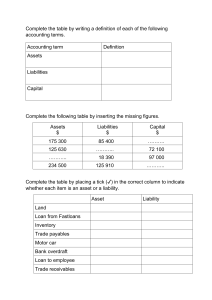
1|Page Visit our website Let‟s tute is an e-learning platform with a goal to provide quality education and making the process of learning fun and easy for everybody. We take pride in our specially designed courses that cover all the basic concepts using various real life examples, short quizzes to test our understanding, helpful documents to make our learning concrete. We believe these courses can cater to any learner as they've been explained in a very simplified manner and can help expand their imagination beyond textbooks, exams, and marks. We‟ve worked hard over the years to deliver best of the content to our users and in order to run our mission successfully; our premium content comes with an affordable price tag. We‟ll also appreciate if one wishes to support us in this journey. All the best Keep Watching. Keep Learning. Website: www.letstute.com 2|Page “Politics is for the present but an equation is for eternity” -Albert Einstein 3|Page Copyright Notice The content material in this document is protected by LETSTUTE. You may not copy, forward, or transfer this publication or any part of it whether in electronic or printed form to another person or entity. Reproduction or translation of any part of this work without the permission of the copyright holder is against the law. Your use and download of this e-book requires and is an indication of your complete acceptance of these „Terms of use‟. You do not have any right to resell or give away part or the whole of this ebook. 4|Page Chapter Contents Particulars What is accounting equation? The accounting equation with examples Objective Type Questions 5|Page Page No. 6 7-9 10-35 What is Accounting Equation? The equation that is the foundation of double entry accounting It shows what a company owns, what a company owes & what stake the owners have in the business. It describes that the total value of assets of a business is always equal to its external liabilities plus owner’s capital. This equation summarizes the essential nature of double entry accounting systems: Debits always equal Credits, and Assets always equal the sum of Capital and Liabilities. The Accounting Equation is as follows: Assets 6|Page = Capital + External Liabilities Need and Importance of Accounting Equation: The accounting equation is the basic accounting equation, represents the relationship among the liabilities, assets, and owner's equity of a business. Double entry principle indicates that the total debits are equal to the total credits for any transaction. It is also known balance sheet equation. The mathematical expression of the accounting equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity or A==L+E. It is most commonly used to balance sheet, the final financial statement for a company. It is the systematic form of representing company status, displaying the total assets of a company is equal to the total liabilities and shareholder equity. The balance sheet is a complex expression of this equation, presenting the total assets of a company is equal to the total of liabilities and owner’s equity. It is helpful to make use of the accounting equation at the time of preparing financial statements, as it would not only help you to maintain the accuracy, but also enable you to track the debits and credits, so that you can balance the equation accordingly. The importance of accounting equation should not be underestimated, as it's very much helpful to serve as a basis for all the accounting transactions. Representing the relationship with the components of the balance sheet, it reveals the financial standing of a business entity. 7|Page Examples of Entries & their effects in the Accounting Equation: 1. Mr. X purchased Furniture for Rs. 50,000 The Accounting Equation is: Asset (Furniture Comes in) Asset (Cash Goes Out) Asset (50,000- 50,000) 0 8|Page = Capital + External Liabilities = 0 + 0 = 0 + 0 2. Mr. X purchased Goods on Credit Rs.10,000 The Accounting Equation is: Assets (Goods Come in) Liabilities (Increase in Creditors) Asset 10,000 = Capital + = 0 + External Liabilities 10,000 3. Mr. X withdrew Rs. 5,000 for his personal use. Liabilities Assets Asset (5,000) 9|Page (Drawings are deducted from Capital) (Cash Going Out) = Capital = 0 + External Liabilities + (5,000) 4. Mr. X borrowed Rs. 2,500 from Bank of India. Assets (Cash Comes In) Liabilities (Liability to pay bank occurs) Asset 2,500 = Capital + External Liabilities = 0 + 2,500 5. Mr. X Paid Rs. 8,000 to Creditors. Assets (Cash Goes Out) Liabilities (Reduction in amount to be paid to Creditors) Asset (8,000) 10 | P a g e = Capital + = 0 + External Liabilities (8,000) Objective Type Questions Q.1.Choose Appropriate Answer 1. The Basic Accounting Equation is Assets = External Liabilities + __________ A. Drawings B. Capital C. Net Profit D. None of the Above 2. The accounting equation should remain in balance because every transaction affects how many accounts? A. Only One B. Only Two C. Two Or More D. None of the Above 3. Which of the following will not cause Assets to increase? A. Owner‟s Drawings B. Purchase of Goods on Credit C. Sale