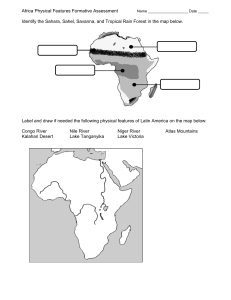
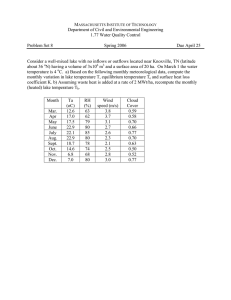
World-Location-Based Topics for UPSC Civil Services Exam by Pmfias.com Contents Africa ...................................................................................................................................................................... 1 Major Rivers of Africa ....................................................................................................................................................... 5 Nile River ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 5 Congo River (formerly Zaire River) ....................................................................................................................................................................... 7 Niger River ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 7 Zambezi River ............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 8 Orange River ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 8 Great Rift Valley ................................................................................................................................................................. 9 East African Rift Valley .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 9 African Great Lakes ......................................................................................................................................................... 11 Lakes in the Albertine Rift...................................................................................................................................................................................... 12 Other Major Lakes in Africa .................................................................................................................................................................................. 13 Major Mountain Ranges of Africa .................................................................................................................................. 13 Major Deserts of Africa ................................................................................................................................................... 14 Sahara Desert ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 14 Other major deserts of Africa ............................................................................................................................................................................... 15 Recently in News (Focus Area for Prelims 2020) .......................................................................................................... 16 Botswana’s Okavango Delta ................................................................................................................................................................................. 16 Mauritius....................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 16 Dallol geothermal field ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 18 Nobel Peace Prize for 2019 ................................................................................................................................................................................... 18 G5 Sahel ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 19 Horn of Africa ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 19 Cote d’Ivoire ................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 20 Important Points are highlighted in Blue and Red Trying to mug up all the facts is counterproductive. Focus only on those that are recently in news. Africa 1 Area Countries • 30.3 million km2 (6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area) • Algeria is Africa's largest country by area. • The majority of the continent and its countries are in the Northern Hemisphere. • Total 54 • Largest countries: Algeria, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Sudan, Libya & Chad. • Smallest countries: Seychelles, São Tomé and Príncipe, Mauritius, Comoros & Cape Verde. 2 • Smallest countries in mainland Africa: Gambia, Eswatini (Swaziland), Djibouti, Rwanda & Burundi. Population • 1.3 billion • Nigeria is Africa’s largest country by population. • Largest countries by population: Nigeria, Ethiopia, Egypt, Democratic Republic of the Congo & Tanzania. • Longitudinal Extent Africa's average population (19.7 years) is the youngest amongst the continents. 51° E to 17° W (~7,400 km — Ras Hafun in Somalia to Cape-Vert in Senegal) of the Mainland Latitudinal Extent of 37° N to 34° S (~8,000 km — Ras ben Sakka in Tunisia to Cape Agulhas in South Africa) the Mainland Coastline • The coastline of Africa is 30,500 km in length. • The coastline of Africa is shorter than that of Europe (38,000 km), because there are few inlets and few large bays or gulfs. Major Cities • Lagos (Nigeria), Kinshasa (Congo), Cairo, Giza & Alexandria (Egypt), Johannesburg, Pretoria & Durban (South Africa), Nairobi (Kenya), Casablanca & Rabat (Morocco), Algiers (Algeria), Addis Ababa (Ethiopia), Kano (Nigeria), Bamako (Mali), Mogadishu (Somalia), Mombasa (Kenya), Harare (Zimbabwe), Tripoli (Libya), Kigali (Rwanda), Tunis (Tunisia) & Benghazi (Libya). • Largest by Area: Lagos & Cairo. • Largest by Population: Lagos, Kinshasa & Cairo . • Pietermaritzburg: On 7 June 1893, young Mahatma Gandhi was thrown out of a train at Pietermaritzburg station. Major Islands/Island • Addis Ababa: Headquarters of the African Union. • Madagascar, Comoros, Seychelles, Mauritius, Reunion (overseas territory of groups France), Cape Verde Islands, Canary Islands (Spain), São Tomé & Príncipe & Madeira Islands (Portugal). Major Lakes • Largest lakes by surface area in Africa: 1) Lake Victoria 2) Lake Tanganyika 3) Lake Malawi (all freshwater lakes) • Largest lake by volume in Africa: 1) Lake Tanganyika 2) Lake Malawi 3) Lake Victoria 3 • Deepest lake in Africa: 1) Lake Tanganyika (2nd deepest lake in the world. Lake Baikal in Russia is the deepest lake) 2) Lake Malawi Highest Mountains 1. Mount Kilimanjaro (5895 m) 2. Mount Kenya (5199 m) Longest Rivers 1. Nile River (Baḥr Al-Nīl – 6,853 km – headwaters of Kagera River to Nile Delta) 2. Congo River (4,700 km) 3. Niger River (4,200 km) 4. Zambezi River 4 Major Rivers of Africa Nile River • The Nile River flows from south to north (Russian rivers Lena River – 4,294 km, Ob River – 3,700 km & Yenisey River – 3,487 km are other major south to north flowing rivers of the world). • It begins in the rivers that flow into Lake Victoria, and empties into the Mediterranean Sea. • From Lake Victoria to the Mediterranean, it is more than 6,600 km long, making it the world’s longest river. • Compared to other major rivers, though, the Nile carries little water. • Its drainage basin covers eleven countries: Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Republic of the Sudan, and Egypt. Source & Credits 5 • Major tributaries: The White Nile, the Blue Nile, and the Atbarah. White Nile • The White Nile is considered to be the headwaters and primary stream of the Nile itself. • The source of the White Nile is sometimes considered to be Lake Victoria. • But Kagera River, which flows into Lake Victoria is a significant feeder river. • Hence, the length of Nile is sometimes considered from the headwaters of the Kagera River. • Kagera River, the largest tributary of L. Victoria, rises in Burundi near the northern tip of Lake Tanganyika. • At Khartoum (capital of Sudan) the White Nile is joined by the Blue Nile. • Mountain Nile: Lake No in South Sudan, the confluence of the Mountain Nile (Bahr al Jabal) and Bahr el Ghazal rivers, marks the transition between the Mountain Nile and White Nile proper. Aswan High Dam • The Aswan High Dam is an embankment dam built across the Nile in Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. • Lake Nasser is the man-made lake formed by the construction of the Aswan Dam. • Asan Dam is developed to better control flooding, provide increased water for irrigation and hydroelectricity. • The High Dam has had a significant effect on the economy of Egypt. • However, the silt and sediment, crucial for the replenishment of the lower reaches and the delta, is now building up behind the Aswan dam instead. • Instead of growing in size through the soil deposits, the delta is now shrinking due to erosion. • In addition, routine annual flooding no longer occurs along parts of the Nile. • These floods were necessary to flush and clean the water and to replenish the soils. Blue Nile • The Blue Nile is the most significant tributary of the Nile. • Though shorter than the White Nile, ~60% of the water that reaches Egypt originates from the Blue Nile. • The White Nile supplies just 15 percent of the total volume entering Lake Nasser. • Blue Nile originates in Lake Tana in the Ethiopian Highlands. • The river flows through Sudan to join the White Nile at Khartoum. Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam • Egypt has been in virtual control of the Nile water for centuries. • Almost 86% of the water reaching Egypt originates from Ethiopia. 6 • Egypt takes 66% of the Nile’s water and Sudan 22%, and the remaining is lost to evaporation. • Despite Ethiopia’s massive contribution, its use of the water from the river system is almost nothing. • Egypt is now alarmed by Ethiopia’s Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (largest hydroelectric dam in Africa). • After a major water-war scare, Egypt, Ethiopia, and Sudan agreed on a deal for managing the dam. Atbarah River • The Atbarah River (Black Nile) flows into Nile at Atbarah, 200 miles north of Khartoum. • It rises in northwest Ethiopia, approximately 50 km north of Lake Tana. • The Atbarah is the last tributary of the Nile before it reaches the Mediterranean. Congo River (formerly Zaire River) • Congo River (4,700 km) is Africa’s second longest river, after the Nile. • It rises in the highlands Zambia between Lakes Tanganyika and Lake Malawi as the Chambeshi River. • Its drainage basin (4,000,000 km2) covers Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), as well as most of the Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic, Cameroon, Zambia, Angola and Tanzania. • Kinshasa (capital of DRC), is situated on the left bank of the Congo River. • Brazzaville (capital of Republic of the Congo), is situated on the right bank. Niger River • Niger River (4,200 km) is the third longest river in Africa, after the Nile and the Congo. • Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea. • It runs in a crescent through Mali, Niger, on the border with Benin and then through Nigeria, discharging through Niger Delta into Gulf of Guinea. 7 Zambezi River • The Zambezi is the fourth-longest river in Africa and the longest east-flowing river in Africa. • The river crosses/forms the boundaries of Angola, Zambia, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe & Mozambique. • Kariba and Cahora Bassa dams, two of Africa’s largest hydroelectric projects, are on the Zambezi River. Victoria Falls • The Zambezi's most noted feature is Victoria Falls. • Victoria Falls is located on the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe. • It is considered to be one of the world's largest waterfalls due to its width of 1,708 metres. • It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Orange River • The Orange River is a river in Southern Africa. • It is the longest river within the borders of South Africa. • Orange River Basin extends extensively from Lesotho into South Africa and Namibia to the north. 8 • It rises in the Drakensberg mountains in Lesotho. • The river forms part of the international borders between South Africa and Lesotho and between South Africa and Namibia. Great Rift Valley • The Great Rift Valley runs for ~6,400 km from northern Syria (Asia) to central Mozambique (East Africa). • The northernmost part of the Rift forms the Beqaa Valley in Lebanon. • Farther south, the valley is the home of the Jordan River which continues south through the Jordan Valley into the Dead Sea on the Israeli-Jordanian border. • From the Dead Sea southward, the Rift is occupied by the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea. • The Afar Triangle of Ethiopia and Eritrea is the location of a triple junction. • The Gulf of Aden is an eastward continuation of the rift, and from this point, the rift extends south-eastward as part of the mid-oceanic ridge of the Indian Ocean. East African Rift Valley • In a southwest direction from the triple junction, the fault continues as East African Rift Valley, which split the older Ethiopian highlands into two halves. • The East African Rift Valley transects through Ethiopia, Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Zambia, Tanzania, Malawi and Mozambique. • Before rifting, enormous continental flood basalts erupted on the surface and uplift of the Ethiopian, Somalian, and East African plateaus occurred. • East African Rift Valley divides into the Eastern Rift and the Western Rift. 9 Source & Credits • The Eastern Rift (also known as Gregory Rift) includes the main Ethiopian Rift, which continues south as the Kenyan Rift Valley. • The Western Rift Valley includes the Albertine Rift, and farther south, the valley of Lake Malawi. • The Western Rift (Albertine Rift) contains some of the deepest lakes in the world. Breaking up of Africa • The East African Rift (EAR) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. • To the south, where the rift is young, extension rates are low. Volcanism and seismicity are limited. 