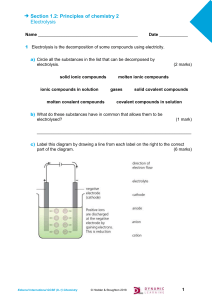
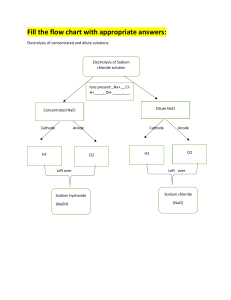
Section 1.2: Principles of chemistry 2 Electrolysis Name __________________________________________ Date ____________ 1 Electrolysis is the decomposition of some compounds using electricity. a) Circle all the substances in the list that can be decomposed by electrolysis. solid ionic compounds ionic compounds in solution molten covalent compounds (2 marks) molten ionic compounds gases solid covalent compounds covalent compounds in solution b) What do these substances have in common that allows them to be electrolysed? (1 mark) _________________________________________________________________ c) Label this diagram by drawing a line from each label on the right to the correct part of the diagram. (6 marks) Edexcel International GCSE (9–1) Chemistry © Hodder & Stoughton 2018 1 Section 1.2: Principles of chemistry 2 Electrolysis d) A student did some investigations into the electrolysis of solutions of sodium chloride, sulfuric acid and copper sulfate. Complete the table to show the student’s results. (3 marks) Solution Ions in solution Product(s) at cathode sodium chloride Na+, Cl−, H+, OH− hydrogen gas Product(s) at anode sodium hydroxide solution sulfuric acid H+, SO42− , OH− copper sulfate Cu2+, SO42− , H+, OH− oxygen gas copper metal e) Explain why each solution contains the ions H+ and OH−. (1 mark) ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 2 The reactions at the cathode and anode for each investigation can be represented by half equations. Write the half equations for: a) the production of hydrogen gas in the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution (1 mark) _________________________________________________________________ b) the production of copper metal in the electrolysis of copper sulfate solution (1 mark) _______________________________________________________________________ c) the production of oxygen gas in the electrolysis of sulfuric acid solution (1 mark) _______________________________________________________________________ 3 Explain why: a) the reactions at the cathode are reduction reactions (1 mark) _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Edexcel International GCSE (9–1) Chemistry © Hodder & Stoughton 2018 2 Section 1.2: Principles of chemistry 2 Electrolysis b) the reactions at the anode are oxidation reactions (1 mark) _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ c) the anode and cathode must be made from inert substances such as carbon or platinum. (1 mark) _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 4 The student repeated the investigation using molten lead(II) bromide instead of a solution of lead bromide. At the cathode lead metal was produced. a) Write a half equation for the production of lead at the cathode during the electrolysis. (1 mark) _____________________________________________________________________ b) Suggest the products that will be made if molten sodium chloride is electrolysed. State where each product will be made. (4 marks) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Edexcel International GCSE (9–1) Chemistry © Hodder & Stoughton 2018 3