w of a rectangular table top. 21M.1.SL.TZ2.1 What is the absolute uncertainty of the perimeter of the table top? A. 0. 3 cm B. 0. 6 cm C. 1.2 cm D. 2.4 cm Markscheme B [1] 19. [Maximum mark: 1] What is the unit of power expressed in fundamental SI units? A. kg m s B. kg m s C. kg m s D. kg m s 21M.1.SL.TZ2.2 −3 −1 2 −1 2 −3 [1] Markscheme D 20. [Maximum mark: 1] Which is a correct unit for gravitational potential? 21M.1.HL.TZ1.31 A. m2 s−2 B. J kg C. m s−2 D. N m−1 kg−1 Markscheme A [1] 21. [Maximum mark: 1] Which quantity has the same units as those for energy stored per unit volume? 20N.1.SL.TZ0.1 A. Density B. Force C. Momentum D. Pressure Markscheme D [1] 22. [Maximum mark: 1] A list of four physical quantities is 20N.1.SL.TZ0.2 acceleration energy mass temperature How many scalar quantities are in this list? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 [1] Markscheme C 23. [Maximum mark: 1] Which quantity has the fundamental SI units of kg m–1 s–2? A. Energy B. Force C. Momentum D. Pressure Markscheme D 19N.1.SL.TZ0.1 [1] 24. [Maximum mark: 1] An object is held in equilibrium by three forces of magnitude F, G and H that act at a point in the same plane. 19N.1.SL.TZ0.2 Three equations for these forces are I. F cos θ = G II. F = G cos θ + H sin θ III. F = G + H Which equations are correct? A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III Markscheme A [1] 25. [Maximum mark: 1] What are the units of specific energy and energy density? 19N.1.SL.TZ0.28 [1] Markscheme B 26. [Maximum mark: 1] A student wants to determine the angular speed ω of a rotating object. The period T is 0.50 s ±5 %. The angular speed ω is 19M.1.SL.TZ1.1 2π ω = T What is the percentage uncertainty of ω? A. 0.2 % B. 2.5 % C. 5 % D. 10 % Markscheme C [1] 27. [Maximum mark: 1] A student models the relationship between the pressure p of a gas and its temperature T as p = x + yT. 19M.1.SL.TZ1.2 The units of p are pascal and the units of T are kelvin. What are the fundamental SI units of x and y? [1] Markscheme A 28. [Maximum mark: 1] A student measures the radius R of a circular plate to determine its area. The absolute uncertainty in R is ΔR. 19M.1.SL.TZ2.1 What is the fractional uncertainty in the area of the plate? A. 2ΔR R B. ( ΔR ) R C. 2 2πΔR R D. π( ΔR ) R 2 [1] Markscheme A 29. [Maximum mark: 1] What is the unit of electrical potential difference expressed in fundamental SI units? 19M.1.SL.TZ2.2 A. kg m s-1 C-1 B. kg m2 s-2 C-1 C. kg m2 s-3 A-1 D. kg m2 s-1 A Markscheme C [1] 30. [Maximum mark: 1] An object has a weight of 6.10 × 102 N. What is the change in gravitational potential energy of the object when it moves through 8.0 m vertically? 19M.1.SL.TZ2.5 A. 5 kJ B. 4.9 kJ C. 4.88 kJ D. 4.880 kJ Markscheme B [1] 31. [Maximum mark: 1] A student is verifying the equation 19M.1.HL.TZ1.1 2λY x = z The percentage uncertainties are: What is the percentage uncertainty in x? A. 5 % B. 15 % C. 25 % D. 30 % Markscheme B [1] 32. [Maximum mark: 1] A proton has momentum 10-20 N s and the uncertainty in the position of the proton is 10-10 m. What is the minimum fractional uncertainty in the momentum of this proton? 19M.1.HL.TZ2.2 A. 5 × 10-25 B. 5 × 10-15 C. 5 × 10-5 D. 2 × 104 [1] Markscheme C 33. [Maximum mark: 1] What is the unit of power expressed in fundamental SI units? 