10 • Towards the Afar region, however, the entire rift valley floor is covered with volcanic rocks. • This suggests that, in this area, the lithosphere has thinned almost to the point of complete break-up. • The African Plate is in the process of splitting into two tectonic plates, called the Somali Plate and the Nubian Plate (African Plate), at a rate of 6–7 mm annually. Volcanism and seismicity along East African Rift Valley • The East African Rift Zone includes many active as well as dormant volcanoes. • Mount Kilimanjaro, is a dormant stratovolcano in Tanzania, Mount Kenya is an extinct stratovolcano. • Although most of these mountains lie outside of the rift valley, the EAR created them. • The EAR is the largest seismically active rift system on Earth today. • The majority of earthquakes occur near the Afar Depression, with the largest occurring along the faults. African Great Lakes • African Great Lakes region (sometimes also called Greater Lakes region) include Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Malawi, Rwanda, Tanzania and Uganda. Lakes that drain into the White Nile river • Lake Victoria • Lake Albert • Lake Edward Lakes that drain into the Congo River • Lake Tanganyika • Lake Kivu Lakes that drain into the Zambezi via the Shire River 11 • Lake Malawi Endorheic lakes • Lake Turkana • Lake Chad African Great Lakes (MellonDor, from Wikimedia Commons) Lakes in the Albertine Rift Lake Victoria • Lake Victoria is the world's second largest freshwater lake by surface area (Lake Superior in the largest). • It is also the world's largest tropical lake. • The lake's area is divided among Tanzania, Uganda & Kenya. • The only outflow from Lake Victoria is the White Nile River. • The uppermost section of the White Nile is generally known as the Victoria Nile until it reaches Lake Albert. 12 Lake Tanganyika • Lake Tanganyika, the second largest freshwater lake by volume (Lake Baikal in Russia is the largest), is in the Albertine Rift. • It is also the world's longest freshwater lake and the second deepest lake in the world (Lake Baikal in Russia is the deepest). • The lake is shared between Tanzania, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Burundi, and Zambia. Lake Malawi (Lake Nyasa) • Lake Malawi is the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system. • It is located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania. • It is the second deepest lake in Africa, after Lake Tanganyika. Other Lakes in the Albertine Rift • Lake Albert & Lake Edward are located on the border between Uganda and the DRC. • Lake Albert is the northernmost of the chain of lakes in the Albertine Rift. • Lake Edward is the smallest of the African Great Lakes. • Lake Kivu lies on the border between the DRC and Rwanda. Other Major Lakes in Africa Lake Turkana in Kenyan Rift • Lake Turkana is a lake in the Kenyan Rift Valley, in northern Kenya. • It is the world's largest permanent desert lake and one of the largest alkaline lakes. • It is an endorheic lake (no outflow to other external bodies of water). Lake Chad • Lake Chad is located at the conjunction of Chad, Cameroon, Nigeria, and Niger. • It is a shallow endorheic freshwater lake. • Lake Chad is one of the most severely endangered lakes in the world. (Central Asia’s Aral Sea & Israel’s Lake Tiberias — also known as the Sea of Galilee — are other notable endangered lakes). Major Mountain Ranges of Africa Range Countries Highest Point 13 Atlas Mountains Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia Mount Toubkal (4,167m) Drakensberg South Africa Thabana Ntlenyana (3,482m) Ethiopian Highlands Ethiopia Mount Abuna Yosef (4,550m) Major Deserts of Africa Source & Credits Sahara Desert • The desert comprises much of North Africa, excluding the fertile region on the Mediterranean Sea coast, the Atlas Mountains of the Maghreb (Northwest Africa), and the Nile Valley in Egypt and Sudan. • To the south, it is bounded by the Sahel, a belt of semi-arid tropical savanna. • The Ahaggar Mountains and the Tibesti Mountains are the major mountains in the desert. Sahel • The Sahel is mostly covered in grassland and savanna, with areas of woodland and shrubland. 14 • The Sahel part of Africa includes northern Senegal, southern Mauritania, central Mali, northern Burkina Faso, south of Algeria, Niger, north of Nigeria, Cameroon and Central African Republic, central Chad, central and southern Sudan, the extreme north of South Sudan, Eritrea, and the extreme north of Ethiopia. Tafilalt, Morocco • Considered one of the biggest oases in the world, Tafilalt is located in the Sahara Desert region of Morocco. • (The largest self-contained oasis in the world is the Al-Ahsa located in south-eastern Saudi Arabia). Other major deserts of Africa Kalahari Desert • The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savannah in Southern Africa covering much of Botswana, parts of Namibia and regions of South Africa. • The salt pans of the Makgadikgadi Pan (Botswana) and Etosha Pan (Namibia) are located in the Kalahari. • The only permanent river, the Okavango, flows into the Okavango delta marshes that are rich in wildlife. Namib Desert • The Namib stretches for more than 2,000 km along the Atlantic coasts of Angola, Namibia, & South Africa. Sinai Peninsula • The Sinai Peninsula is a arid peninsula in Egypt. • It is situated between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south. • The Suez Canal separates the peninsula form the mainland Egypt. • Israel occupied Sinai Peninsula in the aftermath of the 1967 Six-Day War. • The region was returned to Egypt in 1982 after the implementation of the 1979 Egypt–Israel Peace Treaty. Suez Canal • It is a sea-level waterway in Egypt. • It opened in 1869 (Mahatma Gandhi was born in 1869). • The Suez Canal connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez. • The United Kingdom and France owned the canal until July 1956. • Nationalization of Suez Canal by Egypt led to the Suez Crisis of 1956. • The canal is owned and maintained by the Suez Canal Authority (SCA) of Egypt. 15 Recently in News (Focus Area for Prelims 2020) Botswana’s Okavango Delta • Context: Hundreds of elephants have died mysteriously in Botswana’s Okavango Delta. • Botswana is currently home to more elephants than any other African country, & southern Africa remains a stronghold for 293,000, or 70%, of the estimated remaining African elephants. • The Okavango Delta is a vast inland river delta in northern Botswana. • It was inscribed on the World Heritage List in 2014. Botswana • Botswana is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. • Gaborone is the capital and largest city of Botswana. • Botswana is bordered by South Africa to the south & southeast, Namibia to the west & north, Zimbabwe to the northeast & Zambia to the north. • Botswana is the leading diamond-producing country in terms of value, and the second largest in terms of volume (Russia is the largest diamond producer). • The two important diamond mines are Orapa Mine and Debswana Jwaneng Mine. Mauritius • Context: Mauritius Prime Minister Pravind Jugnauth will inaugurate the country’s new Supreme Court building in the island–nation’s capital, Port Louis jointly with PM of India. 16 • Mauritius is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about 2,000 kilometres off the south-east coast of the Africa. • Mauritius is the only country in Africa where Hinduism is the largest religion. • Hindus in Mauritius are the descendants of the Indian indentured labourers brought by the British in the 1840s to work in the sugarcane fields. • Mauritius remained a primarily plantation-based colony of the United Kingdom until independence in 1968. • Nowadays, tourism plays a major role in the country’s economy. Islands in the region • Mauritius includes the main island of Mauritius and Rodrigues, Agaléga and St. Brandon. • The capital and largest city, Port Louis, is located on Mauritius. Mascarene Islands • The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues form part of the Mascarene Islands, along with nearby Réunion, a French overseas department. Disputed Islands • As a British colony, Mauritius included Rodrigues, Agalega, St. Brandon, Tromelin, the Chagos Archipelago, and, until 1906, the Seychelles. • Sovereignty over Tromelin is disputed between Mauritius and France. • In 1965, the U.K. split the Chagos Archipelago from Mauritian territory, and some islands from the Seychelles, to form the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT). • The sovereignty of the Chagos is disputed between Mauritius and the UK. • Diego Garcia (US Naval base), one of the islands in the region, was leased to the United States. 17 • In February 2019, the International Court of Justice issued an advisory opinion ordering the UK to return the Chagos Islands to Mauritius as rapidly as possible, in order to complete the decolonisation of Mauritius. Dallol geothermal field • Researchers have found an aquatic environment with complete absence of any form of life. • The lifeless environment consists of hot, saline, hyperacid ponds of the Dallol geothermal field in Ethiopia. • The discovery may lead to an improved understanding of the limits of habitability. Dallol geothermal field in Ethiopia: A.Savin (Wikimedia); Map Source: Google Maps Nobel Peace Prize for 2019 • Nobel Peace Prize for 2019 was awarded to Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed Ali for his initiative to resolve the border conflict with neighbouring Eritrea. • Abiy Ahmed worked out the principles of a peace agreement with Isaias Afwerki, the President of Eritrea. • The peace declarations were signed in Asmara (capital of Eritrea) and Jeddah (Saudi Arabia). • Abiy Ahmed contributed actively to the normalisation of diplomatic relations between Eritrea and Djibouti. Ethiopia • The major portion of Ethiopia lies in the Horn of Africa. • Ethiopia shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Kenya to the south, South Sudan to the west and Sudan to the northwest. • Ethiopia is the most populous landlocked country in the world and the second-most populous nation on the African continent (after Nigeria). 18 Landlocked countries of the world (Source) • Its capital city, Addis Ababa, serves as the headquarters of the African Union. Eritrea • Eritrea is a country in Eastern Africa, with its capital at Asmara. • It is bordered by Ethiopia in the south, Sudan in the west, and Djibouti in the southeast. G5 Sahel • Militant violence has spread across the vast Sahel region, especially in Burkina Faso and Niger, having started when armed Islamists revolted in northern Mali in 2012. • G5 Sahel is an institutional framework for coordination in security matters in west Africa. • It was formed on in 2014. • Member states: Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, Mauritania, and Niger. Horn of Africa • The area is the easternmost projection of the African continent. 19 • It lies along the southern side of the Red Sea and extends hundreds of kilometres into the Gulf of Aden, Somali Sea and Guardafui Channel. • The locust swarms originate in the desert of Horn of Africa. Cote d’Ivoire • JuIy 2019: India-assisted Mahatma Gandhi IT-biotech park free trade zone was inaugurated in Cote d’Ivoire. • Ivory Coast is a country located on the south coast of West Africa. • Ivory Coast is also known as Côte d'Ivoire. • Ivory Coast's political capital is Yamoussoukro, while its economic capital is the port city of Abidjan. • It borders Guinea to the northwest, Liberia to the west, Mali to the northwest, Burkina Faso to the northeast, Ghana to the east, and the Gulf of Guinea to the south. • The official language of the republic is French. • Coffee and cocoa are the chief source of export. 20 World-Location-Based Topics for UPSC Civil Services Exam by Pmfias.com Contents Asia ......................................................................................................................................................................... 1 In News ............................................................................................................................................................................... 2 Kra Canal (Thai Canal) ....................................................................................................................................................................... 2 Golden Crescent, Golden Triangle .................................................................................................................................................... 3 Taiwan Strait ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 4 Ream Naval Base ............................................................................................................................................................................... 5 Chabahar Port & Zaranj-Delaram Highway ....................................................................................................................................... 6 18th NAM summit in Baku ................................................................................................................................................................. 8 Coral triangle ................................................................................................................................................................................... 10 Taal Volcano .................................................................................................................................................................................... 10 Anak Krakatoa ................................................................................................................................................................................. 11 Land Disputes in South China Sea ................................................................................................................................................... 12 Kajin Sara lake ................................................................................................................................................................................. 