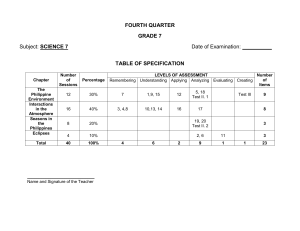
SCRIPT First of all, what is competition, according to the Cambridge dictionary, competition is “read the screen” So, in a market, it is important to have competition because if there is no competition, there will be fewer companies to choose from, prices will go up, quality will suffer, and there will be poor services. But if there is competition in the market, the consumers will have more choices, and companies compete by improving quality and lowering prices. In the Philippines, we have a law about competition called the Republic Act No. 10667 or the Philippine Competition Act. “read the screen” It was enacted on July 21, 2015, and effective on August 8, 2015. Who has original and primary jurisdiction in enforcing and regulating all competition-related issues? “read the screen” Anti-competitive agreements are those that substantially prevent, restrict or lessen competition. Price fixing - Businesses agree to directly or indirectly fix purchase or selling prices, instead of letting supply and demand determine the prices of goods and services. Cartel - A cartel is an organization formed by competitors in a specific industry, which enables them to set prices or control levels of production. Market sharing - Businesses divide the market and claim dominance according to territory, customer demographic, sales volume, or type, creating local monopolies that deprive consumers of choice. Bid rigging - Businesses agree to fix prices at an auction or manipulate bids, forcing buyers to select the higher-priced “pre-selected” bid instead of the best price. Output limitation - Businesses agree to limit production by restricting output or setting quotas, creating an artificial shortage in the market that subsequently drives up prices A business may become dominant in a certain industry by gaining a significant share of the market or becoming an industry leader with years of operation. Limiting production, markets, or technical development – when a dominant firm restricts output or refuses to supply, or restricts access to/use of/ development of new technology, to the detriment of consumers. Exploitative behavior towards consumers, customers, or competitors - A dominant firm charges excessive or unfair prices, or employs other unfair trading conditions. Exploitative – taking unfair advantage of someone or something for personal gain Predatory pricing - A dominant firm deliberately incurs losses in the short term by selling goods or services below the cost of its production, which can eventually force its competitors out of business Price discrimination - A dominant firm sets different prices or conditions for equivalent transactions. It is not illegal to be dominant provided that a business does not take advantage of its dominance to substantially lessen competition in the market What are mergers and acquisitions? A merger refers to the joining of two or more entities into an existing entity or to form a new entity. Acquisition refers to the purchase of securities or assets to obtain control of another entity. They tend to create a monopoly in a relevant market. A monopoly limits available substitutes for its product and creates barriers for competitors to enter the marketplace. This reduction in competition can harm consumers by potentially leading to higher prices or fewer choices for products or services. The PCA prevents M&As only if they substantially lessen, restrict, or prevent market competition in the Philippines What businesses and entities that the PCA cover? The Competition Act is intended to have an extraterritorial effect, being enforceable against "any person or entity engaged in any trade, industry, and commerce in the Republic of the Philippines". It is likewise applicable to "international trade having direct, substantial, and reasonably foreseeable effects in trade, industry, or commerce in the Republic of the Philippines, including those that result from acts done outside the Republic of the Philippines" Only anti-competitive agreements give rise to administrative, civil, and criminal liabilities. While Abuse of dominant position and anti-competitive mergers and acquisitions give rise to administrative and civil liabilities only. How does the Philippine Competition Act (PCA) affect foreign investments in the Philippines? The Philippine Competition Act (PCA) presents a complex scenario for foreign investors. While it aims to create a fairer market by curbing anti-competitive practices, it also adds a layer of complexity for international businesses. On the positive side, the PCA can open up new market opportunities by reducing the dominance of established players and encouraging innovation. Additionally, the increased transparency and predictability can attract investors seeking a stable business environment. However, foreign investors need to navigate the potential drawbacks of the PCA, such as the added compliance burden of understanding and adhering to its provisions, and the risk of subjective interpretations leading to uncertainty and disputes. Ultimately, the PCA's impact on foreign investments depends heavily on the specific industry, investment size, and the investor's risk appetite. Careful consideration and seeking legal guidance are crucial for navigating the PCA's intricacies and making informed investment decisions in the Philippines.