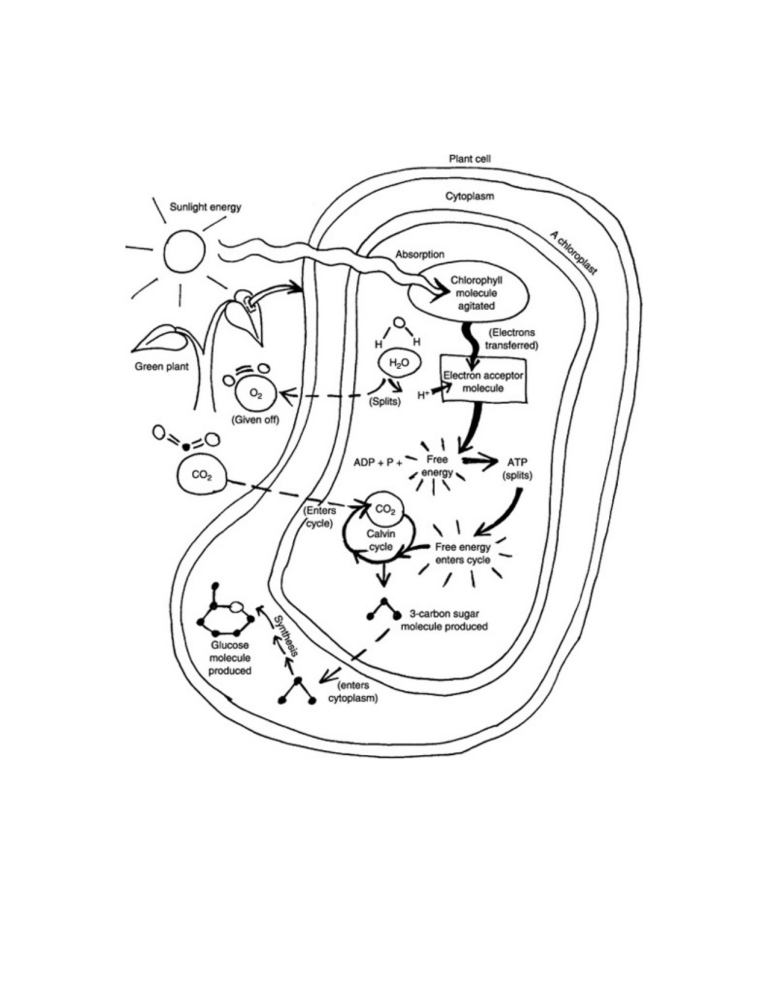
Stages of Photosynthesis Stage 1 ‐‐ Energy is captured from sun. Leaves contain light absorbing substances called pigments Pigments absorb certain wavelengths of light and reflect others Chlorophyll: the primary pigment involved in photosynthesis Absorbs blue & red light Reflects green & yellow light (causes plants to look green) 2 types of chlorophyll: Chlorophyll a (bright green) Chlorophyll b (yellow‐green) Carotenoids: pigments that produce red, orange, & yellow colors (fall leaves, fruits, flowers, etc.) Clusters of pigments are embedded inside the chloroplasts (specifically, in the thylakoids) Light strikes the thylakoids inside the chloroplasts & energy is transferred to the chlorophyll. Water molecules are split to form oxygen gas (O2). ______________________________________________________________________________ Stage 2 ‐‐ Light energy is converted to chemical energy. Excited electrons jump to nearby molecules in the thylakoid membrane Then the electron is passed down a series of molecules along the thylakoid membrane (electron transport chain) Electron transport chains provide the energy needed to make ATP ______________________________________________________________________________ Stage 3 ‐‐ Energy is stored in organic compounds (sugars). Carbon dioxide fixation: the transfer of CO2 from atmosphere to organic compounds Calvin cycle: a series of enzyme‐assisted chemical reactions that produces a 3‐carbon sugar (uses energy from ATP) 3 CO2 molecules enter the cycle & produce a 3‐carbon sugar These sugars provide organisms energy to maintain life