15 Chinese dams on Brahmaputra (Yarlung Tsangpo) ......................................................................................................................... 16 Mekong River (Lancang River in China) ........................................................................................................................................... 16 Important Points are highlighted in Blue and Red Trying to mug up all the facts is counterproductive. Focus only on those that are recently in news. Asia Area Countries Coastline Major Islands/Island groups • 44.58 million km2 • 49 fully recognized countries + Palestine (partially recognized) • 62, 800 km • Greater Sunda Islands (Borneo, Sumatra, Java & Sulawesi) • Lesser Sunda Islands (Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, Sumba, Timor, etc.) • Maluku Islands of Indonesia (Moluccas) • Japan (Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu & Shikoku) • Philippines (Luzon, Visayas & Mindanao) 1 • Kuril Islands (Russia) • Ryukyu Islands (Japan) • Taiwan • Sakhalin (Russia) • Cyprus (is a part of Asia and not Europe) • Disputed Islands: ✓ Paracel Islands, ✓ Spratly Islands & ✓ Senkaku (Diaoyu Dao or Diaoyu) islands (Japan controls the islands and calls them Senkaku; China and Taiwan claim the islands and call then Diaoyu). Major Lakes 1. Caspian Sea (remnant of an ancient sea) 2. Lake Baikal (deepest lake in the world; largest freshwater lake by volume) 3. Lake Balkhash Highest Mountain 1. Mt. Everest (8,848 m) (Nepal – China border) 2. K2 (8,611 m) (India – located in PoK) 3. Kangchenjunga (8,586 m) (India – Nepal border) Longest Rivers 1. Yangtze River (6,300 km) 2. Yellow River (5,464 km) 3. Mekong (4,909) 4. Lena River (4,294 km) In News Kra Canal (Thai Canal) • The Kra Isthmus Canal refers to proposals for a canal that would connect the Gulf of Thailand with the Andaman Sea across the Kra Isthmus in southern Thailand. • It is envisaged that such a canal would improve transportation similar to the Panama Canal and Suez Canal. • China is pitching itself against India, USA and Australia to build the strategically important Kra Canal. 2 • If China constructs the canal, PLA Navy will have direct access to the Andaman Sea bypassing Malacca Straits. Golden Crescent, Golden Triangle • The Golden Crescent and Golden Triangle are regions in Asia know for illicit opium production. • Opium produced her is used to make heroin. • The Golden Crescent overlaps three nations, Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan. 3 • The mountainous, secluded geography provides safe haven for illicit opium production. • The revenue generated from opium and heroine is a major source of terror funding in the region. • Afghanistan is the world’s leading opium producer. • The Golden Triangle coincides with the mountainous trijunction region of Thailand, Laos, and Myanmar. • Myanmar is the world's second largest producer of illicit opium, after Afghanistan. Taiwan Strait • China has objected to the presence of the US warships in the Taiwan Strait. • China, which considers Taiwan its own, has been angered by the Trump administration's increased support for the island, such as more arms sales & frequent military drills in the region. • The Taiwan Strait, also known as the Formosa Strait, is a 180-kilometer wide strait separating Taiwan and Fujian Province of mainland China. • The strait is currently part of the South China Sea and connects to the East China Sea to the north. 4 Ream Naval Base • July 2019: Ream Naval Base is a facility operated by the Royal Cambodian Navy on the coast of the Gulf of Thailand in the province of Sihanoukville, Cambodia. 5 • According to a report, an agreement between China and Cambodia would allow China to use Ream naval base for 30 years, where it would be able to post military, store weapons and berth warships. • This would be China’s second overseas naval foothold, after a base in Djibouti opened in 2017. • Djibouti is strategically situated by the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, which separates Gulf of Aden from Red Sea. • The Chinese base is located at Port of Doraleh to the west of Djibouti City. Chabahar Port & Zaranj-Delaram Highway • Four years after India and Iran signed an agreement to construct a rail line from Chabahar port to Zahedan, along the border with Afghanistan, the Iranian government has decided to proceed with the construction on its own, citing delays from the Indian side in funding and starting the project. 6 • The development comes as China finalises a massive 25-year, $400 billion strategic partnership deal with Iran. • Chabahar-Zahedan line is 628 km long. • It will be extended to Zaranj across the border in Afghanistan. • The entire project would be completed by Iranian Railways without India’s assistance. • The railway project was a major part of an alternate trade route to Afghanistan and Central Asia. • Iran proposed a tie-up between the Chinese-run Pakistani port at Gwadar and Chabahar last year, and has offered interests to China in the Bandar-e-Jask port 350km away from Chabahar. 7 What’s at stake for India? • India has constructed the 200 km long Delaram–Zaranj Highway — also known as Route 606. • The highway connects Delaram (border city of Afghanistan) to Zaranj (Nimruz province of Afghanistan). • The entire project was financed by India. • India wished to access both Afghanistan and other central Asian nations (like Turkmenistan), through Chabahar port-Delaram–Zaranj Highway. • Aleppo, Raqqah, Idlib, Ghouta, Baghouz • Mosul, erbil, Kirkuk, Tikrit, Fallaujah, Mosul, 18th NAM summit in Baku • The 18th Summit of the Non-Aligned Movement was held in October 2019 in Baku, Azerbaijan. • Baku is the capital and the largest city of Azerbaijan 8 Points to remember • Enclave Nakhchivan is a landlocked exclave of Azerbaijan. • Nagorno-Karabakh is a landlocked region covering the south-eastern range of the Lesser Caucasus. • It is a disputed territory, internationally recognized as part of Azerbaijan, but mostly governed by the Republic of Artsakh, a de facto independent state with an Armenian ethnic majority. 9 Coral triangle • The Coral Triangle Day is held on June 9 every year. • Congo Basin, the Amazonas and the Coral Triangle are the 3 mega ecological complexes on our planet. • Coral Triangle is spreads across 6 countries in Asia and the Pacific: Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands, and Timor Leste (East Timor). • It occupies just 1.5% of the world's total ocean area, but represents 30% of the world's coral reefs. • It has the highest coral diversity in the world - 76% of the world’s coral species are found here. Taal Volcano • Jan 2020: The eruption of Taal Volcano in Philippines spewed ashes across Manila, and some parts of Luzon. • Taal Volcano is a large caldera filled by Taal Lake in the Philippines. • It is the second most active volcano in the Philippines, after Mayon Volcano. • Because of its proximity to populated areas, the volcano was designated a Decade Volcano, worthy of close study to prevent future natural disasters. 10 Anak Krakatoa • April 2020: Anak Krakatoa erupted again in 2020 after causing a major disaster in 2018. • The greatest volcanic explosion known to humans is perhaps that of Krakatoa in 1883. • At present, Krakatoa is a group of four small volcanic islands in the Sunda Strait, between Java and Sumatra. 11 • Three of the four islands are the remnants of the previous volcanic structure destroyed in 1883 eruption. • The fourth island, Anak Krakatau (meaning Child of Krakatoa) emerged in the 1920s from the caldera formed in 1883. It is the current location of eruptive activity. • In recent times, Anak Krakatau has become increasingly active with Strombolian type eruptions. 2018 Sunda Strait tsunami • The eruption of Anak Krakatoa in December 2018 and subsequent collapse of the southwest sector of the volcano, including the summit, triggered the tsunami that has killed more than 400 people. Land Disputes in South China Sea Parcel Islands and Spratly Islands • The nine-dash line is a vaguely located demarcation line used by China and Taiwan for their claims of the major part of the South China Sea. 12 Parcel Islands and Spratly Islands in South China Sea (Voice of America, Wikipedia) • The Spratly Islands and Paracel Islands are two of the most contested areas in the South China Sea. • However, unlike other parts of the South China Sea, these areas do not hold large resources of oil or gas. • Most fields containing discovered oil and natural gas are clustered in uncontested parts of the South China Sea, close to shorelines of the coastal countries. • Under the UNCLOS, ownership of habitable islands can, however, extend the exclusive access of a country to surrounding energy resources (200-mile EEZ). • Hence, the country that wins the dispute would have the right to explore and develop whatever the resources that are available in the EEZ. 13 UNCLOS Coastal Zones Oil and Gas reserves around Spratly Islands and Parcel Islands (Source) 14 Natuna Islands • April 2020: China has angered Indonesia by sending Chinese coast guard escort to the Natuna Islands, which are within Indonesia’s exclusive economic zone but are also claimed by China. • The Natuna Regency is an archipelago of 272 islands located in the south part of the South China Sea in the Natuna Sea. • Administratively, the islands constitute a regency within the Riau Islands Province of Indonesia. Kajin Sara lake • The newly discovered Kajin Sara lake in Nepal is likely to set a new record of being the world’s highest lake. • It is located in Manang district of Nepal. • It is located at an altitude of 5,200 metres. This measurement is yet to be officially verified. • Current world’s highest lake is Tilicho Lake (4,919 m) in Nepal. • Lago Titicaca (3,810 m above sea level), in the Andes, is the world's highest lake navigable to large vessels. 15 Chinese dams on Brahmaputra (Yarlung Tsangpo) • India has long expressed concerns over dam-building on the Brahmaputra. • In 2015, China operationalized its first hydropower project at Zangmu Dam. • Three other dams at Dagu, Jiexu and Jiacha are being developed. • Indian officials have said the dams are not likely to impact the quantity of the Brahmaputra’s flows because they are only storing water for power generation. • Moreover, the Brahmaputra is not entirely dependent on upstream flows and an estimated 35% of its basin is in India. • India does not have a water-sharing agreement with China, but both sides share hydrological data. Mekong River (Lancang River in China) • The Mekong, or Mekong River, is a trans-boundary river in Southeast Asia. • It is the world's twelfth longest river and the seventh longest in Asia. 16 • Its estimated length is 4,350 km. • From the Tibetan Plateau the river runs through China, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam. • The extreme seasonal variations in flow and the presence of rapids make navigation difficult. • The river is a major trade route between western China and Southeast Asia. 17 World-Location-Based Topics for UPSC Civil Services Exam by Pmfias.com Contents Australia ................................................................................................................................................................. 1 Australia (Country) ............................................................................................................................................................ 2 Major Geographic Features in Australia ............................................................................................................................................................ 5 Oceania ............................................................................................................................................................................... 8 Melanesia ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 10 Fiji .................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 10 Micronesia ................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 11 Polynesia....................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 12 New Zealand ............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 12 Recently in News (Focus Area for Prelims 2020) .......................................................................................................... 13 Carmichael coal-mining project in Australia .................................................................................................................................................. 13 Bougainville ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 14 Whakaari / White Island ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 15 Tulagi Island ................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 15 Zealandia ...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 16 Practise Questions for Prelims........................................................................................................................................ 16 Australia: Practise Questions .......................................................................................................................................... 17 Solutions ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 23 Important Points for Prelims 2020 are highlighted in Blue and Red Australia 1 Australia (Country) 2 Area 7.68 million km2 (6th largest country) (world’s landmass is 149.45 million km2) Longitudinal Extent 113° E to 153° E (~4000 km) Latitudinal Extent 10° S to 43° S (~3860 km) Coastline 59,681 km Neighbouring coun- • Indonesia, East Timor and Papua New Guinea to the north tries • the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu and the French dependency of New Caledonia to the east, and • New Zealand to the southeast. 