of Goods on Cash D. None of the Above 4. Which of the following will cause Liabilities to decrease? A. Purchase of Goods on Cash B. Sale of Goods on Cash C. Repayment of Bank Loan D. Purchase goods on Credit 5. Capital is the money borrowed from the A. Creditor B. Debtor C. Supplier D. Owner 11 | P a g e Q.2.Tick on the Appropriate Column following the Accounting Equation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The company purchases equipment with its cash. The owner withdraws cash from the business for personal use. The company purchases a significant amount of supplies on credit. The company receives cash as a loan from a bank. The company repays the bank that had lent money to the company. No. Assets Total Liabilities Increase Decrease No Effect Increase Decrease No Effect 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Q.3. Using the Accounting Equation formula, find the Missing Figure No. Assets Capital External Liabilities 1. 50,000 ? 30,000 2. ? 60,000 10,000 3. 15,000 5,000 ? 4. 7,000 2,000 ? 5. ? 9,500 9,500 12 | P a g e Q.4. Solve the Following 1. Show the effects of Accounting Equation from the following transactions: A. Mr. Shah started business with cash Rs.50,000 B. Mr. Shah purchased goods on credit Rs.10,000 C. Mr. Shah purchased Machinery on Credit Rs.15,000 D. Paid to Creditor Rs.5, 000. 2. Show the effects of Accounting Equation from the following transactions A. Mr. Patel commenced business with Rs. 1, 00, 000 B. Mr. Patel bought loose tools of Rs. 20,000 C. Mr. Patel sold goods on Cash 15,000 D. Mr. Patel purchased goods on Cash 10,000 3. Show the effects of Accounting Equation from the following transactions A. Mr. Mehta started business with Rs.10,000 B. He withdrew Rs.500 for personal use. C. Paid Salary Rs.5,000 D. Purchased Goods on Credit 10,000 4. Show the effects of Accounting Equation from the following transactions A. Mr. Parekh started business with 60,000 B. Paid for Repairs Rs. 1,050 C. Loan taken from Bank Rs. 15,000 D. Received interest Rs. 3,500. 5. Show the effects of Accounting Equation from the following transactions A. Mr. Desai started business with cash Rs. 55,000 B. Purchased goods on credit Rs. 6,500 C. Paid to Creditor Rs. 5,000 D. Additional Capital Introduced in business Rs. 18,000 13 | P a g e Answers Q1. 12345- B C A C D Q2. No. Assets Increase 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Q3. 1. 20,000 2. 70,000 3. 10,000 4. 5,000 5. 19,000 14 | P a g e Liabilities External Liabilities Decrease No Effect Increase Decrease Liabilities Capital No Increase Effect Decrease No Effect Q4. 1. The first solution provides the Steps and method to solve the Problem A. The accounting equation will be Assets= External Liabilities + Capital 50,000(Cash) = 0 + 50,000 B. The Accounting Equation will be Assets = External Liabilities+ Capital 50,000+ 10,000(increase in assets -goods) = 10,000(increase in creditors) + 50,000 C. The Accounting Equation will be Assets = External Liabilities+ Capital 50,000+10,000+15,000(increase in assets-Machinery) = 10,000+ 15,000(increase in creditors) + 50,000 D. The Accounting Equation will be Assets = External Liabilities+ Capital 50,000-5,000(cash paid) + 10,000 + 15,000 = 10,000+ 15,000- 5,000(Decrease in liabilities as paid to creditors) + 50,000 Therefore, The Accounting Equation will be Assets = External Liabilities+ Capital 70,000= 70,000 Transaction Accounting Equation Assets = External Liabilities + Capital A. Mr. Shah started business with cash Rs.50,000 50,000 0 50,000 B. Mr. Shah purchased goods on credit Rs.10,000 10,000 10,000 0 15 | P a g e C. Mr. Shah purchased Machinery on Credit Rs.15,000 15,000 15,000 0 D. Paid to Creditor Rs.5, 000 (-)10,000 (-)10,000 0 65,000 = 15,000 + 50,000 2. Transaction Accounting Equation Assets = External Liabilities + Capital A. Mr Patel commenced business with Rs. 1, 00, 000 1,00,000 0 1,00,000 B. Mr Patel bought loose tools of Rs. 20,000 20,000 0 0 C. Mr Patel sold goods on Cash 15,000 15,000 0 0 D. Mr Patel purchased goods on Cash 10,000 10,000 0 0 (-)20,000 (-)15,000 (-)10,000 1,00,000 16 | P a g e = 0 + 1,00,000 3. Transaction Accounting Equation Assets = External Liabilities + Capital A. Mr. Mehta commenced business with Rs. 10,000 10,000 0 10,000 B. Withdrew for personal use Rs. 500 (-)500 0 (-)500 C. Paid Salary Rs. 5,000 (-)5,000 0 (-)5,000 D. Purchased goods on Credit 10,000 10,000 0 Rs. 10,000 14,500 17 | P a g e = 10,000 + 4,500 4. Transaction Accounting Equation Assets A. Mr Parekh started business with 60,000 60,000 B. Paid for Repairs 1,050 (-)1,050 = External Liabilities 0 + Capital 60,000 0 (-)1,050 C. Loan taken from Bank Rs.15,000 15,000 15,000 0 D. Interest Received 3,500 0 3,500 3,500 77,450 18 | P a g e = 15,000 + 62,450 5. Transaction Accounting Equation Assets = External Liabilities 0 + Capital A. Mr. Desai started business with cash Rs. 55,000 55,000 B. Purchased goods on credit Rs. 6,500 6,500 6,500 0 C. Paid to Creditor Rs. 5,000 (-)5,000 (-)5,000 0 0 18,000 D. Additional Capital Introduced in 18,000 business Rs. 18,000 74,500 19 | P a g e = 1,500 55,000 + 73,000 Hope you have enjoyed Learning 20 | P a g e