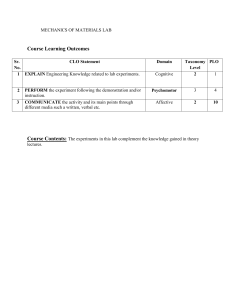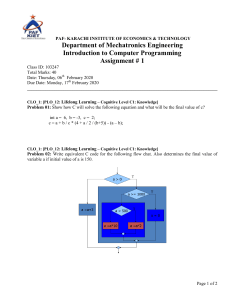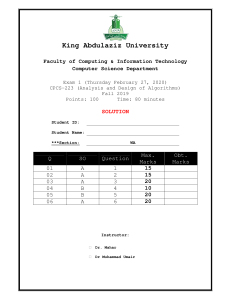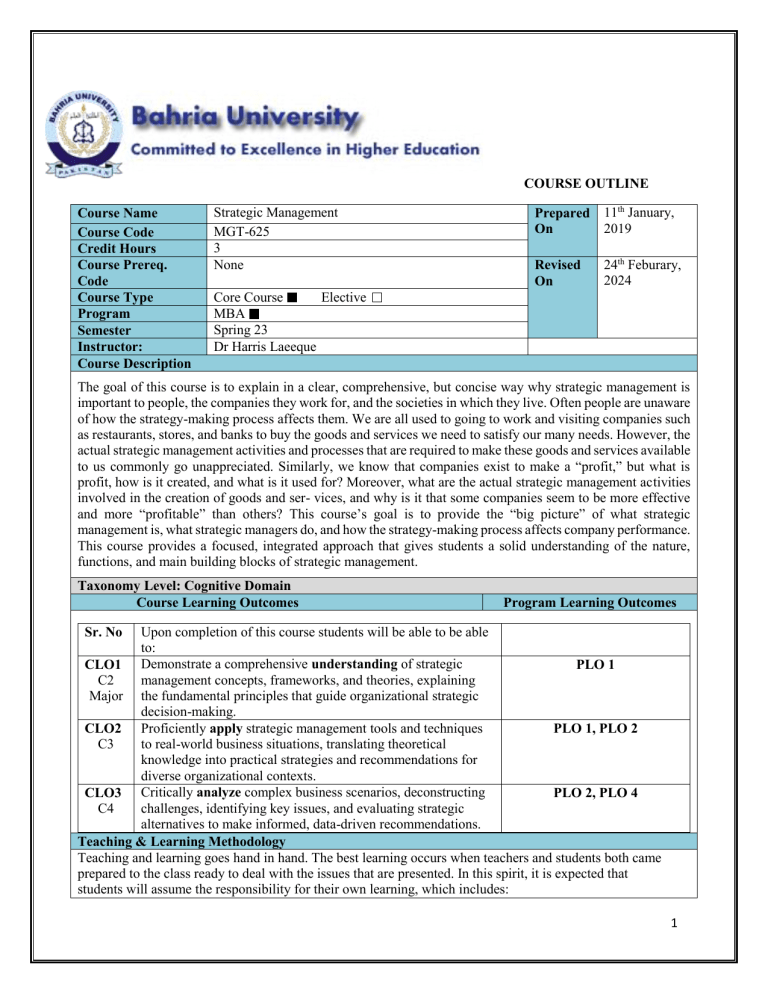
COURSE OUTLINE Course Name Course Code Credit Hours Course Prereq. Code Course Type Program Semester Instructor: Course Description Strategic Management MGT-625 3 None Prepared On 11th January, 2019 Revised On 24th Feburary, 2024 Core Course Elective MBA Spring 23 Dr Harris Laeeque The goal of this course is to explain in a clear, comprehensive, but concise way why strategic management is important to people, the companies they work for, and the societies in which they live. Often people are unaware of how the strategy-making process affects them. We are all used to going to work and visiting companies such as restaurants, stores, and banks to buy the goods and services we need to satisfy our many needs. However, the actual strategic management activities and processes that are required to make these goods and services available to us commonly go unappreciated. Similarly, we know that companies exist to make a “profit,” but what is profit, how is it created, and what is it used for? Moreover, what are the actual strategic management activities involved in the creation of goods and ser- vices, and why is it that some companies seem to be more effective and more “profitable” than others? This course’s goal is to provide the “big picture” of what strategic management is, what strategic managers do, and how the strategy-making process affects company performance. This course provides a focused, integrated approach that gives students a solid understanding of the nature, functions, and main building blocks of strategic management. Taxonomy Level: Cognitive Domain Course Learning Outcomes Program Learning Outcomes Upon completion of this course students will be able to be able to: CLO1 Demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of strategic PLO 1 C2 management concepts, frameworks, and theories, explaining Major the fundamental principles that guide organizational strategic decision-making. CLO2 Proficiently apply strategic management tools and techniques PLO 1, PLO 2 C3 to real-world business situations, translating theoretical knowledge into practical strategies and recommendations for diverse organizational contexts. CLO3 Critically analyze complex business scenarios, deconstructing PLO 2, PLO 4 C4 challenges, identifying key issues, and evaluating strategic alternatives to make informed, data-driven recommendations. Teaching & Learning Methodology Teaching and learning goes hand in hand. The best learning occurs when teachers and students both came prepared to the class ready to deal with the issues that are presented. In this spirit, it is expected that students will assume the responsibility for their own learning, which includes: Sr. No 1 Regularly attending the class (atleast 75 % attendance is compulsory to take your final exam) Respect & listen to the one who is talking Present their ideas in a clear and articulate way The teaching methodology will include: Lectures Articles / Case Studies Discussions Activities Small Scenario Analysis Group Project Textbook(s) Thompson, A. A., Strickland, A. J., & Gamble, J. E. (2021). Crafting and executing strategy. McGraw-Hill US Higher Ed USE. Reference Book(s) Dess, G. G. (2007). Strategic management: Text and cases. Mc Graw Hill. Hill, C. W., & Jones, G. R. (2011). Essentials of strategic management. Cengage Learning. David, F. R. (2011). Strategic management concepts and cases. Prentice hall. Case Studies Will be provided in the class. Magazine Articles/ Published Material Will be assigned as reading assignments in the class. Grading Policy Assessment Instruments Percentage Quizzes 15% Assignments + project 20% Mid Term Exam 25% Final Exam 40% 2 Week/ Contents Session What Is Strategy and Why Is It Important? Week 1 What do we mean by strategy? A company’s strategy and its business model What makes a strategy a winner? Why crafting and executing strategy are important tasks Charting a Company’s Direction: Its Vision, Mission, Objectives, and Strategy Week 2 Week 3 Interactive Discussion: Initiate a discussion on real-world examples of successful and unsuccessful strategies. Reading: Honda’s dominance of the US motorcycle industry: Deliberate or emergent strategies? What does the strategy-making, strategy-executing process entail? Stage 1: Developing a strategic vision, Debate: Organize a debate on the statement: "The mission statement, and set of core development of a strategic vision is more values important than setting objectives." Stage 2: Setting objectives Stage 3: Crafting a strategy