3 States • New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria & Western Australia Major cities • In decreasing order of population: Sydney (the largest and most populated city in Australia), Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Adelaide, Canberra, Hobart & Darwin. • From north to south: Darwin, Brisbane, Perth, Sydney, Adelaide, Canberra & Hobart. • From east to west: Brisbane, Sydney, Canberra, Hobart, Adelaide, Darwin & Perth. Major Islands Largest Lake Highest Mountain • Tasmania (also known as Apple Isle for its cultivation of apple) • It is a significant horticulture region of Australia. • Lake Eyre (9,500 km2) • It is also the lowest point (-15m below sea level) • Mawson Peak (2,745 m) (Located in Heard Island, an external Australian territory near Antarctica) • Mount Kosciuszko (2,228 m) in mainland Australia Longest River • Murray River (~2,500 km) Geography & vege- • Tropical rainforests in the north-east, temperate forests in the eastern highlands, tation snow-capped mountains of the Australian Alps and Tasmania, and extensive interior deserts 4 • Australian temperate forests (east Australia) are mostly made up of evergreen eucalyptus trees. Notable Fauna • Only egg-laying mammals on Earth, the platypus and echidna • Marsupials: Kangaroo (National Animal of Australia), Tasmanian devil, etc. Major Geographic Features in Australia 1. Marginal Seas around Australia 5 2. • The Great Barrier Reef The Coral Sea contains numerous islands and reefs, as well as the world’s largest reef system, the Great Barrier Reef (GBR), which was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1981. • 3. GBR covers an area of 348,000 km2 and extends for over 2,000 kilometres (10oS to 24oS). The Great Dividing Range 6 • The Australian Alps are part of the Great Dividing Range, the series of mountains, and highlands that runs about 3,000 kilometres from northern Queensland to the northern Victoria. • The Great Dividing Range reaches its greatest heights in the Australian Alps. • The highest peak in the Australian Alps is Mt Kosciuszko (2,228 m). • This chain of highlands divides the drainage of the rivers that flow to the east into the Tasman Sea from those that flow west into the drainage of the Murray–Darling Basin. • 4. The Alps, particularly the Victorian Alps, are periodically subject to major bushfires. Major Deserts in Australia • Australia is the driest inhabited continent. • The Great Victoria Desert in southern Australia is Australia’s largest desert. 5. Uluru (Ayers Rock) • It is a large sandstone rock formation in central Australia. • Uluru is notable for appearing to change colour at different times of the day and year. 7 6. Pilbara Region • Pilbara is a vast, dry, thinly populated region in the north of Western Australia. • It is known for its vast mineral deposits, in particular iron ore. 7. Kimberley Plateau • The Argyle Diamond Mine is located in the East Kimberley region. • The mine is one of the largest producers of diamonds in the world. Oceania • Oceania has traditionally been divided into four parts: 1. Australasia (Australia and New Zealand), 2. Melanesia, 3. Micronesia, and 4. Polynesia. 8 9 Oceania (Australia, Melanesia, Micronesia and Polynesia) (Jailbird, via Wikimedia Commons) Melanesia • Melanesia extends from New Guinea island to Tonga. • The region includes the independent countries of Fiji, Vanuatu, Solomon Islands, Papua New Guinea, as well as the French special collectively of New Caledonia, and parts of Indonesia (Western New Guinea). • Most of the region is in the Southern Hemisphere, with only a few small north-western islands of Western New Guinea lying in the Northern Hemisphere. Fiji 10 • British established the Colony of Fiji in 1874. • In the late 19th century, the British imported indentured labourers from India to work on sugarcane fields. • The British granted Fiji independence in 1970. • The population of Fiji is mostly made up of native Fijians (54%) and Indo-Fijians (38.1%). • Relationships between ethnic Fijians and Indo-Fijians have often been strained. • In 2014, PM Modi visited Fiji. Micronesia • There are four main island groups in Micronesia. • They are divided between six sovereign nations: 1. the Caroline Islands (divided between Federated States of Micronesia and Palau); 2. the Gilbert Islands (Republic of Kiribati); 3. the Mariana Islands (Northern Mariana Islands and Guam are unincorporated territory of the United States; Guam is the largest island) 4. the Marshall Islands (a sovereign nation) (Wake Island is claimed by the Marshall Islands but controlled by United States Air Force); • Nauru is a small sovereign nation in the region. 11 Polynesia • Samoa: Independent nation. • American Samoa: Unincorporated territory of the United States; located to the southeast of Samoa. • Cook Islands: Self-governing state in free association with New Zealand. • Easter Island: Province and special territory of Chile. • French Polynesia: Overseas country of the French Republic. • Hawaii: In 1959, Hawaii became the 50th state of the US (Alaska is the 49th state; it was purchased from Russia). • Tonga: Independent nation located to the east of Fiji. • Tuvalu: Independent nation. New Zealand • New Zealand is the largest country in Polynesia. • The country comprises two main islands — the North and South Islands — and a number of small islands. • Three in four New Zealanders (total population is 4.9 million) live in the North Island. • The South Island is important for forestry (Western side of Southern Alps), agriculture, sheep rearing and dairy farming (Marlborough, Canterbury Plains). • The capital city is Wellington and the largest urban area is Auckland — both located on the North Island. • Southern Alps (900-3000 m) on the South Island is the major mountain range. 12 • The western slopes are wet and forested. • The rain shadow region on the eastern side has vast pasture lands and fertile Canterbury Plains. Canterbury Plains Recently in News (Focus Area for Prelims 2020) Carmichael coal-mining project in Australia • Adani is building the $16.5 billion Carmichael coal-mining project in Queensland, Australia. • The Australian government approved its construction in 2018. • Adani has faced country-wide protests against the Queensland project. • The project can increase global warming and threaten the Great Barrier Reef. • Carmichael is located in the Galilee Basin. • The Galilee Basin is one of the largest untapped reserves of coal in the world. • Carmichael mine will be connected to the Abbot Port operated by Adani.⸻ 13 Galilee Basin in Australia (Wikipedia) Bougainville • Bougainville is a part of the archipelago that includes the Solomon Islands. • It is a resource-rich autonomous island inherited by Papua New Guinea from Australia. Why is it in the news? • Voters backing Bougainville’s independence from Papua New Guinea have won a referendum victory. • 97% of voters opted for independence from Papua New Guinea (PNG). 14 • The outcome of the poll is however not binding on the government of Papua New Guinea. • Things to remember for prelims: Solomon Islands, Solomon Sea, Bismark Sea and Papua New Guinea. Why does Bougainville want to secede? • PNG failed to honour the many agreed arrangements of the autonomy clause. • Bougainville/Panguna Copper Mine holds some of the world’s largest reserves of copper. • Copper extracted from the Panguna mine contributed significantly to Papua New Guinea’s economy. • The mine created opportunities for people from PNG & Australia, leading to conflicts with Bougainvilleans. Whakaari / White Island • The volcanic island Whakaari / White Island in New Zealand’s north-eastern Bay of Plenty region explosively erupted on 9 December 2019, killing several people. • Whakaari / White Island is an active andesite stratovolcano. Tulagi Island • A Beijing-based company has secured exclusive development rights for the entire island of Tulagi. 15 • Tulagi is an island within the Solomon Islands. • The secretive deal was signed with the provincial government in the Solomon Islands. • China is also pushing to end the region’s status as a diplomatic stronghold for Taiwan. • The Solomons cut ties to Taiwan and allied with Beijing just a few days before the Tulagi deal. • A second Pacific nation, Kiribati, followed suit the same week. • The US sees the island chains of the Pacific as crucial to keep China in check and protect important sea routes. Zealandia • Zealandia (microcontinent – broke away from Australian continental landmass) is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust that subsided after splitting from Gondwanaland 80 million years ago. • New Zealand is the largest part of Zealandia that is above sea level, followed by New Caledonia. Practise Questions for Prelims 16 Australia: Practise Questions 1. With reference to the Indo-Australian lithospheric plate, which of the following statements are true? 1) Indian lithospheric plate is moving away from Eurasia 2) Australian lithospheric plate is moving towards Eurasia Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 1 only b) 2 only c) Both d) None 2. Which of the following statements are true? 1) The latitudinal extent of India is greater than the latitudinal extent of Australia 2) The longitudinal extent of Australia is greater than the longitudinal extent of India Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 1 only b) 2 only c) Both d) None 3. Which of the following statements are true? 1) Most of the geographical area of Australia lies to the north of the Tropic of Capricorn. 2) Arid and semiarid regions occupy more than 60% of the geographical area of Australia. Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 1 only b) 2 only c) Both d) None 4. Which of the following statements are true? 17 1) Kimberley Diamond mine is located in the Kimberley Plateau of Australia. 2) Pilbara region of Australia, known for its rich mineral resources, is located in South-Western Australia Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 1 only b) 2 only c) Both d) None 5. Which of the following statements are true? 1) Most of the major coal mines in Australia are located in the eastern region. 2) Carmichael coal-mining project in located in Queensland, Australia. 3) Port Abbot is the major iron ore exporting port of Australia. Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 1 & 2 only b) 2 only c) 1 only d) All 6. What is the correct order of the major Australian cities from north to south? a) Darwin, Sydney, Perth, Canberra & Adelaide b) Darwin, Perth, Sydney, Adelaide & Hobart c) Perth, Sydney, Canberra, Adelaide & Hobart d) Sydney, Perth, Adelaide, Canberra & Hobart 7. Which of the following statements are true? 1) Murry River is the longest river in Australia 2) Murray-Darling Basin is the largest river basin of Australia, and most of its drainage is located in the Queensland region. 3) Murray River flows into the Tasman Sea Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 1 only 18 b) 1 & 2 only c) 1 & 3 only d) None 8. Which of the following are correctly matched? 1) Koolyanobbing ⸻ Iron Ore Mine 2) Kalgoorlie ⸻ Gold Mine 3) Olympic Dam ⸻ Polymetallic Mine 4) Carmichael ⸻ Coal Mine Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) All b) 1 & 2 only c) 1, 2 & 4 only d) 1, 3 & 4 only 9. What is the correct north-south order of major Australian landforms/geographic features? a) Tanami Desert, Great Barrier Reef, Ayers Rock & Eyre Lake b) Great Barrier Reef, Kimberley Plateau, Great Sandy Desert & Tanami Desert c) Great Barrier Reef, Kimberley Plateau, Great Sandy Desert & Lake Eyre d) Great Barrier Reef, Kimberley Plateau, Australian Alps & Great Victorian Desert 10. Which of the following are correctly matched? 1) Port Darwin ⸻ Timor Sea 2) Port Abbot ⸻ Coral Sea 3) Port Brisbane ⸻ Tasman Sea 4) Port Melbourne ⸻ Bass Strait Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) All b) 1 & 2 only c) 1, 2 & 3 only d) 1, 2 & 4 only 19 11. Which of the following statements are true? 1) The highest mountain of Australia is Mount Kosciuszko 2) There are no active volcanoes in Australia 3) Australia is a part of Oceania Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) All b) 2 & 3 only c) 3 only d) 1 & 3 only 12. Which of the following statements are true? 1) Port Darwin is the northern-most point of Australia 2) The Timor Sea and the Arafura Sea are a part of the Pacific Ocean 3) In Timor Island, West Timor is a part of Indonesia, and East Timor is a part of Australia Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 2 only b) 2 & 3 only c) 3 only d) None 13. Which of the following statements are false? 1) Denmark is the country with the largest island. 2) Greenland is the largest island country. 3) Greenland is the largest island in the world. 4) Greenland is larger than Australia Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 1 & 3 only b) 2, 3 & 4 only c) 2 & 4 only d) 2, 3 & 4 only 20 14. Which of the following statements are true? 1) Bass Strait separates Australia from the Melanesian island of New Guinea 2) Torres Strait separates Australian mainland from Tasmania 3) Cook Strait separates the two major Islands of New Zealand Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 2 only b) 1 & 2 only c) 2 & 3 only d) None 15. Which of the following statements are true? 1) The Solomon Islands is a province of Papua New Guinea 2) Bougainville Island, which was in the news recently, is a part of the Solomon Islands Archipelago 3) Solomon Islands Archipelago lies entirely in the southern hemisphere Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 1 & 2 only b) 2 & 3 only c) 2 only’ d) 3 only 16. Which of the following statements are true? 1) The Galápagos Islands are a part of Oceania 2) Oceania includes the entire continent of Australia 3) New Guinea is the largest Island of Oceania Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 1 & 2 only b) 2 & 3 only c) 2 only’ d) 3 only 17. Which of the following statements are true? 21 1) The Solomon Sea is between the Coral Sea and the Bismarck Sea 2) The Bismarck Archipelago separates the Bismarck Sea from the Solomon Sea 3) The Bismarck Archipelago is an island chain of Papua New Guinea 4) Bougainville Island of Papua New Guinea, which was in the news recently, is in the Bismarck Sea Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 1 & 2 only b) 1, 2 & 3 only c) 3 only d) All 18. Which of the following volcanic landforms are built by layer over layer of basaltic magma? 