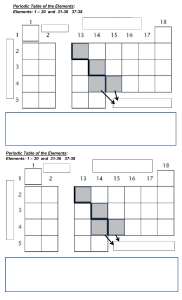
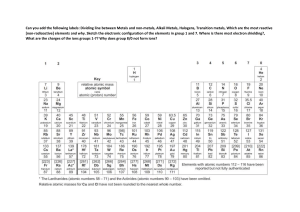
AM IN Periodic Table +1 +2 8 +3 -+4 2 3 2 3 4 5 6 0 4 5 6 7 SA DI Q 7 https://ptable.com/#Properties Periodic law Properties of the elements of the periodic function of their increasing atomic number . Mr Mr.Sadiq Amin -1 8/0 1 1 -3_ -2 or AM IN elements are arranged in the periodic table on the basis of increasing atomic number . There are groups and periods in the periodic table . groups are the vertical columns of elements in the periodic table . Q periods are the horizontal rows of elements in the periodic table . DI There are seven PERIODS in the periodic table. SA and there are 18 groups in the periodic table . group number one is called the alkali metals where highly reactive metals . Mr group #2 is called alkaline earth metals they are less reactive than alkali metals . in the middle of the periodic table there are transition metals . AM IN on the right side of the periodic table mostly from group #13 to group #18 are nonmetals. Group #13 is called boron family . group #14 is called carbon family Q group #15 is called nitrogen family group #16 is called oxygen family DI group #17 is called the halogen family SA group #18 is called the Noble gases . Mr WE will Work on the electronic configuration of the elements starting from hydrogen which is element NO#1 in the periodic table ,and ending up on calcium which is the 20th element of the periodic table . AM IN what is the atomic number ? that is the number of protons in an element ,periodic table is arranged on the basis of increasing atomic number . what is atomic mass ? the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an element . 2He SA 1H DI Q protons and neutrons are in the centre of an element (Atom ),and electrons are revolving around the nucleus (centre the Atom ). Mr 5B 6C 3Li 7N 4Be 8O 13Al 15P 14Si 17Cl Mr SA 18Ar DI Q 16S AM IN 12Mg 19K Those elements which are in the same group they have the same outer most 20Ca AM IN electronic configuration will take the example of group number one lithium sodium and potassium and will cheque the electronic configuration of the outer most shell . Q GROUP NO 1. 11Na 19K DI 3Li SA GROUP NO 2.These elements have two electrons in their outer most shell (the last shell ) Mr 4Be 12Mg 20Ca AM IN NOTE:The electrons in the outer most shell are showing the group number . and the total number of shells are telling us about the period number . period no# 3 = 3 Q Example. group no# 5= outer electrons first shell =2 SA middle=8 DI the element is phosphorus last shell=5 total electron=15 Mr PERIODIC TABLE LINK https://ptable.com/#Properties AM IN There are two types of elements in the periodic table . SA DI Q 1. the metals (mostly on the left side of the periodic table ) 2. the nonmetals (mostly on the right side of the periodic table ) 3. Metalloids those elements of the periodic table which are having both the properties of metals and nonmetals . 2n2 Is used to fill the electrons in the shells ,where n stands for the number of shell ,(shell NO# 1,2,3,4,5,6,7) ELECTRONS IN THE SHELLS USING THE FORMULA 2n2 Formula Total electrons Mr 2(n)2 Shell Shell Shell Shell NO4 NO1 NO2 NO3 2(1)2=2x(1x1)=2 2 2(2)2=2x(2x2)=8 8 2(3)2=2x(3x3)=18 18 2(4)2=2x(4x4)=32 2x(4x4)=32 AM IN SA DI Q Properties of metals and nonmetals S.no Metals Non Metals 1 Ductile Non Ductile 2 Malleable Non Malleable 3 Sonorous Non Sonorous 4 NonBrittle Brittle 5 Conductors Non conductors except graphite 6 Shiny non shiny /Dull 7 High Low density density 8 high low melting and melting boiling points and boiling point Mr Ductile: to be drawn out into a thin wire Malleable: That can be hammered into sheets . DI Q AM IN Sonorous :Having ringing sound . Brittle: it means can be shattered into pieces . Q. Group 0 Noble gases are non reactive /inert ,why they don't react ? Ans: because their outer most shells are having complete electronic configuration ,that's why they don't react at all .The complete electronic configuration should be 2/8/18/32. NEXT TOPIC Acidic and basic characters of the oxides of metals and nonmetals SA Oxides are the binary(only made of Mr two elements ) compounds of oxygen with other elements. There are SEVEN types of oxides . 4 of the oxides are the part of our course . 1. acidic oxides 2. basic oxides neutral oxides amphoteric oxides sub oxides PER oxides superoxides Acidic Oxides . AM IN 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Q These are the binary compounds of oxygen with nonmetals . their solutions are acidic in nature . DI they turn blue litmus paper red Their pH is less than 7 . SA examples are . CO2,NO2,SO2,SO3 These oxide produce acidic solution and dissolved in water . CO2+H2O→H2CO3 (CARBONIC ACID) 2. NO2+H2O→HNO3 (NITRIC ACID) 3. SO2+H2O→H2SO3 (SULPHUROUS ACID) 4. SO3+H2O→H2SO4 (SULPHURIC ACID) Mr 1. AM IN BASIC OXIDES. These are the binary compounds of oxygen with metals . they are alkaline in nature . they change red litmus paper blue . their Ph is more than 7 . the examples are. Q Na2O,MgO,CaO,K2O SA DI Reactions of metal oxides with water will always make an alkaline solution ,the pH will be more than 7 and it will be turning blue litmus paper to red . 