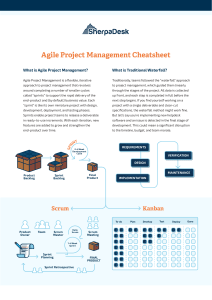
23/10/2023 AGILE 4 values of Agile: 1) Individuals of Interactions over process and tools -> The Agile methodology is based on value 2) Working product over comprehensive documentation 3) Customer collaboration over contract negotiation 4) Responding to change over following a plan Watrfall approch is a sequence of steps to reach the objective. Agile approch is a continuous providing of value better for the customer. SCRUM - Agile approch based on Scrum Scrum is an Agile process that allow us to focus on delivering maximum business in the shortest is possible. Scrum is time boxed scrum allows us to quickly and repeatedly test working software (every 2 weeks to every month). Business defines priorities. The team self-organizes to find the best way to deliver the highest-value features. Every two weeks or a month anyone can see real working software and decide whether to release it to users or continue improving it for another cycle. Properties of Scrum: Self-organised working groups Products whose development is in a progression in cycles (sprints) Requirements are defined as a micro-items in a list (product backlog) There are no particular practices to follow It is based on an adaptive approach to create an agile environment for carrying out projects One of the “agile frameworks” SCRUM – AGILE MANIFESTO – VALUES People and interactions over Process and tools Working software over documentation Collaboration with the clients over contract negotiation Respond to change over follow a plan A Scrum project progresses througha series of “sprints” Typically duration is 2-4 weeks or a month A constant duration leads to a better rythm … No change during the sprint: plan the duration of the sprint based on how long it is possibile to “reject” the request for a change. SCRUM FRAMEWORK: ROLES Pruduct Owners (define the features of the product, the requirements; the release dates and content; he is responsible for profitability (ROI) of the product; he defines priorities between functions based on their market value; adapt features after each cycle: accept or reject results of the team’s work). PO does Product Backlog. ScrumMaster (is not a Project Manager; is the management function in the project; responsible for executing and improving Scrum practices and values; removes any blockages, he is a facilitator between roles and functions; ensures the team is smoothly functioning and operational; protect the team from external interference). SM doesn’t priorities work. Scrum Team (5-9 people; cross functional; participants must be full-time; team is self-organised; changes between participants only between one sprint and another (no internal sprint). ST doesn’t priorities work. CERIMONIES Team Capacity: Sprint planning Product backlog: manage priority sprint Business Conditions Product State Technology Analyse and evaluate Product backlog Define the sprint goal Sprint goal: is to finish all the tasks Sprint planning: Design: defines how to achieve the sprint goal Create sprint backlog (tasks) starting from teams items in the product backlog (user stories/functions) Estimate sprint backlog Sprint backlog: is the single task Team selects product backlog items that they commit to completing in the sprint. Daily scrum partecipano tutti Sprint reviewpartecipano PO e clienti the last cerimony -> The team presents to PO what he accomplished during the sprint. It tipically takes the form of a demo of the application’s functionality or architectureinformale. Sprint retrospective (is based on the process) partecipano SM e development team another cerimony that we do the last day of the sprint in which we analyze what didn’t work. TOOLS - Product backlog: is a list of requirements/features required; ideally built so that each element has value for customers of the product; priorities managed by PO are verified at the start of each sprint.