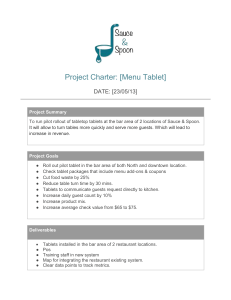
GROUP 1 CHAPTER II – PROJECT MANAGEMENT & INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY ! GROUP MEMBERS: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. ANDAYA, VICTOR MARVIN KEITH C. ALAVADO GENALYN D. VILLAFUERTE PATRICK JUSTIN L. ARIADO MINALYN LADYONG CHAPTER II 2 CHAPTER II - TOPICS 1 2 3 4 5 a) A Systems view of Project Management a) Focusing on Stakeholder Needs a) Project Phases and the Project Life Cycle a) The Context of Information Technology Projects a) Recent Trends Affecting Information Technology Project Management b) Understanding Organizations 3 1 Project Management helps project managers take a holistic approach to project planning, execution, and control by considering the interconnected nature of the project's components. a) It provides a comprehensive framework for managing complex IT projects, enabling project managers and IT professionals to make informed decisions, effectively manage risks, and achieve successful project outcomes. b) Addressing the three spheres of systems management business, organization, and technology can have a huge impact on selecting and managing projects successfully. “ • What will the tablet project cost the college? • What will it cost students? • What will support cost be? • Will the tablet project affect all students, just traditional students, or only certain majors? • How will the project affect students who already have tablets or laptops? • Who will develop special applications or books for the tablets? • Who will train students, faculty, and staff? • What will the enrollments? impact be on • Should the tablets be based on Apple, Microsoft, Android, or another system? • What application will be required? BUSINESS • What will the hardware specifications be? ORGANIZATION TECHNOLOGY • How will the tablets affect various networks and speed? • Will more power cords be required in the classroom? 2 To improve the success rate of IT projects, it is important for project managers to develop a better understanding of people as well as organizations. a) You can try to understand organizations better by focusing on different perspectives. Organizations can be viewed as having four different frames: structural, human resources, political, and symbolic. a) Structural Frame Human Resource Frame • Roles and responsibilities, coordination, and control. Organizational charts help describe this frame. • Providing harmony between needs of the organization and needs of people. Political Frame Symbolic Frame • Coalitions composed of varied individuals and interest groups. Conflict and power are key issues. • Symbols and meanings related to events. Culture, language, traditions, and image are all parts of this frame. b) The three general classifications of organizational structures are the functional, project, and matrix. b) b) b) Organizational Structure and its influences on projects. c) It is very powerful, and many people believe the underlying causes of many companies’ problems are not in the organizational structure or staff; they are in the culture. c) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Member Identity Group Emphasis People Focus Unit Integration Control 6. Risk Tolerance 7. Reward Criteria 8. Conflict Tolerance 9. Means-ends Orientation 10. Open-Systems Focus THANK YOU! 18