1. Na2O + H2O→ NaOH (sodium hydroxide) 2. MgO + H2O→ Mg(OH)2(magnesium hydroxide ) 3. CaO + H2O→ Ca(OH)2(calcium hydroxide ) Mr 4. K2O + H2O→ KOH (potassium hydroxide) Neutral oxides . AM IN these are also the binary compounds of oxygen with other elements . they don't change the colour of the litmus paper . their pH is at 7 exactly . Examples are :water(H2O) ,carbon monoxide(CO) ,nitrogen monoxide (NO). Q Amphoteric oxides : DI these oxides are having dual properties ,when they reacted with acids they behave like alkalies,And when they reacted with alkalies,they behave like acids. SA examples are . Mr ZnO,Al2O3,PbO. Next AM IN Chemical reaction of amphoteric oxides • Reaction with an acid ZnO(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2O(l) Reaction with a alkali ZnO(s) + 2NaOH(a) → Na2ZnO2(aq) + H2O(l) • Reaction with an acid Al2O3(s) + 6HCl(aq) → 2AlCl3(aq) + 3H2O(l) • Reaction with a alkali Al2O3(s) + 2NaOH(aq) → 2NaAlO2(aq) + H2O(l) • Q. Why elements in the same group have Similar chemical properties ? DI Q Ans: Because they have the same number of valence electron in their outer most shell . SA Q.Why metals are good conductors of electricity? Ans: Because they are having delocalised mobile electrons which are responsible for the conductance of electricity . Mr Properties of Group One elements Group One elements are also called alkali metals . AM IN okay this start with lithium ,sodium ,potassium ,Rubidium ,caesium ,francium 1.All the elements in Group one react violently with water, releases hydrogen immediately,which catches fire .the reaction with air is also very fast their freshly cut surface is are shiny but they get dull very quickly . Group1 reaction with water. Group One elements are highly vigorous while reacting with with cold water ,The rate of reaction is increasing down the group and we can see some intensifying chemical reactions . 2K + 2H2O→ 2KOH + H2 Q 2Na + 2H2O→ 2NaOH + H2 DI The reactivity of Group One elements increases down the group ,so we can say that francium is more reactive than lithium . SA The highly reactive metals are at the bottom and the low reactive metals are at the top of the group . Physical properties Mr 1. They are soft metals ,can be easily cut with knife . 2. their freshly cut surfaces are shiny ,and get dull quickly reacting with oxygen in the air . 3. as they are highly reactive so they are kept under kerosene oil for safety. 4. They have only one electron in their outer most shell. AM IN 5. they make positively charged ions Na1+ 6. they react with group 7 elements to make ionic salt's 7. These elements are not freely(It means elemental form original form ) available ,they are extracted from compounds by electrolysis method . 8. their solutions are alkaline it means they have a pH above 7 . Properties of group 7 elements . Mr SA DI Q 1. group7 elements are called halogens(salt making). 2. They all have 7 electrons in their outer most shell. 3. they have a charge of minus one on the negative ions . 4. their names are ,flourine ,chlorine ,bromine , iodine, Astatine. 5. The first 2 elements of this group fluorine and chlorine are in the gaseous state ,bromine is in the liquid state ,iodine and astatine are in the solid state. 6. Colours of group 7 halogens . i. florine yellow ii. chlorine yellowish green/greenish yellow iii. Bromine Brown. iv. Iodine grey astatine black AM IN v. Chemical reactions of halogens . there are 3 types of reactions of the halogens . a. Reaction with hydrogen F2 + H2 → 2HF → This reaction happens in darkness it doesn't need any energy .vigorous reaction Cl2 + H2→ 2HCl Q → this reaction needs a little bit of energy but still it's vigorous enough DI Br2 + H2→2HBr →this reaction needs more energy a little heat can initiate the reaction is vigorous I2 + H2→ 2HI SA →more heat energy is required to start this reaction but once it's started it's vigorous as well . They are all diatomic in nature. Mr The reactivity of the halogens decreases down the group ,the highly reactive elements are at the top unlike Group One elements where the highly reactive are at the bottom . AM IN Q. Working with bromine water in the laboratory ,if there's a spillage of bromine water on the table ,how will you clean it ? Ans:if there's a spillage of bromine water on the table in the laboratory ,we will use sodiumthiosulphate(Na2S2O4)to neutralise the effects of bromine water ,only this chemical can neutralise its poisonous effects. b. reactions with alkali metals. Q These reactions are also vigorous in nature ,very explosive sort of reactions can be seen . SA DI if we take molten sodium in the gas jar of chlorine ,we will see an explosive reaction ,with orange colour flame ,releasing a white smoke ,and a huge amount of heat energy . This will result in making an ionic salt of sodium chloride . 2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl 2K + Cl2 → 2KCl Mr c. displacement reactions Displacement reactions are those reactions in which a highly reactive element displaces the low reactive element . fluorine is more powerful than chlorine and the rest of the elements . F2>Cl2>Br2>I2 AM IN every top element of the group is reactive more then the bottom element . If we have a solution of sodium chloride and we add flourine to it ,it will displace chlorine out of the solution and takes its place . 2NaCl + F2→ 2NaF+ Cl2 Q NOTE : Halogens are all poisonous in nature ,they can only be neutralised with a solution of sodiumthiosulphate(Na2S2O4) . Mr SA DI https://ptable.com/#Properties