Real-World Examples: Provide examples of companies with distinct strategic visions. Charting a Company’s Direction: Its Strategic Initiatives Analysis: Assign students to Vision, Mission, Objectives, and Strategy analyze recent strategic initiatives of a chosen company. Evaluate how well these initiatives Stage 4: Executing the strategy were executed, and discuss the implications for Stage 5: Evaluating performance and the company's performance. initiating corrective adjustments Corporate governance: The role of the Interactive Debates: Organize debates on topics related to strategy execution and corporate board of directors in the strategygovernance. crafting, strategy-executing process The strategically relevant factors in the company’s Macro-environment Assessing the company’s industry and competitive environment Learning Objectives Addressed CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 Reading: How perceptual limited succeeded by rallying around the founder’s original mission Class Discussion: Facilitate a class discussion on companies that have successfully or unsuccessfully implemented strategic visions. Evaluating a Company’s External Environment Week 4 Activities (Critical Thinking) Discussions Topics, Case Studies, Roleplays, Movie Clips, Assignments, Research Papers, Presentations CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 External Environment Scanning Exercise: Assign students to scan the external environment of a real company. Have them identify and categorize factors from the macro-environment. Industry Trends Debate: Organize a debate on emerging trends in a specific industry. CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 Mini-case: Disruptive innovation from Netflix Case Study: Husain, S., Naheed, K., & Isa, M. (2016). Veet: facing a cultural challenge in 3 Evaluating a Company’s External Environment Week 5 The five forces framework Complementors and the value net Industry dynamics and the forces driving change Strategic group analysis Competitor analysis Key success factors Pakistan. Emerald Emerging Markets Case Studies, 6(2), 1-16. Five Forces Analysis Workshop: Conduct a workshop where students apply Porter's Five Forces framework to analyze a specific industry. Strategic Group Analysis: Guide students in analyzing strategic groups within an industry. Case study: Qureshi, J. A., Shamsi, A. F., & Arif, F. (2022). Pakistan State Oil: multidimensional strategic issues of a market leader. Emerald Emerging Markets Case Studies, 12(1), 1-27. CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 Quiz 1 Evaluating a Company’s Resources, Capabilities, and Competitiveness Week 6 What are the company’s most important resources and capabilities, and will they give the company a lasting competitive advantage over rival companies? What are the company’s strengths and weaknesses in relation to the market opportunities and external threats? How do a company’s value chain activities impact its cost structure and customer value proposition? Is the company competitively stronger or weaker than key rivals? What strategic issues and problems merit front-burner managerial attention? Company Benchmarking Task: Have students select two companies from the same industry and conduct a benchmarking task. Resource and Capability Audit Exercise: Assign students to conduct a resource and capability audit for a chosen company. Competitive Advantage Debate: Organize a debate on what constitutes a lasting competitive advantage. CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 Case Study: Nasreen, K., & Afzal, M. T. (2020). Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats in higher education: a SWOT analysis of Allama Iqbal Open University Islamabad (Pakistan). Asian Association of Open Universities Journal, 15(3), 321-333. Reading: Differentiated product Jaguar F-Pace SUV The five generic competitive strategies Week 7 Types of generic competitive strategies Low-cost provider strategies Broad differentiation strategies Competitive Strategy Debate: Organize a debate where students defend and critique the effectiveness of low-cost provider and broad differentiation strategies. Brand Positioning Exercise: Engage students in a brand positioning exercise, focusing on how companies employing differentiation strategies position their brands in the market. CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 Marketing Campaign Analysis: Analyze marketing campaigns of companies following either low-cost or differentiation strategies. 