18N.1.SL.TZ0.1 A. kg m s–2 B. kg m2 s–2 C. kg m s–3 D. kg m2 s–3 Markscheme D [1] 34. [Maximum mark: 1] The length of the side of a cube is 2.0 cm ± 4 %. The mass of the cube is 24.0 g ± 8 %. What is the percentage uncertainty of the density of the cube? 18N.1.SL.TZ0.2 A. ± 2 % B. ± 8 % C. ± 12 % D. ± 20 % Markscheme D [1] 35. [Maximum mark: 1] 18N.1.SL.TZ0.15 The graphs show the variation of the displacement y of a medium with distance x and with time t for a travelling wave. What is the speed of the wave? A. 0.6 m s–1 B. 0.8 m s–1 C. 600 m s–1 D. 800 m s–1 Markscheme [1] D 36. [Maximum mark: 1] 18N.1.SL.TZ0.21 Two parallel wires are perpendicular to the page. The wires carry equal currents in opposite directions. Point S is at the same distance from both wires. What is the direction of the magnetic field at point S? [1] Markscheme A 37. [Maximum mark: 1] A student measures the radius r of a sphere with an absolute uncertainty Δr. What is the fractional uncertainty in the volume of the sphere? A. ( B. 3 C. 4π D. 4π( Δr r ) 3 Δr r Δr r Δr r 3 ) Markscheme B 18M.1.SL.TZ1.1 [1] 38. [Maximum mark: 1] A river flows north. A boat crosses the river so that it only moves in the direction east of its starting point. 18M.1.SL.TZ1.2 What is the direction in which the boat must be steered? [1] Markscheme C 39. [Maximum mark: 1] What is the best estimate for the diameter of a helium nucleus? 18M.1.SL.TZ2.1 A. 10–21 m B. 10–18 m C. 10–15 m D. 10–10 m Markscheme C [1] 40. [Maximum mark: 1] The velocities vX and vY of two boats, X and Y, are shown. 18M.1.SL.TZ2.2 Which arrow represents the direction of the vector vX – vY? [1] Markscheme D 41. [Maximum mark: 1] Which is a unit of force? 18M.1.SL.TZ2.10 A. J m B. J m–1 C. J m s–1 D. J m–1 s [1] Markscheme B 42. [Maximum mark: 1] How many significant figures are there in the number 0.0450? 17N.1.SL.TZ0.1 A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5 Markscheme B [1] 43. [Maximum mark: 1] An object is positioned in a gravitational field. The measurement of gravitational force acting on the object has an uncertainty of 3 % and the uncertainty in the mass of the object is 9 %. What is the uncertainty in the gravitational field strength of the field? 17N.1.SL.TZ0.2 A. 3 % B. 6 % C. 12 % D. 27 % Markscheme C [1] 44. [Maximum mark: 1] The diagram shows an analogue meter with a mirror behind the pointer. 17N.1.SL.TZ0.30 What is the main purpose of the mirror? A. To provide extra light when reading the scale B. To reduce the risk of parallax error when reading the scale C. To enable the pointer to be seen from different angles D. To magnify the image of the pointer Markscheme B [1] 45. [Maximum mark: 1] What is a correct value for the charge on an electron? 17N.1.HL.TZ0.1 A. 1.60 x 10–12 μC B. 1.60 x 10–15 mC C. 1.60 x 10–22 kC D. 1.60 x 10–24 MC Markscheme C [1] 46. [Maximum mark: 1] The kinetic energy of a body is determined from measurements of its momentum p and its mass m. 23M.1.HL.TZ1.2 The percentage uncertainties in the measurements are: p ±3% m ±4% What is the percentage uncertainty in the kinetic energy? A. 7 % B. 10 % C. 13 % D. 14 % Markscheme B [1] 47. [Maximum mark: 1] The kinetic energy of a body is determined from measurements of its momentum p and its mass m. 23M.1.HL.TZ1.2 The percentage uncertainties in the measurements are: p ±3% m ±4% What is the percentage uncertainty in the kinetic energy? A. 7 % B. 10 % C. 13 % D. 14 % Markscheme B [1] 48. [Maximum mark: 1] Which is correct for a black-body radiator? 21N.1.SL.TZ0.30 A. The power it emits from a unit surface area depends on the temperature only. B. It has an albedo of 1. C. It emits monochromatic radiation whose wavelength depends on the temperature only. D. It emits radiation of equal intensity at all wavelengths. Markscheme A © International Baccalaureate Organization, 2024 [1]