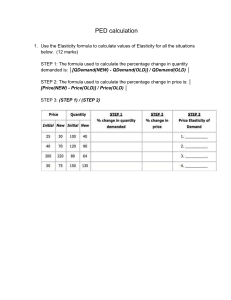
lOMoARcPSD|37809919 ECON247v11 Assignment 1B Microeconomics (Athabasca University) Scan to open on Studocu Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by susan said (susansaid557112@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|37809919 1 ECON 247: Assignment 1B Due Date: After you have completed Unit 5 Credit Weight: 10% of your final grade 1. Which economic principle is applicable in each of the following cases? Justify your answer. (2 marks each) a. David is a sportsperson who makes an annual average salary of $1 million. He started his professional career right after completing high school. David’s father wanted him to get a four-year university degree. The total annual cost of attending university is $15,000. After long discussion with his father, David decided not to go to university. The Cost of Something is What You Give Up to Get It. This is an example of opportunity cost because he chose to work instead of going to college, and the time he was working he could’ve gone to school. ECON247v11_Assignment_1B © Athabasca University May 2020 Downloaded by susan said (susansaid557112@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|37809919 2 Answer: This is talking about opportunity cost, where a cost is what you give up to get it. This is because David chose to work and give up the chance to go to university. b. When the government imposes a price ceiling (rent control), landlords do not build new apartments and do not maintain the existing ones. Answer: The example of Government step-in into market and influence the economic outcomes, to make housing price more affordable for people within the country. c. To tackle the problem of recession, the Bank of Canada increases the money supply by lowering the overnight interest rate. The increase in money supply lowers the interest rate which in turn increases investment. This increase in investment would increase employment in the short run, but will increase the price level at the same time. Answer: Once government increased money quantity supply, more money entering the market, and people have more money on hand, and they will spend more for any goods and services. When the demand in the market increased, suppliers have to produce more products, when supply increase, price also increase. 2. a. Identify each of the following topics as being part of microeconomics or macroeconomics: (1 mark each) i. ii. iii. iv. The average wage rate for unskilled workers is low in the developing world. Answer: macroeconomics An increase in government expenditures is used to increase employment during a recession. Answer: macroeconomics total production of automobiles in Canada. Answer: microeconomics Under balanced budget fiscal policy, the government attempts to balance the budget every year. Answer: microeconomics b. Which of the following statements are positive and which are normative? (1 mark each) i. If consumer income increases, other things being equal, the demand for normal goods will increase. Answer: positive Canadian workers deserve an increase in minimum wage. Answer: normative During recession, unemployment can be expected to increase. Answer: positive Class sizes should not be more than 35. Answer: normative ii. iii. iv. 3. Suppose the following table shows the production possibilities for an economy. (1 mark each) Production Good X Good Y Point A 5 10 ECON247v11_Assignment_1B © Athabasca University May 2020 B 8 5 U 5 5 Downloaded by susan said (susansaid557112@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|37809919 3 a. What is the opportunity cost of moving from point A to B? answer: 5 of goof y b. What is the opportunity cost of moving from point B to A? answer: 3 of goof x c. What is the opportunity cost of moving from point U to A? answer: 5 of goof y d. Suppose points A and B are on the production possibility frontier. What conclusion can be drawn about production point U? answer: point u its production is inefficient 4. Answer the questions below using the data in the following table, which shows a market for a product that has significant social benefits. Price $16ffff 12ffff 8ffff 4ffff 2ffff Quantity Demanded 30 35 40 45 55 Quantity Supplied 70 55 40 25 20 a. What would the equilibrium price and quantity be? Answer: $8 mark) (1 b. Suppose the price is currently at $2. What problem would exist in the economy? What would you expect to happen to price? Answer: demand higher than supply, the price will increase. (2 marks) c. Suppose the price is currently $12. What problem exists in the economy? What would you expect to happen to price? Answer: demand lower than supply, that meant there has excessive supply, price will decrease to attract more demand. (2 marks) d. Using the midpoint method, calculate the price elasticity of demand if price changes from $12 to $16. Is this elastic or inelastic? Answer: inelastic and price elasticity of demand is 0.077 (2 marks) ECON247v11_Assignment_1B © Athabasca University May 2020 Downloaded by susan said (susansaid557112@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|37809919 4 e. A government subsidy is given to the consumers that increases quantity demand by 20 units at each price. what is the new equilibrium price and quantity? (2 marks) Answer: new equilibrium price is $12 with quantity 55. ECON247v11_Assignment_1B © Athabasca University May 2020 Downloaded by susan said (susansaid557112@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|37809919 5 5. a. Describe the short run and long run impact of a binding price ceiling (rent control) on the housing market. Include the important role of elasticity of demand and supply in your answer. Answer: in short run housing become more affordable while in long run risk may occurs such as housing shortage. Apply elasticity to prevent excessive demand or supply. (3 marks) b. Consider the following labour market: QDL = 70 – 2W QSL = 10 + 4W Calculate the equilibrium level of wage rate and level of employment. Calculate the level of unemployment and deadweight loss if the price floor (minimum wage) is set at $15. Answer: deadweight is -50, unemployment is 60. (3 marks) 6. How would the following changes in price affect total revenue? That is, would total revenue increase, decrease, or remain unchanged? (3 marks) c. 7. a. Price rises and demand is inelastic. Answer: increase