4 The five generic competitive strategies Week 8 Focused (or market niche) strategies Best-cost provider strategies The contrasting features of the five generic competitive strategies: A summary Market Entry Simulation: Use a market entry simulation where students must choose between a broad market approach or a focused/niche strategy. Niche Identification: Assign students to analyze different industries and identify potential niche markets within those industries. CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 Reading: Amazon’s blue ocean strategy Quiz 2 Week 9 Week 10 MIDTERM EXAMS Strengthening a Company’s Competitive Position Reading: Tinder swipes right for first-mover success Launching strategic offensives to improve a company’s market position Defensive strategies—protecting market position and competitive advantage Timing a company’s offensive and defensive strategic moves Strengthening a company’s market position via its scope of operations Strategic Timing Analysis: Explore case studies or real-world examples to analyze instances of strategic timing in business. Strengthening a Company’s Competitive Position Week 11 Week 12 Horizontal merger and acquisition strategies Vertical integration strategies Outsourcing strategies: Narrowing the scope of operations Strategic alliances and partnerships Strategies for Competing in International Markets Analysis of Failed Strategies: Analyze cases of companies that failed to execute successful offensives or defensive strategies. CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 Debate on Defensive Strategies: Organize a debate where students argue for or against the effectiveness of various defensive strategies. Case Study: Shaikh, A. R., & Qazi, A. A. (2020). Chohan decoration services Pakistan–survival amid covid-19. Emerald Emerging Markets Case Studies, 10(4), 1-17. Mini-case: Cementing a merger of equals between Lafarge and Holcim has been difficult Analysis of Failed M&A Cases: Analyze cases of failed mergers and acquisitions, discussing the reasons behind the failures and the impact on the companies involved. Industry Trends Presentation: Assign student groups specific industries and have them present on current trends related to mergers, outsourcing, and strategic alliances. Reading: The global delivery services industry: Economic disruption of tariffs and trade wars CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 5 Why companies decide to enter foreign markets Why competing across national borders makes strategy making more complex Strategic options for entering international markets Strategies for Competing in International Markets Week 13 International strategy: The three main approaches International operations and the quest for competitive advantage Cross-border strategic moves Strategies for competing in the markets of developing countries Defending against global giants: Strategies for local companies in developing countries Corporate strategy Week 14 What does crafting a diversification strategy entail When to consider diversifying Building shareholder value: The ultimate justification for diversifying Approaches to diversifying the business lineup Choosing the diversification path: Related versus unrelated businesses Corporate strategy Week 15 Diversification into related businesses Diversification into unrelated businesses Combination related-unrelated diversification strategies Evaluating the strategy of a diversified company Market Entry Strategy Workshop: Conduct a workshop where students work in groups to develop market entry strategies for a hypothetical company. Interactive Cross-Cultural Exercise: Engage students in a cross-cultural exercise where they explore the cultural dimensions impacting international strategy. Quiz 3 Case Study: Kashif, M., Mingione, M., & Noori, M. F. (2017). Peri-Peri Original: the expansion decision in Pakistan. Emerald Emerging Markets Case Studies, 7(2), 1-15. Market Expansion Simulation: Create a simulation focused on market expansion in developing countries. CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 Industry-Specific International Challenges: Break the class into groups based on industry focus. Each group analyzes the unique challenges and opportunities of competing internationally within their specific industry. Interactive Discussion: Facilitate an interactive discussion on the timing of diversification. Strategic Group Analysis: Task students to analyze how companies within the same industry diversify and position themselves differently to gain a competitive advantage. CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 Case Study: Dogar, M. N. (2018). Business case for diversification–Adult Basic Education society (ABES), Pakistan. Emerald Emerging Markets Case Studies, 8(4), 1-23. Class Polls: Use live polls or surveys