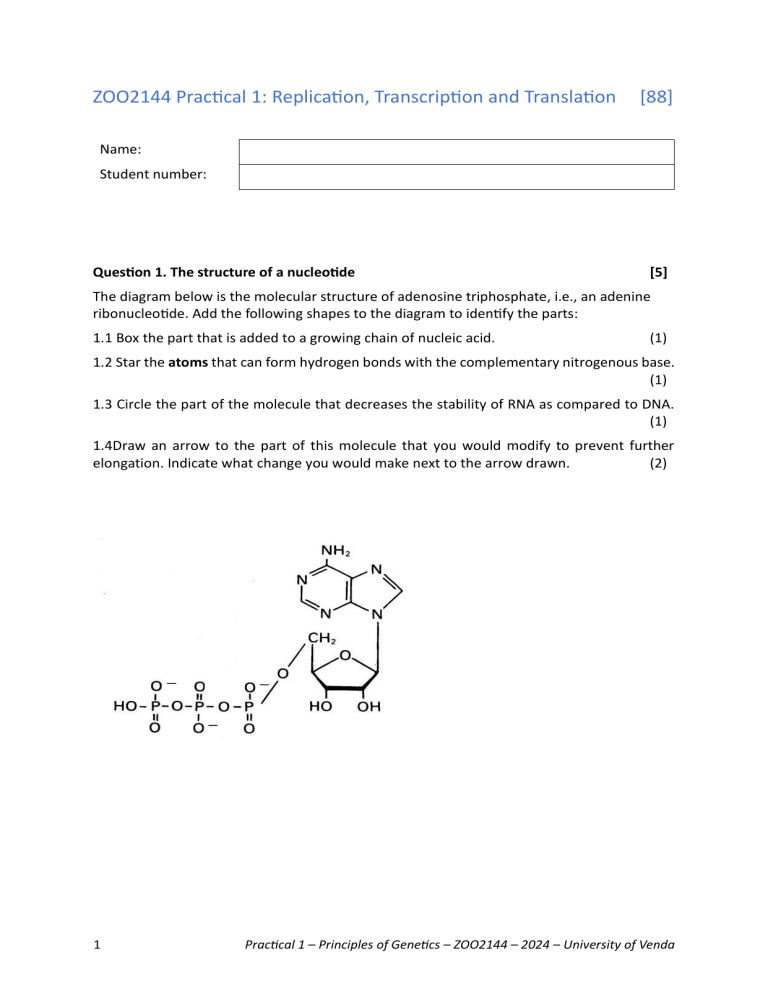
ZOO2144 Practical 1: Replication, Transcription and Translation [88] Name: Student number: Question 1. The structure of a nucleotide [5] The diagram below is the molecular structure of adenosine triphosphate, i.e., an adenine ribonucleotide. Add the following shapes to the diagram to identify the parts: 1.1 Box the part that is added to a growing chain of nucleic acid. (1) 1.2 Star the atoms that can form hydrogen bonds with the complementary nitrogenous base. (1) 1.3 Circle the part of the molecule that decreases the stability of RNA as compared to DNA. (1) 1.4Draw an arrow to the part of this molecule that you would modify to prevent further elongation. Indicate what change you would make next to the arrow drawn. (2) 1 Practical 1 – Principles of Genetics – ZOO2144 – 2024 – University of Venda Question 2. Briefly describe the functions of the following enzymes: [12] 2.1 DNA polymerase (main function) 2.2 Exonuclease (part of DNA polymerase) 2.3 RNA primase 2.4 Helicase 2.5 Gyrase 2.6 RNA polymerase 2.7 Telomerase 2 Practical 1 – Principles of Genetics – ZOO2144 – 2024 – University of Venda 2.8 Spliceosome 2.9 Ribosome 2.10 DNA ligase 2.11 DNA glycosylase 2.12 AP endonuclease 3 Practical 1 – Principles of Genetics – ZOO2144 – 2024 – University of Venda Question 3. Fill in the following table [30] Replication Transcription Translation Where does this process occur in a eukaryotic cell? What is the enzyme that carries out this process? What is the template that is read during this process? In what direction is the template read? What is the start signal/sequence for this process? What is the polymer that is formed? What monomer is used to form this polymer? What type of bond is formed between monomers? In what direction is the new polymer formed? What is the stop signal/sequence for this process? 4 Practical 1 – Principles of Genetics – ZOO2144 – 2024 – University of Venda Question 4. replication bubble [15] The diagram below depicts a replication bubble with two replication forks. Blue lines are DNA single strands and red lines are RNA single strands. 4.1 Indicate all 3’ and 5’ ends on ALL DNA single strands. One mark for each correct pair of 3’ and 5’ ends. (10) 4.2 Indicate all parent strands. (1) 4.3 Indicate all leading strands. (1) 4.4 Indicate approximately where the origin of replication was on each parent strand. (1) 4.4 Indicate all the lagging strands, and give another name for these strands. (2) 5 Practical 1 – Principles of Genetics – ZOO2144 – 2024 – University of Venda Question 5. Templates, codons, anticodons and amino acids [4] The diagram below shows a few codons in the middle of a gene. Follow each step using the illustration below: 1.Fill in the complimentary DNA strand using DNA base pairing rules. 