b. Price falls and demand is elastic. Answer: increase Price rises and demand is of unit elasticity. Answer: remain unchanged a. List four determinants of price elasticity of demand? Answer: proportion of income/ time/ substitutability/luxury or necessity (2 marks) b. Evaluate the following statement: “A farmer is producing wheat (a necessity) on his land. The total production of wheat is Q1 bushels. The price per bushel is $P1. Due to the introduction of new hybrid seed, the farmer’s productivity increases, and total production increases from Q1 to Q2. At the same time, the increase in production lowers the price from $P1 to $P2. The introduction of new hybrid seed improves the living standard of the farmer.” Answer: the introduction of new seed allows farmer to produce more and lower the price. (3 marks) c. Assume that the income elasticity of demand for good X is –3.69 and the cross-price elasticity is –1.16. What would happen to demand for X if there is an increase in income and an increase in price of Y at the same time? Explain your answer. Answer: Since income increase, people have extra money on hand will be given more purchasing power, people will buy more. (5 marks) ECON247v11_Assignment_1B © Athabasca University May 2020 Downloaded by susan said (susansaid557112@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|37809919 6 8. Data on price of Y, quantity demand for X when income is 100, and quantity demand for X when income is 200 are given in the following table. The price of X is fixed at $7. Py 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a. QDx (Income $100) 121.5 120.2 118.9 117.6 116.3 115 113.7 112.4 111.1 109.8 108.5 QDx (Income $200) 196.5 195.2 193.9 192.6 191.3 190 188.7 187.4 186.1 184.8 183.5 Calculate income elasticity of demand for X using the midpoint method when income increases from $100 to $200 and when price of Y is fixed at $9. Explain (5 marks) your answer. Answer: (109.8/184.8)/(100/200)= 1.188= 1.19 b. Calculate cross price elasticity of demand for X when price of Y decreases from $9 to $8 and when income is $100. Explain your answer. Answer: %change in quantity/ % change in price. (5 marks) 9. a. What is the difference between a “change in supply” and a “change in quantity supplied”? Answer: change in supply= movement of supply curve respond to factor other than price. Change in quantity supplied. = movement of supply curve respond to price change. (5 marks) b. How will each of the following events shift the demand and/or the supply curve for bread? Also, indicate the effect of each event on equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. That is, do equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity rise, fall, or remain unchanged? Or, is the answer indeterminate because it depends on the magnitude of the shift? (8 marks) i. ii. iii. The price of flour decreases. Answer: equilibrium quantity will rise, equilibrium price will fall, demand will rise. Consumer income increases, and bread is a normal good. Answer: demand will rise, equilibrium price will rise. The price of lettuce wraps (a substitute of bread) increases, and sellers expect the price of bread to fall next month. Answer: demand will rise, and equilibrium factors remain unchanged. ECON247v11_Assignment_1B © Athabasca University May 2020 Downloaded by susan said (susansaid557112@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|37809919 7 iv. The number of buyers decrease, and consumers expect the price of bread to be higher next month. Answer: demand will fall, equilibrium price will fall. ECON247v11_Assignment_1B © Athabasca University May 2020 Downloaded by susan said (susansaid557112@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|37809919 8 10. a. Based on the following data on taxable income and amount of tax, identify each type of tax system as progressive, regressive, proportional, or lump sum. (4 marks) i. Tax System A: Answer: lump sum ii. Tax System B: Answer: proportional iii. Tax System C: Answer: progressive iv. Tax System D: Answer: regressive Taxable Income $40,000 $80,000 $120,000 11. a. Tax System A Tax System B Tax System C Tax System D $6,000 $12,000 $18,000 $4,000 $8,000 $12,000 $6,000 $9,600 $12,000 $6,000 $6,000 $6,000 b. An increase in the tax rate will always increase the tax revenue and decrease the deadweight loss. Explain. Answer: this is because people will spend less when the tax is high, and tax reduce income from seller too, so sellers also produce less. Therefore, entire market will fall below optimum equilibrium. (6 marks) List and define different policy options that a government can apply to correct for negative externalities. Answer: government can implement tax to lower negative externalities, while provide subsidies for positive externalities. (4 marks) b. The Coase Theorem suggests that efficient solutions to externalities can be achieved through bargaining. Under what circumstances does this fail to produce a solution? Answer: 1/bargaining process discontinued, 2/numerous bargaining occur , 3/ when there has transaction cost (3 marks) 12. c. Define private goods and public goods and give at least two examples of each. Answer: private goods- good that is excludable and rival such as coke and clothes. Public good- good that is non- excludable and non-rivalrous such as air, drinking water. (4 marks) The following table shows the production of meat and wheat produced in tonnes per day for Germany and Canada. (2 marks each) Germany Canada Meat 200 200 Wheat 300 150 a. Which country has absolute advantage in producing wheat? Why? Answer: Germany, because they are able more than Canada. b. What is the opportunity cost of producing one tonne of meat in Germany? Answer: 1.5 tonnes of wheat. ECON247v11_Assignment_1B © Athabasca University May 2020 Downloaded by susan said (susansaid557112@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|37809919 9 c. What is the opportunity cost of producing one tonne of wheat in Germany? Answer: 0.67 tonnes of meat. d. Which country has the comparative advantage in producing meat? Why? Answer: Canada, because Canada has lower opportunities cost in producing meat. e. Which country has the comparative advantage in producing wheat? Why? Answer: Germany because they have lower cost. ECON247v11_Assignment_1B © Athabasca University May 2020 Downloaded by susan said (susansaid557112@gmail.com)