1) Hawaii Island 2) Whakaari / White Island in New Zealand 3) Mariana Islands Select the correct answer using the code given below. a) 1 only b) 1 & 2 only c) 2 & 3 only d) 1 & 3 only 19. Consider the following statements 1) Zealandia is a part of the Australian Continental Plate 2) Except for the Islands of New Zealand, the rest of Zealandia is submerged underwater. 3) Zealandia is a microcontinent Which of the above statements are true? a) All b) 1 only c) 1 & 3 only d) 3 only 22 Solutions 1) b 7) a 13) c 2) b 8) a 14) d 3) b 9) c 15) b 4) d 10) d 16) b 5) a 11) c 17) b 6) b 12) d 18) a 19) d The detailed explaination is provided in a separate file. 23 World-Location-Based Topics for UPSC Civil Services Exam by Pmfias.com Contents Europe .................................................................................................................................................................... 2 Major Geographic Features of Europe ............................................................................................................................. 6 Major Mountain Ranges of Europe ..................................................................................................................................................................... 6 Major Rivers of Europe ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 7 Major Inland Waterways in Europe ...................................................................................................................................................................... 8 Political, Economic & Geographical Regions of Europe ............................................................................................... 11 European Union (EU) ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 11 Schengen Area ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 12 Eurozone....................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 13 European Free Trade Association (EFTA) ......................................................................................................................................................... 14 Baltic states (Baltics, Baltic nations) ................................................................................................................................................................... 14 Nordic Countries ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 14 European Countries that were a part of the Erstwhile USSR ................................................................................................................... 15 Balkans .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 16 Erstwhile Yugoslavia................................................................................................................................................................................................. 17 Turkish Straits ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 19 Great European Plain ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 19 Pannonian Basin ........................................................................................................................................................................................................ 19 Iberian Peninsula ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 20 In News ............................................................................................................................................................................. 20 Matterhorn .................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 20 Iceland commemorates first glacier lost to climate change .................................................................................................................... 21 Economist Intelligence Unit's Global Liveability Index 2019 ................................................................................................................... 21 India attended the virtual XI Petersberg Climate Dialogue (PCD)......................................................................................................... 21 2020 Belarusian protests ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 21 Hagia Sophia............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 22 Scotland Independence Referendum ............................................................................................................................................................... 23 Important Points are highlighted in Blue and Red Trying to mug up all the facts is counterproductive. Focus more on those that are recently in news. Download High Resolution Maps: 1 https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1hWbzmAwjX37nUsepsr8ucigbJPbeiW8S Europe • Europe, just like North America, is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere. • Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. Area • 10.2 million km2 (2% of the Earth's surface – 6th largest continent) Coastline • 38,000 km Sovereign Countries • 51 sovereign states 2 • Largest countries in Europe (European part only): Russia, Ukraine, France, Spain, Sweden & Norway. • Smallest Countries in Europe: 1. Vatican City (enclave in Rome – 0.44 km2), 2. Monaco (bordered by France and the Mediterranean Sea – 2 km2), 3. San Marino (enclave in Italy), 4. Liechtenstein (located between Switzerland and Austria), 5. Malta (an island in the Mediterranean near Sicily), 6. Andorra (located in eastern Pyrenees, bordered by France to the north and Spain to the south) etc. The 6 Microstates of Europe Major Cities • Largest urban areas in terms of population: Istanbul, Moscow, London, Saint Petersburg, Berlin, Madrid, etc. Major Islands/Island • Novaya Zemlya (Russia), Franz Josef Land (Russia), groups • Svalbard (Norway), • Iceland, • the Faroe Islands (Denmark), Zealand (Denmark), • the Channel Islands (France), • the Shetland (U.K), the British Isles (Ireland, Great Britain & Isle of Man), • the Balearic Islands (Spain), • Corsica (France), 3 Largest Lakes • Sardinia (Italy), Sicily (Italy), Aeolian Islands (Italy), • Malta (sovereign nation in the Mediterranean) & • Crete (Greece) 1. Lake Ladoga (Russia) 2. Lake Onega (Russia) 3. Kuybyshev Reservoir (Russia) 4. Lake Vänern (Sweden) 5. Rybinsk Reservoir (Russia) Highest Mountains 1. Mount Elbrus (5642 m) 2. Mont Blanc (4808 m) Longest Rivers 1. Volga (3,690 km) 2. Danube (2,860 km) 3. Ural (2,428 km) 4. Dnieper (2,290 km) 5. Don (1,950 km) 4 5 Major Geographic Features of Europe Major Mountain Ranges of Europe Ural Mountains • (2500 km) The mountain range forms part of the conventional boundary between the continents of Europe and Asia. Scandinavian • They run through the Scandinavian Peninsula. Mountains • The western sides of the mountains drop into the North Sea and Norwegian Sea, form- (1,762 km) Carpathian ing the fjords (long, narrow inlet with steep sides) of Norway. • Mountains (1,500) Alps (1,200 km) The highest range within the Carpathians is known as the Tatra mountains in Slovakia and Poland. • Western Carpathians: Austria, Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia and Hungary • Eastern Carpathians: south-eastern Poland, eastern Slovakia, Ukraine, and Romania • Southern Carpathians: Romania and eastern Serbia • The Alps are the highest mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe. • They stretch across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia. • Mont Blanc (French–Italian border) at 4,808 m is the highest mountain in the Alps. • The Alpine region area contains about a hundred peaks higher than 4,000 metres (four thousanders). Foehn • Foehn is a hot wind which develops on the leeward side of Alps. • The wind helps animal grazing by melting snow and aids the ripening of grapes. Mistral • Mistral blows from the Alps over France towards the Mediterranean. • It is channelled through the Rhone valley. • It is very cold and dry with a high speed. • It brings blizzards into southern France. Caucasus Moun- • The Greater Caucasus range is a natural barrier between Europe and Asia. tains (1,100 km) • The Greater Caucasus is mostly shared by Russia (Europe) and Georgia (Asia), as well as the northernmost parts of Azerbaijan. • Europe's highest mountain, Mount Elbrus, at 5,642 m is in the Greater Caucasus. 6 • The Lesser Caucasus are a part of Asia. • They are occupied by Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, but also extending to parts of north-eastern Turkey and northern Iran. Major Rivers of Europe River Origin Mouth 1. Volga Valdai Hills Caspian Sea • (3,690 km) 2. Danube It is economically the most important river of Europe. Black Forest Black Sea • (2,860 km) The river runs through the second largest number of countries in the world (after the Nile, which runs through 11). • Originating in Germany, the Danube passes through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova and Ukraine. 3. Ural Ural Mountains Caspian Sea • River in Russia and Kazakhstan. Valdai Hills • It flows through Belarus and Ukraine. (2,428 km) 4. Dnieper Black Sea 7 (2,290 km) • It is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus. • The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine. 5. Don — Sea of Azov • (1,950 km) Rhine (1,236 km) It is the second major river of Western Russia. Lake Toma North Sea • The most important waterway of Europe. • It runs through many important industrial centres. Vistuala (1047 km) — Baltic Sea • Poland’s largest river Loire (1,012 km) Massif Central Bay of Biscay • Longest river in France Oder (854 km) — Baltic Sea • For a small distance, it constitutes the boundary between Poland and Germany. Rhone (815 km) Swiss Alps Mediterranean • The river is an important waterway. • It is the only major river flowing directly to Sea the Mediterranean Sea. Seine — English Channel • Important waterway within Paris basin. Elbe — North Sea • Czech Republic & Germany. Major Inland Waterways in Europe Volga–Baltic Wa- • The Volga–Baltic Waterway links the Volga River with the Baltic Sea. terway (Mariinsk • It connects the biggest lake on Earth, the Caspian Sea, to the Ocean. Canal) 8 Volga–Don Ship- • ping Canal Volga–Don Shipping Canal connects the Volga River and the Don River at their closest points. • It provides the most direct navigable connection between the Caspian Sea and the world's oceans via the Sea of Azov and the Black Sea. White Sea–Baltic • Connects the White Sea to Lake Onega, where it joins the Volga-Baltic Waterway. Canal 9 Main-Danube Canal • Connects Main River (a tributary of the Rhine River) to the Danube River, permitting traffic to flow between the North Sea and the Black Sea. Rhone–Rhine Canal • Connects the Rhine (at Basel) to the Rhône (Saone River) and thereby North Sea and the Mediterranean. Amsterdam-Rhine • Connects the port of Amsterdam with the Rhine River. • Connects the Paris Basin with the industrial regions of Alsace-Lorraine. Canal Marne-Rhine waterway 10 Political, Economic & Geographical Regions of Europe European Union (EU) • The EU was established when the Maastricht (Netherlands) Treaty came into force in 1993. • The EU traces its origins to the 1. European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), established by 1951 Treaty of Paris, and 2. European Economic Community (EEC), established by 1957 Treaty of Rome • The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 member states. 11 • Its members have a combined area of 4.2 million km2 and an estimated total population of about 44.7 crore. • The EU has developed an internal single market through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states in those matters where members have agreed to act as one. • EU policies aim to ensure the ✓ free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market; ✓ enact legislation in justice and home affairs; and ✓ maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, fisheries and regional development. • Passport controls have been abolished for travel within the Schengen Area. Members • The original members: Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany. • Members that have adopted the Euro: Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia & Spain. • Members that have not adopted the Euro: Hungary, Czech Republic, Sweden, Denmark, Croatia, Romania & Bulgaria. • On 31 January 2020, the United Kingdom became the first member state to leave the EU. • Earlier, French Algeria (Colonial Algeria), Greenland (Denmark) & Saint Barthélemy (French Overseas Territory in the Lesser Antilles) — had left the EU. • The only member state of the EU which is wholly outside of Europe is Cyprus, which is in Asia. Schengen Area • The Schengen Area comprises European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. • The area is named after the 1985 Schengen Agreement signed in Schengen, Luxembourg. Members • 22 of the 27 EU member states participate in the Schengen Area. • The 5 EU member that are not a part of Schengen Area are Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Romania & Ireland. • Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, and Romania are legally obliged to join the area in the future. • 4 European Free Trade Association (EFTA) members: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland. • 3 European microstates that are not members of the EU: Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City. 12 Eurozone • The eurozone is a monetary union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro as their primary currency and sole legal tender. 