to gather students' opinions on diversification preferences. Debate on Related vs. Unrelated Diversification: Divide the class into groups and conduct a debate on the merits and drawbacks of related and unrelated diversification. CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 Company Analysis Presentations: Assign student groups to analyze and present on a diversified company of their choice. Quiz 4 6 Ethics, Corporate Social Responsibility, Environmental Sustainability, and Strategy Week 16 What do we mean by business ethics? Where do ethical standards come from How and why ethical standards impact the tasks of crafting and executing strategy Drivers of unethical business strategies and behavior Why should company strategies be ethical? Strategy, corporate social responsibility, and environmental sustainability Week 17 Students’ projects Week 18 Final Exams Debate: Organize a structured debate where students discuss the drivers of unethical business strategies. Ethical Dilemma Role-Play: Create scenarios depicting ethical dilemmas in business. Group Discussions: Conduct group discussions on the origins of ethical standards. CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 Case Study: Fatima, T., Bilal, A. R., & Imran, M. K. (2019). Dhuan ‘n’Dukhaan: a case of successful green venture start-up in Pakistan. Emerald Emerging Markets Case Studies, 9(1), 1-31. Final project presentations CLO 1 CLO 2 CLO 3 ASSIGNMENTS Assignment-I: Strategy Critique and Analysis The assignment requires students to select two companies—one recognized for successful strategy execution and another for strategy failure. Students analyze and compare the business models of the chosen companies, identifying key success factors contributing to the effective strategy of the successful company. They then delve into the reasons behind the failure of the second company's strategy, proposing revised strategies based on course concepts and presenting their findings in a comprehensive report. Assignment-II: Environmental Analysis and Competitive Intelligence Report Students analyze a real company's macro-environment, industry dynamics, and competitive factors. Using tools like the five forces framework, they assess complementors, industry changes, and perform strategic group and competitor analysis. The goal is to offer strategic insights for informed decision-making and improved competitive position. Assignment-III: Why competing across national borders makes strategy making more complex: Compare and contrast the strategic challenges faced by companies operating solely in their domestic market with those operating internationally. Identify and analyze the unique complexities and complexities associated with international competition. FINAL PROJECT 7 The final project, due 10 days before exams with a 5000-word limit, focuses on Zara's strategic management. Task 1 involves analyzing Zara's external and internal environment, identifying three critical factors, and evaluating current competitive advantages. Task 2 requires a critical evaluation of Zara's motives for global expansion, proposing at least three global entry strategies. Task 3 centers on improving Zara's global supply chain through horizontal and vertical integration, outsourcing, and strategic alliances, with recommendations for profitability using a relevant model. Course Instructor: Dr Harris Laeeque Senior Assistant Professor Department of Business Studies Email: shlaeeque@bahria.edu.pk 8 MBA Program Goals PLO 1- Application of Business Knowledge Demonstrate understanding and analysis of specialized business issues or problems by making decisions and recommendations for improvements based on the practical application of concepts, skills, knowledge and techniques. PLO 2- Effective Communication Emphasize on oral communication skills for professional connections and effective written communication including official documentation and correspondence in a business environment. PLO 3- Leadership skills Depict Leadership skills and abilities to lead and manage in teams along with effective decision making for solution of business problems. PLO 4- Critical thinking Develop skills that can be used to critically analyse and evaluate business problems in a range of applied business situations through application of concepts, skills, knowledge and techniques learned in various functional areas for effective decision making. PLO 5- Ethical Consideration and Behavior Ensure students are able to identify ethical concerns in a business situation and demonstrate the application of ethical guidelines to address business problems ways in that are ethically and socially responsible. 9