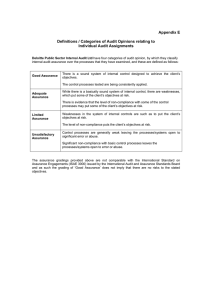
Audit and Assurance Chapter 1: Intro to Audit and Assurance What is assurance? o An assurance engagement in which a practitioner obtains sufficient appropriate evidence in order to express a conclusion designed to enhance the degree of confidence of the intended user other than the responsible party about the outcome of the evaluation or measurement of a subject matter against criteria (IFRS) Elements of Assurance Engagement (5 mark question possible) * o Three Parties Involvement Practitioner – Auditor Intended Use – Shareholder (also public) Responsible Party (Directors) o Appropriate Subject Matter – Financial Statements o Suitable Criteria – IFRS (fr framework) o Sufficient Appropriate Evidence Sufficient (quantity) and appropriateness (quantity) Needed to provide a basis for the opinion o Written Assurance Report – Independent Auditors Report Report vs opinion is different Assurance Engagements: o Audit of f/s o Review of f/s o Systems reliability report o Verification of social and environmental information (some are mandatory/or as a sign of marketing) o Review of internal controls (well designed and functioning) o VMF audit in public sector organisations Value for Money: the 3 E’s Economy: most economical, not overspending but also not sacrificing quality Efficiency: maximum output Effective: objective should be met Types of Assurance Engagements: * o Reasonable Assurance Engagement: (audit of f/s) The practitioner: Gathers sufficient appropriate evidence to be able to draw reasonable conclusions Perform very thorough procedures (increase sample size, verify as many transactions) Conclude that subject matter (f/s) conforms in all material respects with the suitable criterea (IFRS) Gives positive worded assurance opinion Gives high level of assurance (confidence) Gives TRUE AND FAIR view o Limited Assurance Engagements (all other assignments except f/s) The practitioner: o o o o o Gathers sufficient appropriate evidence to be able to draw limited conclusions Performs significantly fewer procedures, mainly enquiries and analytical procedures (comparisons) Concludes that the subject matter, in respect to the suitable criteria, is plausible in the circumstances Gives negatively worded assurance conclusion Gives moderate or lower level of assurance than that of an audit Nothing has come to our attention that causes us to believe that the f/s are not true and fair The confidence inspired by a reasonable assurance report > limited assurance report o Therefore: There are more regulations/standards governing a reasonable assurance assignment The procedures carried out will be more thorough and evidence gathered will be of a higher quality Objective of an Auditor Obtain reasonable assurance (True and Fair view) Express an opinion (Audit Opinion – objective of an auditor) Need for External Audit Agency Relationship (shareholders vs directors = external audit) Benefit of an Audit Higher quality information which is more reliable Independent scrutiny and verification may be valuable to management (may learn) Reduces risk of fraud and errors Enhances credibility of f/s (loan providers) Deficiencies in the Internal Control Systems (ICS) – and report and recommend Expectation Gap * Some users incorrectly believe that an audit provides absolute assurance that the audit opinion is a guarantee the f/s is “correct.” This and other misconceptions about the role of an auditor are referred to as the “expectations gap.” A belief that auditor tests all transactions and balances A belief that auditors are required to detect all fraud A belief that auditors are responsible for preparing the f/s Review Engagements Is an example of a limited assurance engagement Purpose and objective of a review engagement: o Company is required to have an audit may choose to have a review of it’s financial statement instead. o The review will still provide some assurance to users but is likely to cost less and less disruptive than the audit. o The procedure will mainly focus on analytical procedures and enquiries of management. o Stakeholder Groups with an interest in the f/s: Shareholders Employees (wages, future career prospects) Those charged with Governance (NED’s) Customers and Suppliers Lenders The Government (Tax)