13 • The eight remaining members of the European Union continue to use their own national currencies, although most of them will be obliged to adopt the euro in the future. European Free Trade Association (EFTA) • EFTA is free trade area consisting of Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland. • The organization operates in parallel with the European Union (EU). • All four member states are part of the Schengen Area. Baltic states (Baltics, Baltic nations) • Baltics is a geopolitical term, typically used to group the three countries on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. • The three countries do not form an official union but cooperate in the matters of security & defence. • All three countries are members of NATO (to counter the bullying by Russia), the eurozone, the OECD, and the European Union. Nordic Countries Scandinavian • Geographical area consisting of mainland Norway, Sweden and Northern Finland. • Fennoscandian Peninsula is the geographical region comprising the Scandinavian and Peninsula Fennoscandia Kola Peninsulas, mainland Finland, and a small region of North Western Russa. Nordic Countries • The Nordics are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe. • The term includes Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden, as well as the Faroe Islands and Greenland, which are both part of the Kingdom of Denmark. 14 • The Nordic countries have much in common in their way of life, history, religion and social structure. Scandinavia • Scandinavia = Norway + Sweden + Denmark. • In English usage, the term Scandinavia is sometimes used as a synonym or near-synonym for Nordic countries on the grounds that their inhabitants speak Scandinavian languages (related to Norway and Sweden). European Countries that were a part of the Erstwhile USSR • Baltic states: Estonia, Latvia & Lithuania. • Eastern Europe: Belarus, Moldova, Ukraine & Russia. • The three Baltic states were the first to declare their independence from USSR in 1990. 15 Balkans • Balkans (Balkan Peninsula) is usually characterized as comprising Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, and Slovenia. • Moldova, Romania, parts of Turkey and Greece are also often included in the Balkans. 16 Erstwhile Yugoslavia • Yugoslavia was a country that came into existence after WW I in 1918. • It constituted the provisional State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. • The monarchy was replaced by the communist government in 1946. • The six constituent republics that made up Yugoslavia were: 1. Bosnia and Herzegovina (50% of the population is Muslim), 2. Croatia (majority Catholic Christians), 3. Macedonia (majority Orthodox Christians), 4. Montenegro (majority Orthodox Christians), 5. Serbia (majority Orthodox Christians), and 6. Slovenia (majority Catholic Christians). • Serbia contained two autonomous provinces, Vojvodina and Kosovo. Factors that led to the breakup of Yugoslavia 17 Countries where a West Slavic language is the national language Countries where an East Slavic language is the national language Countries where a South Slavic language is the national language • Slavs are peoples who speak the various Slavic languages. • There are three major ethnic groups among people that speak the South Slavic languages. • These ethnic groups are the Bosniaks (predominantly Muslim), Serbs (predominantly Orthodox Christians) & Croats Catholic. • Economic and political crisis in the 1980s (weakened communist regime after the death of Tito), ethnic & religious conflicts among the ethnic groups & rise of nationalism led to the breakup of the Yugoslav state. • Yugoslavia subsequently broke up along its republics' borders, at first into five countries. • Montenegro and Serbia became independent states in 2006 • Kosovo proclaimed its independence from Serbia in 2008. • It has since gained diplomatic recognition as a sovereign state by 112 United Nations member states. • Serbia does not recognize Kosovo as a sovereign state. • India does not recognise Kosovo as an independent nation (we have Kashmir & Khalistan to care for!). Present • At present, the erstwhile Yugoslavia is divided into: 1. Bosnia and Herzegovina 2. Croatia 3. Kosovo (majority Albanian Muslims; minority Serbs) 4. Montenegro 5. North Macedonia (Macedonia until February 2019) 18 6. Serbia 7. Slovenia Turkish Straits • The straits create a series of passages that connect the Aegean and Mediterranean seas to the Black Sea. • They consist of the Dardanelles and the Bosporus. Great European Plain • The European Plain or Great European Plain is the largest mountain-free landform in Europe. • The plain stretches from the Pyrenees mountains and the French coast of the Bay of Biscay in the west to the Russian Ural Mountains in the east. Pannonian Basin • The Pannonian Basin is the region enclosed by the Carpathians and the Transylvanian Alps. • Most of the basin consists of the Great Hungarian Plain. • The Danube River divides the basin roughly in half. 19 Iberian Peninsula • The Iberian Peninsula consists of Spain and Portugal, as well as a small area of Southern France, Andorra and the British overseas territory of Gibraltar. Gibraltar • Area: 6.7 km2 • In 1704, Anglo-Dutch forces captured Gibraltar from Spain. • The sovereignty of Gibraltar is a point of contention in Anglo-Spanish relations. • Gibraltarians rejected proposals for Spanish sovereignty in 2002 referendum. In News Matterhorn • April 2020: Switzerland has shown solidarity for India reeling under coronavirus pandemic by projecting the national tricolor flag on the Matterhorn mountain in the Swiss Alps. • Matterhorn (4478 m) is located border between Switzerland and Italy. 20 Iceland commemorates first glacier lost to climate change • August 20019: Scientists and locals unveil a plaque to the Okjokull ice sheet. • Ok (Okjokull) is the first Icelandic glacier to lose its status as a glacier. • Icelanders call their nation the “Land of Fire and Ice” for its other-worldly landscape of volcanoes & glaciers. Economist Intelligence Unit's Global Liveability Index 2019 • The survey ranks countries across indicators including stability, healthcare, education, infrastructure, etc. • Vienna in Austria, Melbourne and Sydney in Australia make the top three cities in the list. • In India, New Delhi and Mumbai rank 118th and 119th out of 140 cities. • Damascus in Syria, Lagos in Nigeria and Dhaka in Bangladesh rank in the bottom. India attended the virtual XI Petersberg Climate Dialogue (PCD) • PCD is a series of negotiations held in preparation for the yearly UN Climate Change Conferences. • The appointed next COP-president usually is the co-host of PCD. • It has been hosted by Germany since 2010. • The virtual XI Petersberg Climate Dialogue was co-chaired by Germany and the UK (incoming Presidency of the 26th Conference of Parties (COP 26) to UNFCCC). • COP 25 was held at Madrid, Spain in December 2019. 2020 Belarusian protests • The 2020 Belarusian protests are a series of political demonstrations against the last standing dictator in Europe —the Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko. • The demonstrations, which are part of the Belarusian democracy movement, began in the lead-up to and during the 2020 presidential election, in which Lukashenko sought a sixth term in office. Belarus 21 • Belarus is a landlocked country. • Borders: Russia to east, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. • Capital: Minsk. • Belarus broke out of USSR in 1991. • Alexander Lukashenko has served as the country's first president since. • Belarus is the only "dictatorship" in Europe. • The Dnieper is longest river of Belarus. Hagia Sophia Turkey's decision to convert Istanbul's Hagia Sophia back into a mosque. • In the 6th century, Hagia Sophia was built as a Christian place of worship in Constantinople (Istanbul). • It is located in the western half of Istanbul (on the west bank of Bosporus Strait). • In 1453, after the Fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire, it was converted into a mosque. • In 1935 the secular Turkish Republic established it as a museum. • In 2020, it re-opened as a mosque (Recep Tayyip Erdoğan’s vote bank politics). 22 Istanbul • Formerly known as Byzantium and Constantinople. • In 1923, after the Turkish War of Independence, Ankara was chosen as the new Turkish capital, and Constantinople's name was changed to Istanbul. • Istanbul is the most populous city in Turkey and the largest city in Europe. • It is a transcontinental city straddling the Bosporus strait (which separates Europe and Asia). Scotland Independence Referendum • In 2014 Scotland Independence Referendum, 55% of the voters voted against independence. • In 2016, Scotland voted in favour of “Remain in the EU” by 62% to 38%. • The U.K. left EU in 2020. • Scotland being taken out of the EU against their will, are demanding an independence referendum in 2020. The United Kingdom • In 1707, the Kingdom of Scotland entered into a political union with the Kingdom of England to create the new Kingdom of Great Britain. • In 1801, the Kingdom of Great Britain entered into a political union with the Kingdom of Ireland to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. • In 1921, after the Irish War of Independence, Ireland was partitioned to create Northern Ireland. • The Irish Free State was created and the Northern Ireland remained within the United Kingdom. 23 24 World-Location-Based Topics for UPSC Civil Services Exam by Pmfias.com Contents North America ....................................................................................................................................................... 1 Major Geographic features of North America ................................................................................................................ 2 Major Lakes of North America .......................................................................................................................................................... 3 Major Rivers of North America ......................................................................................................................................................... 5 Major Deserts of North America ....................................................................................................................................................... 5 Major Islands/Island groups of North America ................................................................................................................................. 6 Geographic Regions of North America ............................................................................................................................................ 11 In News ............................................................................................................................................................................. 12 Caribbean Community and Common Market (CARICOM) .............................................................................................................. 12 Hurricane Dorian (August 2019) ..................................................................................................................................................... 13 Hurricane Laura (August 2020) ....................................................................................................................................................... 13 Trump wants to purchase Greenland ............................................................................................................................................. 14 Important Points are highlighted in Blue and Red Trying to mug up all the facts is counterproductive. Focus only on those that are recently in news. Download High Resolution Maps: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1hWbzmAwjX37nUsepsr8ucigbJPbeiW8S North America Area Longitudinal Extent • 24.7 million km2 (3rd largest continent) • 168° W to 55° W — Cape Prince of Wales (Alaska) to Cape Saint Charles (Labra- of the Mainland Latitudinal Extent of dor) • 7° N to 72° N — Punta Mariato (Panama) to Murchison Promontory (Canada) Coastline • ~ 60,000 km Sovereign Countries • 23 • In the decreasing order of population: United States, Mexico, Canada, Guate- the Mainland mala, Cuba, Haiti, Dominican Republic, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa 1 Rica, Panama, Jamaica, Trinidad and Tobago, Bahamas, Belize, Barbados, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Grenada, Antigua and Barbuda, Dominica & Saint Kitts and Nevis. Major Cities • In the decreasing order of population: Mexico City, New York City, Los Angeles, Toronto & Chicago. Largest Lake • Lake Superior (world's largest freshwater lake by surface area, and the third largest freshwater lake by volume — after Lake Baikal & Lake Tanganyika) Highest Mountains Longest Rivers • Mount Denali (Mount McKinley) (6190 m) 1. Missouri (4087 km) 2. Mississippi (3765 km) 3. Yukon (3186 km) Major Geographic features of North America 2 Major Lakes of North America Great Lakes West to East ➔ Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie & Ontario In decreasing order of surface area ➔ Superior > Huron > Michigan > Erie > Ontario • Great Lakes of North America are a series of interconnected freshwater lakes which connect to the Atlantic Ocean through the Saint Lawrence Seaway. 