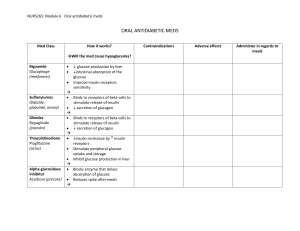
AHMET & JESSIE INSULIN & GLUCAGON GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS INSULIN Insulin is a hormone that reduces blood sugar levels. It is secreted by the beta cells of the pancreas. The main targets for insulin are the liver, muscle, and adipose tissue. It helps cells in the body use glucose for energy. Insulin is a key part of glucose homeostasis in the body.Without enough insulin, blood sugar levels can rise and lead to diabetes. People with diabetes may use insulin medication to manage their blood sugar levels. Insulin GLUCAGON Glucagon is secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas. The liver is the main target of glucagon. This hormone triggers your liver to release stored glucose, or glycogen, into the bloodstream after converting it into a form that can be used. Glucagon generally elevates the blood glucose levels by promoting gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis. Excessive amounts of glucagon can contribute to hyperglycemia (high blood suger) and a glucagon deficiency can lead to hypoclycemia (low blood sugar. Blood sugar irregularities are most common in people with diabetes. Glucagon