2. Fill in the correct mRNA bases by transcribing the bottom DNA strand. 3. Write the correct anti-codon on each tRNA molecule. 4. Translate the mRNA codons using the genetic code table found on the last page. Write the name of each amino acid in the oval on the tRNA molecules. G 6 T A A A G T C T C A T G T G T Practical 1 – Principles of Genetics – ZOO2144 – 2024 – University of Venda Question 6. Translating a gene [10] Below is the double-stranded DNA sequence which contains a small gene. Transcription starts at the Transcription Start Site. Transcription stops at the termination site (up arrow). Transcription start site termination 5’–GTCTAGATGGCGCTCTCGCCTATAGACGCAGCCGGTATATAGCTAACGA –3’ 3’–CAGATCTACCGCGAGAGCGGATATCTGCGTCGGCCATATATCGATTGCT –5’ 6.1 Where is the promoter relative to the above sequence? (1) 6.2 Which strand is the template and which strand is the coding strand? (2) 6.3 Write the mRNA that would be produced from transcription of this strand. Show the 5’ and 3’ ends. (3) 6.4 Write the polypeptide that would be produced from the mRNA. Show the amino (N) and carboxyl (C) ends. Remember you can use the genetic code table on the last page. (4) 7 Practical 1 – Principles of Genetics – ZOO2144 – 2024 – University of Venda Question. 7 Translation with alternative splicing [12] Below is a DNA double strand of a gene. Four exons are shown in bold and three introns are underlined. The bottom strand is the antisense strand. Write the polypeptides that would be produced from the alternative splicing combinations described below the diagram. Show the N and C ends in every answer. Exon 1 Exon 2 Exon 3 Exon 4 5’–GTACTATGATATGCTAGCTAGCCTATCGCTACCTTTAGTAGCAGGCATGTTACACATACCTACAAGCGATGAACGTGGA–3’ 3’–CATGATACTATACGATCGATCGGATAGCGATGGAA ATCATCGTCCGTACAATGTGTATGGATGTTCGCTACTTG CACCT–5’ 7.1 The polypeptide resulting from Exons 1 and 4 spliced together, in that order. (4) 7.2 The polypeptide resulting from Exons 1, 2 and 3 spliced together, in that order. (4) 7.3 The polypeptide resulting from Exons 1, 2 and 4 spliced together, in that order. (4) 8 Practical 1 – Principles of Genetics – ZOO2144 – 2024 – University of Venda Appendix. Genetic code table. Translate the mRNA. You can also translate the coding strand of DNA if you remember that T in DNA = U in RNA. 9 Practical 1 – Principles of Genetics – ZOO2144 – 2024 – University of Venda