3 • The Great Lakes are formed in a fault zone of highly deformed rocks near the Canada–United States border. • The Great Lakes are the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total area. • They are the second-largest by total volume, containing 21% of the world's surface fresh water. • Lake Baikal is the largest freshwater lake by volume, containing 22–23% of the world's fresh surface water. • Lake Superior is the largest freshwater lake in th world by surface area. • It is the second-largest lake in the world by surface area — Caspian Sea is the largest lake by surface area. • Lake Michigan is the largest lake that is entirely within one country. • The Lake Superior is the deepest among the Great Lakes. Niagara Falls 4 • Niagara Falls is a group of three waterfalls situated across the boder between Canada and the US. • The largest of the three is Horseshoe Falls, also known as Canadian Falls. • The smaller American Falls and Bridal Veil Falls lie within the United States. • The falls are located on the Niagara River, which drains Lake Erie into Lake Ontario. Other major lakes Great Salt Lake • The Great Salt Lake is an endorheic ( no outlet) lake in the the U.S. state of Utah. • Its salinity levels are comparable to that of the Dea Sea. Great Bear Lake • It is the largest lake entirely in Canada. Great Slave Lake • Great Slave Lake is the deepest lake in North America. Major Rivers of North America Missouri (4087 km) • Longest river in North America. • Source: Rocky Mountains • Joins Mississippi near St. Louis (in Missouri) • Source: Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota • Mouth: Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico Yukon (3186 km) • Longest river in Alaska Rio Grande (3051 km) • Longest river of Mexico St. Lawrence • The Saint Lawrence Seaway is a system of locks, canals, and that permits ves- Mississippi (3765 km) sels to travel between the Atlantic Ocean and the Great Lakes. • The seaway is named for the Saint Lawrence River, which flows from Lake Ontario to the Atlantic Ocean. Colorado • The Grand Canyon is carved by the Colorado River. • The Grand Canyon is over 400 km long, up to 29 km wide and attains a depth of over a mile in some places. Major Deserts of North America 5 Great Basin Desert Chihuahuan Desert • It is between the Sierra Nevada and the eastern edge of the Rocky Mountains. • It is a temperate desert with hot, dry summers and snowy winters. • The Great Salt Lake is located in this desert. • It is the largest desert of North America. • It covers parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. • It is bordered on the west by the Sonoran Desert, Sierra Madre Occidental range and on the east by the Sierra Madre Oriental range. Mojave Desert • It is in the Southwestern United States, primarily within south-eastern California and southern Nevada. • The Mojave Desert contains the lowest, driest and hottest place in North America: Death Valley at 86 m below sea level, where the temperature often surpasses 49 °C in summer. Sonoran Desert • It covers large parts of the Southwestern United States in Arizona and California and of North-western Mexico. Major Islands/Island groups of North America Greenland • Greenland is the world's largest island. • It is an autonomous territory within the Kingdom of Denmark (takes care of defence and foreign policy). • Three-quarters of Greenland is covered by the only permanent ice sheet outside Antarctica. • With a population of about 53,000, it is the least densely populated territory in the world. • Nuuk is the capital and largest city of Greenland. • The majority of its residents are Inuit (indigenous peoples inhabiting Greenland, Canada and Alaska). Thule Air Base • Thule Air Base in Greenland is the United States Air Force's northernmost base. Canadian Arctic Archipelago • The Arctic Archipelago is a group of all islands lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland excluding Greenland (an autonomous territory of Denmark). • Baffin Island is the largest island of Canada and the world's 5th largest island. • Victoria Island is the world's 8th largest island. • Ellesmere Island is the world's 10th largest island. 6 Newfoundland • The island is separated from the Labrador Peninsula by the Strait of Belle Isle and from Cape Breton Island by the Cabot Strait. The Grand Banks • The Grand Banks of Newfoundland are a series of underwater plateaus south-east of the island of Newfoundland on the North American continental shelf. • The Grand Banks are one of the world's richest fishing grounds. Antilles • The Antillean islands are divided into two smaller groupings: The Greater Antilles and the Lesser Antilles. • The islands of the Lesser Antilles along the north-western Venezuelan coast are called the Leeward Antilles. • In terms of geology, the Greater Antilles are made up of continental rock, as distinct from the Lesser Antilles, which are mostly young volcanic or coral islands. • The Greater Antilles includes the larger islands of the Cayman Islands, Cuba, Hispaniola (subdivided into the nations of the Dominican Republic and Haiti), Jamaica, and Puerto Rico (unincorporated overseas territory of the US). 7 The Greater Antilles and Lesser Antilles Island Arcs (Map from Google Earth) Major Passages in the Antilles 8 Islands in the Lesser Antilles Island Arcs (Map from Google Earth) Lucayan Archipelago • The Lucayan Archipelago consists of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands (UK). • The Lucayan Archipelago is usually not included in the Greater Antilles. West Indies • The West Indies is the subregion that includes all the islands in the Antilles, plus Lucayan Archipelago. • Nowadays, the term West Indies is often interchangeable with the term Caribbean, although the latter may also include some North and South American mainland countries which have Caribbean coastlines. Hawaiian Islands 9 • The Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of 8 major islands, several atolls & seamounts in the North Pacific. • They are the exposed peaks of a great undersea mountain range known as the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain, formed by volcanic activity over a hotspot in the Earth's mantle. • Hawaii island is the biggest and youngest island in the chain, built from five volcanoes. • Mauna Loa, taking up over half of the Big Island, is the largest shield volcano on the Earth. • The Hawaiian Islands have many earthquakes, generally caused by volcanic activity. • The majority of eruptions in Hawaii are Hawaiian-type eruptions (fluid basaltic magma). Mauna Kea • Mauna Kea (4169) is a dormant volcano on the island of Hawaii. • It is the highest point in the state of Hawaii. • When measured from its underwater base, Mauna Kea is the tallest mountain in the world (~10 km). • With its high elevation, dry environment, and stable airflow, Mauna Kea's summit is one of the best sites in the world for astronomical observation. • Thirteen telescopes funded by eleven countries have been constructed at the summit. • Their construction on a landscape considered sacred by Native Hawaiians continues to be controversial. 10 Mauna Loa • Mauna Loa is an active shield volcano with relatively gentle slope. • Lava eruptions from Mauna Loa are silica-poor and very fluid, and they tend to be non-explosive. • Mauna Loa's most recent eruption occurred in 1984. Kīlauea • Kīlauea is an active shield volcano in the Hawaiian Islands that last erupted in 2018. • Historically, Kīlauea is the most active of the five volcanoes that together form the island of Hawaii. Aleutian Islands • Aleutian Islands are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. • Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russia. • They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean. • The islands form the northernmost part of the Pacific Ring of Fire. Geographic Regions of North America Dependent/Overseas Territories in North America Dependent Territories of UK Dependent Territories of France ✓ Anguilla (Lesser Antilles) ✓ Guadeloupe (Lesser Antilles) ✓ Bermuda ✓ Martinique (Lesser Antilles) ✓ British Virgin Islands (Lesser Antilles) ✓ Saint Barthélemy (near Anguilla in Lesser Antilles) ✓ Cayman Islands (Greater Antilles) ✓ Saint Martin (near Anguilla in Lesser Antilles) ✓ Montserrat (Lesser Antilles) ✓ Saint Pierre and Miquelon (near Newfoundland) ✓ Turks and Caicos Islands (Lucayan Archipelago) Dependent Territories of Netherlands Dependent Territories of US ✓ Caribbean Netherlands (Leeward Antilles) Sint Maarten (near Anguilla in Lesser Antilles) ✓ Puerto Rico (Greater Antilles) ✓ ✓ United States Virgin Islands (Lesser Antilles) Others: Greenland (Kingdom of Denmark) Central America • Central America consists of seven countries: El Salvador, Costa Rica, Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and Panama. 11 • Central America is a part of the Mesoamerican biodiversity hotspot — northern Guatemala to central Panama. • Central America Volcanic Arc is a seismically active zone. In News Caribbean Community and Common Market (CARICOM) • Sep 2019: PM Modi met with the leaders of the CARICOM group of countries on the side lines of the UN General Assembly in New York. • The CARICOM grouping has 15 members-states — Haiti, Jamaica, Bahamas, Belize, Guyana, Suriname, Antigua and Barbuda, Dominica, Barbados, St. Kitts and Nevis, Montserrat, St Lucia, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, Grenada, and Trinidad & Tobago. 12 Hurricane Dorian (August 2019) • Category 5 hurricane. • It was the most intense tropical cyclone on record to strike the Bahamas. • The hurricane made landfall on Cape Hatteras at Category 2 intensity. • It transitioned into an extratropical cyclone before striking first Nova Scotia and then Newfoundland. Hurricane Laura (August 2020) 13 • Category 4 hurricane. • Path ➔ Lesser Antilles ➔ Greater Antilles ➔ Gulf of Mexico ➔ Louisiana Most hurricane vulnerable states in USA 1. Florida 3. North Carolina 5. South Carolina 7. Georgia 2. Texas 4. Louisiana 6. Alabama 8. Mississippi Trump wants to purchase Greenland 14 • US President Donald Trump’s recent offer to buy Greenland led to a little diplomatic tiff with Denmark. USA land deals • Alaska: purchased in 1867 from Russia. • Louisiana: purchased from France. • Florida: purchased from Spain. • Philippine Island: Bought from Spain in 1946, given up later. • Danish West Indies: (Now known as US Virgin Islands). Bought from the Danes in 1916. • The US has been trying to buy Greenland for a long time. Other land deals • Pamir Mountains: China struck a deal with Tajikistan in 2011 to buy 1,000 sq km in the Pamir Mountains area. • Gwadar: Pakistan bought the port city from Oman in 1958. • Caribbean islands: France bought Saint Barthelemy in the West Indies from Sweden in 1878. Greenland’s strategic value • Greenland’s strategic value is linked to 15 1. new shorter North Atlantic shipping lanes opening up due to melting polar ice caps, 2. vast natural resources, including coal, zinc, copper, iron ore and rare minerals, and 3. efforts by China (Polar Silk Road through the North Atlantic shipping lanes) to gain strategic influence, and 4. advantageous location for the U.S. armed forces. • The U.S. and Greenland have had an agreement since WW II to house American military assets on the island. • Thule Air Base, America’s northernmost Air Force base, has operated since 1943 in Greenland. • The US is opening a consulate in Greenland after closing its first consulate after the Second World War. 16 World-Location-Based Topics for UPSC Civil Services Exam by Pmfias.com Contents South America ....................................................................................................................................................... 1 Major Geographic Features of South America ................................................................................................................ 4 Amazon River................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 4 Major Mountain & Highlands in South America ............................................................................................................................................ 5 Major islands/island groups of South America ............................................................................................................................................... 7 Major Agricultural Regions ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 8 Major Deserts of South America ......................................................................................................................................................................... 10 Major Water bodies ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 11 Other major geographic features in South America ................................................................................................................................... 11 In News ............................................................................................................................................................................. 12 Drake Passage ............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 12 Puerto Williams & Beagle Channel .................................................................................................................................................................... 12 Ecuador & Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) ............................................................................................ 13 Latin America .............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 15 Important Points are highlighted in Blue and Red Trying to mug up all the facts is counterproductive. Focus only on those that are recently in news. Download High Resolution Maps: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1hWbzmAwjX37nUsepsr8ucigbJPbeiW8S South America 1 2 3 Area • 17.84 million km2 (4th largest continent) Longitudinal Extent • 81° W to 34° W (~5300 km — Point Pariñas (Peru) to Cape Branco (Brazil)) • 12° N to 55° S (~7560 km — Point Gallinas (Colombia) to Cape Horn (Chile)) Coastline • ~25,400 km Sovereign Countries • 12 • In decreasing order of area: Brazil (8.5 million km2 – 5th largest country in the of the Mainland Latitudinal Extent of the Mainland world), Argentina (2.8 million km2 – 8th largest), Peru, Colombia, Bolivia, Venezuela, Chile, Paraguay, Ecuador, Guyana, Uruguay & Suriname. • In decreasing order of population: Brazil (19.8 crore), Colombia (4.5 crore), Argentina, Peru & Venezuela. Dependent Territo- • ries Major Cities French Guiana (France), Falkland Islands (UK) & South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (UK) • Most of the population lives near the continent's western or eastern coasts. • In decreasing order of population: São Paulo (Brazil), Lima (Peru), Bogotá (Colombia), Rio de Janeiro (Brazil), Santiago (Chile), Caracas (Venezuela), Buenos Aires (Argentina), Salvador (Brazil), Brasília (Brazil), Fortaleza (Brazil), etc. Major Islands/Island • groups Galapagos Islands (Ecuador), Tierra del Fuego Archipelago (Chile & Argentina), Falkland Islands (UK) & South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (UK) Largest Lake • Lake Titicaca Highest Mountains 1) Mount Aconcagua (6960 m) 2) Mount Ojos del Salado (6893 m) — highest active volcano in the world Longest and largest • Amazon River (6575 km) River Major Geographic Features of South America • The geography of South America: Andes mountains; highlands of Brazil; highlands between Amazon River and Orinoco River and lowlands of Amazon, Orinoco, and Paraná Rivers. Amazon River 4 • Source: Mantaro River (in Andes Mountains) • Mouth: Atlantic Ocean • Length: 6,575 km • The Amazon River is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world. Amazon rainforest • The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. • It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname and Venezuela. • The Amazon basin encompasses 7 million km2 of which 5.5 million km2 is covered by the Amazon rainforest. • The forest is contained within Brazil (60%), Peru (13%), Colombia (10%), Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, Guyana, Suriname and French Guiana. • The Amazon represents over half of the planet's remaining rainforests. • More than 50% of the dust fertilizing the Amazon rainforest comes from the depression in Northern Chad in the Sahara Desert. The dust contains phosphorus, important for plant growth. Major Mountain & Highlands in South America Mount Aconcagua 5 • Aconcagua (6960 m) is the highest mountain in the Americas and the highest outside of Asia. • It located in Argentina close to the Chilean border. • The mountain is one of the so-called Seven Summits of the seven continents. Seven Summits of the seven continents • Seven Summits are the highest mountains of each of the seven continents. 1. Asia: Mount Everest (8,850 meters) 2. South America: Mount Aconcagua (6,960 m) 3. North America: Denali (also called Mount McKinley) (6,190 m) 4. Africa: Kilimanjaro (5,895 m) 5. Europe: Mount Elbrus (5,642 m) 6. Antarctica: Vinson Massif (4,892 m) 7. Australia: Mount Kosciuszko (2,228 m) (The westerners consider the mainland Australia as a separate continent) • Puncak Jaya Peak (4884 m) in the Indonesian part of New Guinea Island is the highest peak of the Australian Continent. However, in the west, Australian continent is referred to as Oceania. Mount Ojos Del Salado • Ojos del Salado is an active stratovolcano in the Andes on the Argentina–Chile border. 6 • It is the highest active volcano in the world at 6,893 m. • It is also the second highest mountain in both the Western Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. Brazilian Highlands • Brazilian Highlands is an eroded plateau region of central and south-eastern Brazil. • Ancient basaltic lava flows gave birth to much of the region. • The region comprises more than half of the country’s landmass and settlements. • It is the main source of Brazil's abundant mineral wealth. • The highlands are also significant for coffee, sugarcane, and other plantation agriculture. Guiana Highlands • Guiana Highlands region is located north of the Amazon and south of the Orinoco River. • They cover the southern half of Venezuela, the northern part of Brazil, and a portion of eastern Colombia. • They are geologically similar to the Brazilian Highlands. Major islands/island groups of South America Falkland Islands (UK) • The Falkland Islands is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. • As a British overseas territory, the United Kingdom takes responsibility for their defence and foreign affairs. • Its sovereignty status is part of an ongoing dispute between Argentina and the United Kingdom. • Major economic activities include fishing, and sheep farming, with an emphasis on high-quality wool exports. South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (UK) • South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (SGSSI) is a British Overseas Territory. • Argentina continues to claim sovereignty over South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. • The Argentine claim over South Georgia contributed to the 1982 Falklands War. Tierra del Fuego • Tierra del Fuego is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. • The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego and a group of many islands. • Tierra del Fuego is divided between Chile and Argentina, with the latter controlling the eastern half of the main island and the former the western half plus the islands south of Beagle Channel. 7 • Patagonian sheep farming and petroleum extraction dominates economic activity in the region. Strait of Magellan • The Strait of Magellan is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. • The strait is more sheltered than the Drake Passage (stormy open sea route around Cape Horn). Galápagos Islands • The Galápagos Islands are a part of Ecuador. • They are an archipelago of hotspot volcanic islands distributed on either side of the equator. • The mantle plume beneath the eastward moving Nazca Plate has given rise to island chain and seamounts. Major Agricultural Regions Los Llanos or Llanos • Los Llanos is a vast tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela. • It is an ecoregion of the flooded grasslands and savannas biome. • The Llanos' main river is the Orinoco, which forms part of the border between Colombia and Venezuela. Pampas • The Pampas are fertile lowlands covering parts of Argentina, all of Uruguay and Brazil's southern state. • The climate is temperate, with precipitation more or less evenly distributed through the year, making the soils appropriate for agriculture. 8 • Frequent wildfires ensure that only small plants such as grasses flourish, and trees are less common. Gran Chaco (Chaco plain) • The Gran Chaco is a semiarid lowland located west of the Paraguay River and east of the Andes. • It is mostly an alluvial sedimentary plain shared among Paraguay, Bolivia, and Argentina. • The Chaco is one of South America's last agricultural frontiers. • Agricultural expansion has made it one of the most deforested areas on the planet. Patagonia • Patagonia is a sparsely populated region at the southern end of South America. • The region lies in Argentina and Chile. • The region has lakes, fjords, and glaciers in the west and deserts and steppes to the east. • In late 19th and early 20th centuries, sheep farming expanded across the Patagonian grasslands making the southern regions of Argentina and Chile one of the world's foremost sheep farming areas. 9 Major Deserts of South America Atacama Desert • The Atacama or Peruvian Desert is the driest place on earth. What makes it so dry? • Rain shadow effect of the Andes. • Off-shore trade winds & westerlies that blow far to the south of Tropic of Capricorn • Cold ocean currents: cold Humboldt current and upwelling of cold water due to Walker Circulation. • The most arid region is situated between the Andes and the Chilean Coast Range (two-sided rain shadow). Patagonian Desert • The Patagonian Desert (Patagonian Steppe) is the largest desert in Argentina. • It is located primarily in Argentina and is bounded by the Andes, to its west, and the Atlantic Ocean to its east, in the region of Patagonia, southern Argentina. 10 Major Water bodies Lake Titicaca • Lake Titicaca is a large, deep, freshwater lake in the Andes on the border of Bolivia and Peru. • It is often called the "highest navigable lake (3,812 m)" in the world. • By volume of water and by surface area, it is the largest lake in South America. Lake Maracaibo • Lake Maracaibo is a brackish tidal bay in Venezuela and an "inlet of the Caribbean Sea". • Lake Maracaibo has a larger surface area than Lake Titicaca, but it is a tidal bay, not a lake. Other major geographic features in South America Orinoco River • Length: 2,250 km • Its drainage basin is shared between Venezuela and Colombia. • Orinoco forms part of the border between Colombia and Venezuela and flows through the Llanos. Paraná River Angel falls • Length: 4,880 km • The Paraná River runs through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina. • It is the second longest river of South America. • It merges with the Paraguay and Uruguay Rivers and flows into Río de la Plata. • Angel Falls is a waterfall in Venezuela. 11 • It is the world's highest uninterrupted waterfall, with a height of 979 metres and a plunge of 807 m. Machu Picchu • Machu Picchu is a 15th-century citadel, located in the Eastern Cordillera (a branch of Andes) of southern Peru. • Machu Picchu is UNESCO World Heritage Site and is one of the New Seven Wonders of the World. La Paz • La Paz, Bolivia, is the highest capital city in the world. • It is 3,500 m above sea level. In News Drake Passage • In 2019, a group of men become the first to traverse the infamous Drake Passage without outside assistance. • Drake Passage is the body of water between Cape Horn, Chile & the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. • Navigation through Drake Passage is dangerous because of its violent cold gusts of westerlies and icebergs. Puerto Williams & Beagle Channel • Puerto Williams in Chile has become the world’s southernmost city after its status was upgraded to city. • It took over the title from Ushuaia in Argentina which was world’s southernmost city till recently. • Ushuaia is located on northern bank of the Beagle Channel. 12 • Puerto Williams is located on southern bank of the Beagle Channel. • Beagle Channel is a strait in Tierra del Fuego Archipelago (shared by Chile and Argentina). Ecuador & Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) • Ecuador decided to withdraw its membership of OPEC effective 1 January 2020. Ecuador • Capital: Quito • Official language: Spanish • Neighbourhood: Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west • Ecuador also includes the Galápagos Islands in the Pacific. • It is one of the 17 megadiverse countries in the world. 13 17 megadiverse countries of the world OPEC • OPEC is an intergovernmental organization founded in Baghdad, Iraq, in 1960. • It is headquartered in Vienna, Austria. Members • It currently has 13 Member Countries. • Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela are the founding members. • Other members: Libya, the United Arab Emirates, Algeria, Nigeria, Gabon, Angola, Equatorial Guinea and Republic of the Congo. • The 13 member countries account for ~40 percent of global oil production and ~80 percent of the world's "proven" oil reserves. • In October 2019, Saudi Arabia invited Brazil to join OPEC. • Ecuador withdrew its membership of OPEC effective 1 January 2020. • Indonesia & Qatar have also terminated their membership earlier. Objective • OPEC’s objective is to unify the petroleum policies and ensure the stabilization of oil markets. 14 • OPEC decisions have come to play a prominent role in the global oil market and international relations. • Economists often cite OPEC as a textbook example of a cartel that cooperates to reduce market competition. OPEC+ • A larger group called OPEC+ was formed in late 2016, to have more control on global crude oil market. • OPEC plus countries include OPEC members plus 10 other members — Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Russia, South Sudan and Sudan. Note: Ecuador is not a part of OPEC anymore Russia–Saudi Arabia oil price war of 2020 • The price war was triggered by a break-up in dialogue between the OPEC and Russia over proposed oilproduction cuts in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. • Russia walked out of the agreement, leading to the fall of the OPEC+ alliance. • This economic conflict resulted in a sheer drop of oil price in March & April. Latin America • Countries in Latin America were constantly in news due to protests and political instability. • Latin America is the region in the Western Hemisphere where Spanish, Portuguese, and French are predominantly spoken. 15 • It is generally understood to consist of the continent of South America, Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean Islands. Venezuela • The Venezuelan economic crisis started in 2010 during the presidency of Hugo Chávez. • It is marked by hyperinflation & starvation, resulting in massive emigration of Venezuelans into Colombia. • Overdependence on oil, falling oil prices, corruption, international sanctions & unsustainable welfare schemes were the primary reasons for the crisis. • The crisis continues even today, and Venezuela has one of the highest crime rates in the world. Other Countries • Bolivia: disputed election results led to massive protests in November 2019. • Peru: political instability has become a recurrent feature since 2017.’ • Ecuador: the 2019 Ecuadorian protests forced the President to move his administration from capital Quito to the port city of Guayaquil. 16